1 min read
Dark Clouds in Rosette Nebula Compass Image

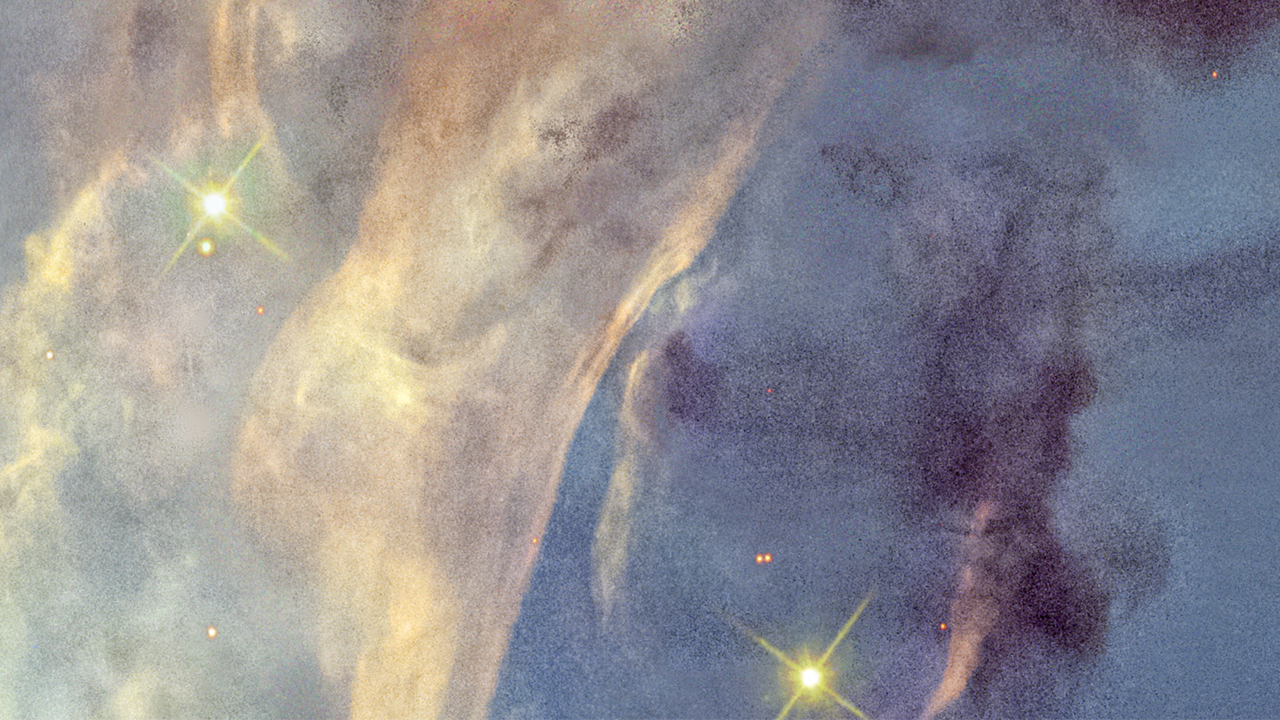
This image of dark clouds in the Rosette Nebula was captured by the Hubble Space Telescope’s Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3).
The image shows a scale bar, compass arrows, and color key for reference.
The scale bar is labeled in light-years along the top, which is the distance that light travels in one Earth-year. (It takes three-quarters of a year for light to travel a distance equal to the length of the scale bar.) One light-year is equal to about 5.88 trillion miles or 9.46 trillion kilometers.
The scale bar is also labeled in arcseconds, which is a measure of angular distance on the sky. One arcsecond is equal an angular measurement of 1/3600 of one degree. There are 60 arcminutes in a degree and 60 arcseconds in an arcminute. (The full Moon has an angular diameter of about 30 arcminutes.) The actual size of an object that covers one arcsecond on the sky depends on its distance from the telescope.
The north and east compass arrows show the orientation of the image on the sky. Note that the relationship between north and east on the sky (as seen from below) is flipped relative to direction arrows on a map of the ground (as seen from above).
This image shows visible wavelengths of light that have been translated into visible-light colors. The color key shows which WFC3 filters were used when collecting the light. The color of each filter name is the visible-light color used to represent the light that passes through that filter.
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Rosette Nebula
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Emission Nebula
- Release DateApril 23, 2025
- Science ReleaseEye on Infinity: NASA Celebrates Hubble’s 35th Year in Orbit
- CreditImage: NASA, ESA, STScI; Image Processing: Joseph DePasquale (STScI)
Related Images & Videos

Mosaic of Hubble 35th Anniversary Targets
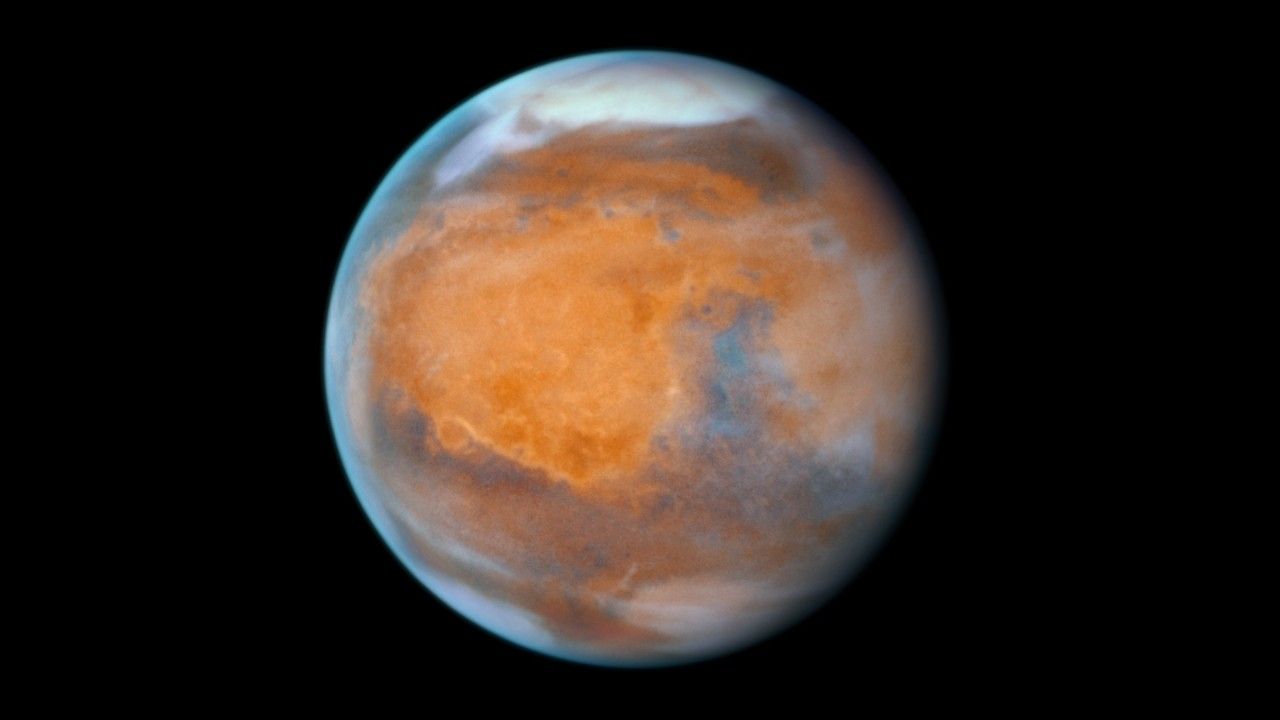
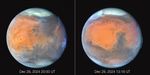
A selection of photogenic space targets to celebrate the 35th anniversary of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. Upper left: Mars. Upper right: planetary nebula NGC 2899. Lower left: a small portion of the Rosette Nebula. Lower right: barred spiral galaxy NGC 5335.

Rosette Nebula Context Image
The Rosette Nebula is a vast star-forming region, 100 light-years across, that lies at one end of a giant molecular cloud. The background image is from the Digitized Sky Survey, while the inset is a small portion of the nebula as photographed by the Hubble Space Telescope.
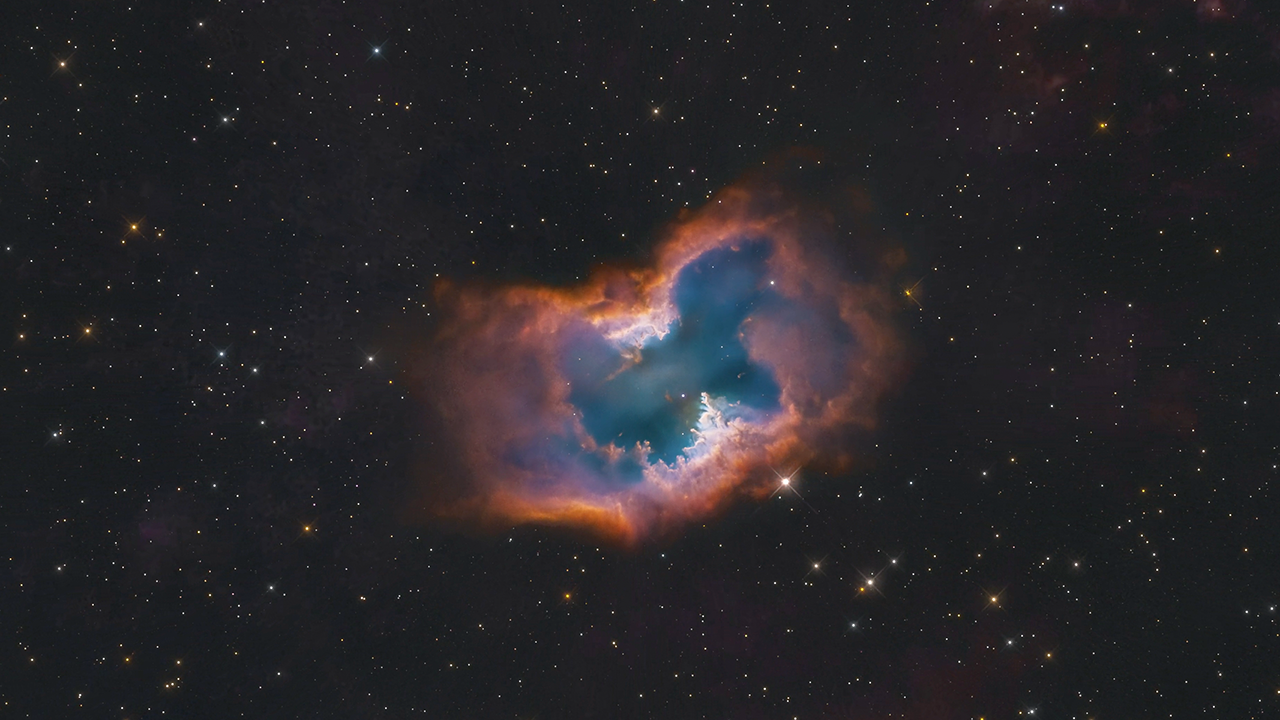

Planetary Nebula NGC 2899
This video zooms across 6,500 light-years through a star-studding field to visit the planetary nebula NGC 2899, as photographed by the Hubble Space Telescope. The nebula has a diagonal bipolar structure formed by a cylindrical-shaped outflow of hot gasses and radiation from the c...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov