1 min read
ERO Images NGC 2392 and Abell 2218

About the Object
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.NGC 2392: 5,000 light-years (1,500 parsecs), Abell 2218 (right): 2 billion light-years (600 million parsecs)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.NGC 2392 Principal Astronomers: A. Fruchter (STScI), C. Christian (STScI), A. Kinney (NASA), A. Fruchter (STScI), S. Baggett (STScI), R. Hook (ST-ECF), Z. Levay (STScI) Abell 2218 Principal Astronomers: A. Fruchter (STScI), C. Christian (STScI), A. Kinney (NASA), A. Fruchter (STScI), S. Baggett (STScI), R. Hook (ST-ECF), Z. Levay (STScI) - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>WFPC2
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.January 10 - 13, 2000
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.NGC 2392: F469N (He II), F502N ([O III]), F656N (H-alpha), F658N ([N II]) Abell 2218: F450W (Wide B), F606W (Wide V), and F814 W (I)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.NGC 2392, Abell 2218
- Release DateJanuary 24, 2000
- Science ReleaseHubble Reopens Its Eye on the Universe
- Credit
Related Images & Videos

Gravity of Galaxy Cluster Abell 2218 Creates Giant "Lens"
Scanning the heavens for the first time since the successful December 1999 servicing mission, NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has imaged a giant, cosmic magnifying glass, a massive cluster of galaxies called Abell 2218. This "hefty" cluster resides in the constellation Draco, some...
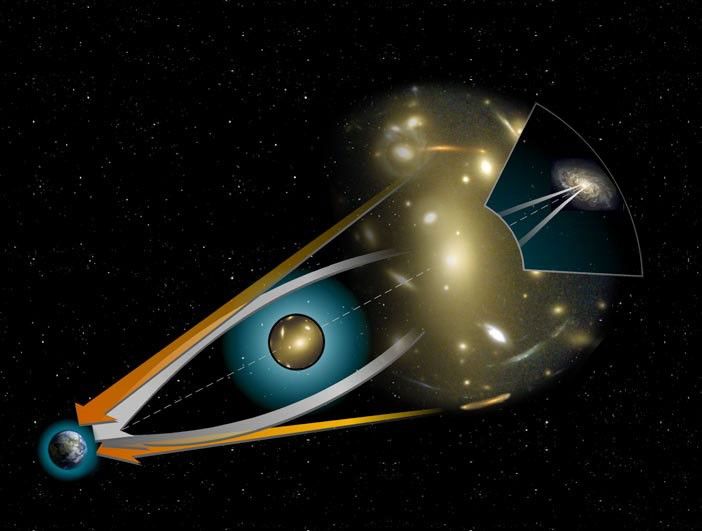
The Gravitational Field of the Cluster Acts like a Zoom Lens
Gravitational Lenses - Cosmic Mirages Just as a wanderer in the desert can experience mirages, when light from remote objects is bent by the warm air hovering just above the sand, we may also see mirages in the Universe. The mirages we see with modern telescope like the Hubble...
Share
Details
Last Updated
Aug 17, 2025
Contact
Media
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov




























