1 min read
Exoplanet GJ 3470 b Structure
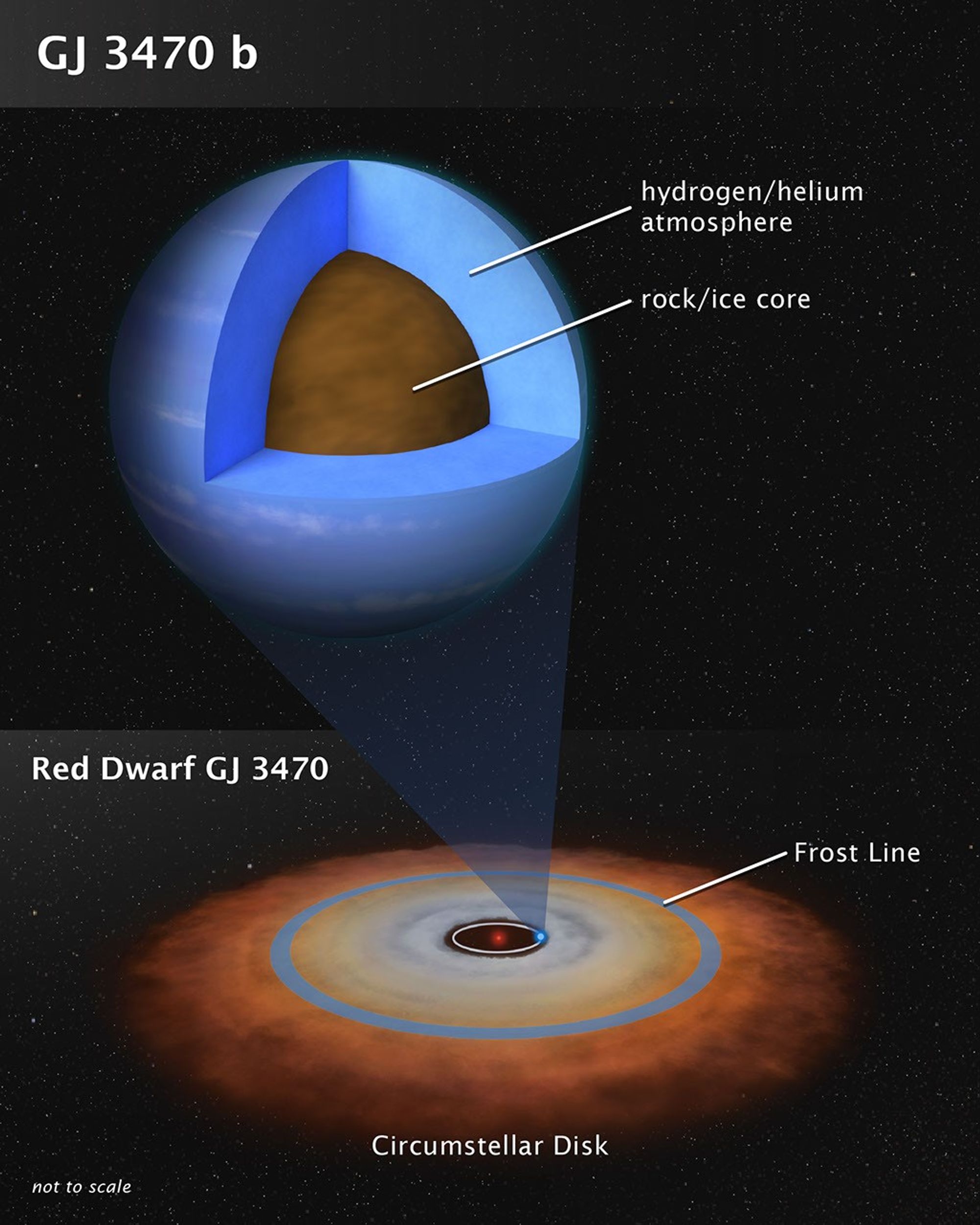
This artist's illustration shows the theoretical internal structure of the exoplanet GJ 3470 b. It is unlike any planet found in the Solar System. Weighing in at 12.6 Earth masses the planet is more massive than Earth but less massive than Neptune. Unlike Neptune, which is 3 billion miles from the Sun, GJ 3470 b may have formed very close to its red dwarf star as a dry, rocky object. It then gravitationally pulled in hydrogen and helium gas from a circumstellar disk to build up a thick atmosphere. The disk dissipated many billions of years ago, and the planet stopped growing. The bottom illustration shows the disk as the system may have looked long ago. Observations by NASA's Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes have chemically analyzed the composition of GJ 3470 b's very clear and deep atmosphere, yielding clues to the planet's origin. Many planets of this mass exist in our galaxy.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.07:59:05.69
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.+15:23:28.71
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Cancer
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.About 100 light-years
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The HST observations include those from program 13665 (B. Benneke) - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.WFC3/IR; STIS/CCD
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.Jan 2015 - Apr 2016
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.GJ 3470 b
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Exoplanet
- Release DateJuly 2, 2019
- Science ReleaseAtmosphere of Mid-Size Planet Revealed by Hubble and Spitzer
- Credit
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov




























