1 min read
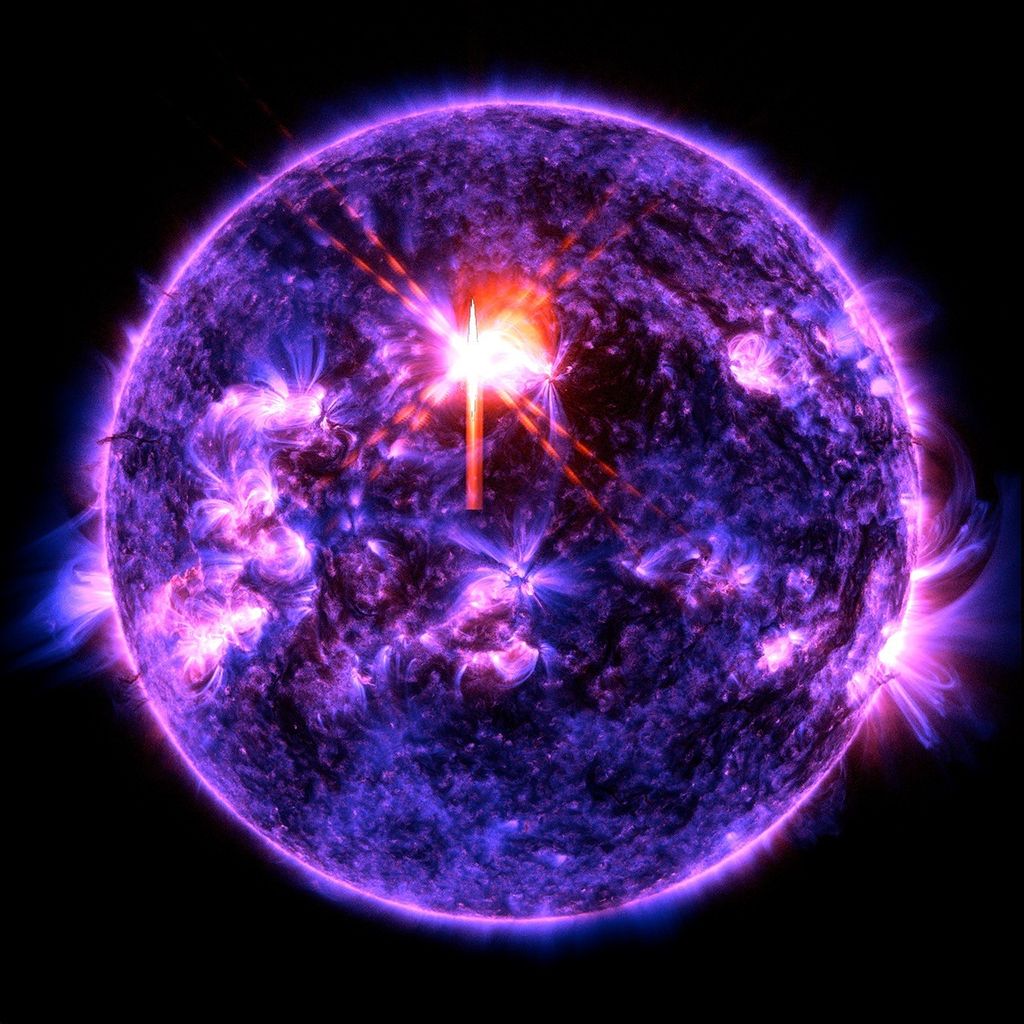
Exoplanet HD 189733b (Artist’s Illustration)

This artist's rendering illustrates the evaporation of HD 189733b's atmosphere in response to a powerful eruption from its host star. NASA's Hubble Space Telescope detected the escaping gases and NASA's Swift satellite caught the stellar flare.
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The international team of astronomers in this study consists of A. Lecavelier des Etangs (Institut d'astrophysique de Paris, CNRS, UPMC, France), V. Bourrier (Institut d'astrophysique de Paris, CNRS, UPMC, France), P. J. Wheatley (Department of Physics, University of Warwick, UK), H. Dupuy (Institut d'astrophysique de Paris, CNRS, UPMC, France), D. Ehrenreich (Institut de Planetologie et d'Astrophysique de Grenoble, UJF/CNRS, Grenoble, France), A. Vidal-Madjar (Institut d'astrophysique de Paris, CNRS, UPMC, France), G. Hebrard (Institut d'astrophysique de Paris, CNRS, UPMC, France), G. E. Ballester (Lunar and Planetary Laboratory, University of Arizona, USA), J.-M. Desert (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, USA), R. Ferlet (Institut d'astrophysique de Paris, CNRS, UPMC, France), and D. K. Sing (Astrophysics Group, School of Physics, University of Exeter, UK).
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.HD 189733b
- Release DateJune 28, 2012
- Science ReleaseHubble, Swift Detect First-Ever Changes in an Exoplanet Atmosphere
- CreditIllustration: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center; Science: NASA, ESA, A. Lecavelier des Etangs (CNRS-UMPC, France), and P. Wheatley (University of Warwick)
Related Images & Videos
Share
Details
Last Updated
Aug 17, 2025
Contact
Media
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov
Illustration Credit
NASA-GSFC
Science Credit
NASA, ESA, Alain Lecavelier des Etangs (CNRS, UPMC), Peter Wheatley (Warw)