1 min read
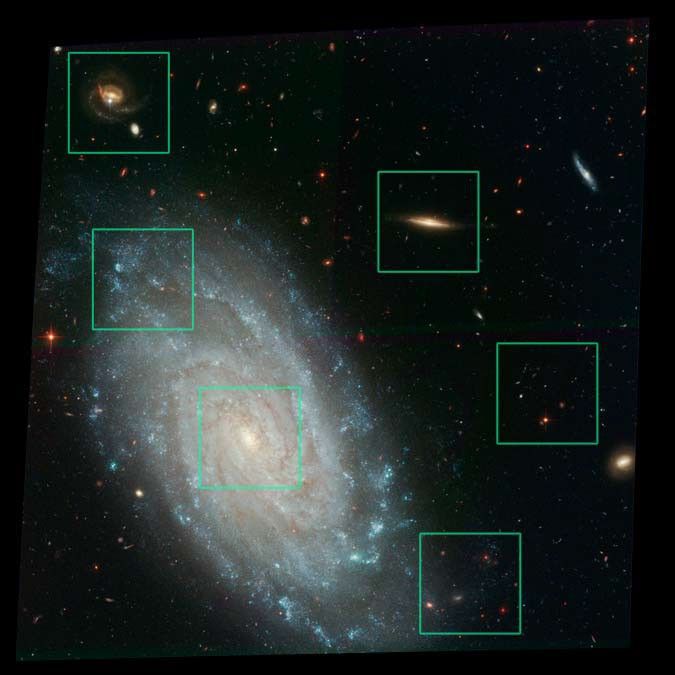
Galaxy NGC 3370 Comparison of Ground and ACS Images
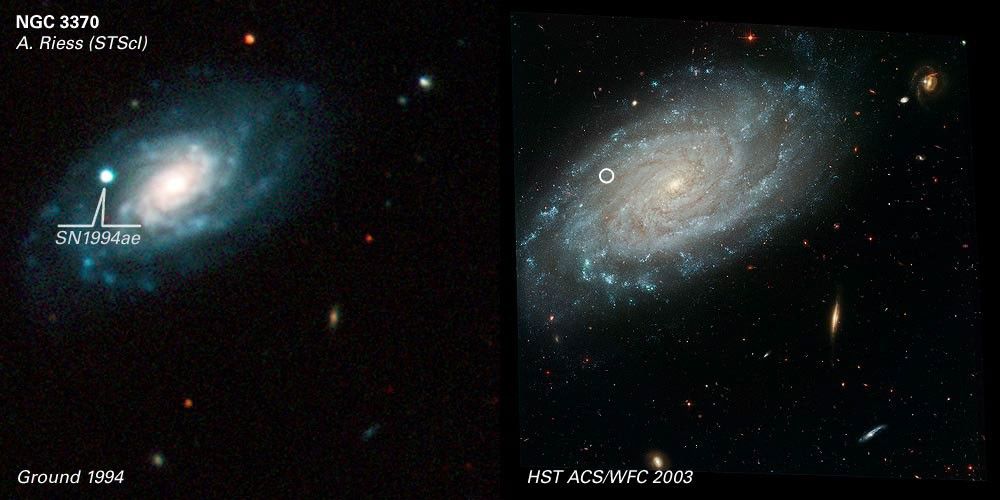

About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.10h 47m 4.17s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.17° 16' 22.8"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Leo
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.98 million light-years (30 megaparsecs)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The Hubble image (right) was created from HST data from the following proposals: 9351: A. Riess (STScI), P. Stetson (NRC), A. Filippenko (UC Berkeley); and 9696: K. Noll (STScI), A. Riess (STScI), L. Frattare, H. Bond, C. Christian, F. Hamilton, Z. Levay, and T. Royle (STScI).
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS/WFC (right)
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.April - May 2003, Exposure Time: 25 hours (HST image, right)
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.ACS: F435W (B), F555W (V), F814W (I)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.NGC 3370
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Spiral Galaxy
- Release DateSeptember 4, 2003
- Science ReleaseCelestial Composition
- Credit
Related Images & Videos

Spiral Galaxy NGC 3370, Home to Supernova Seen in 1994
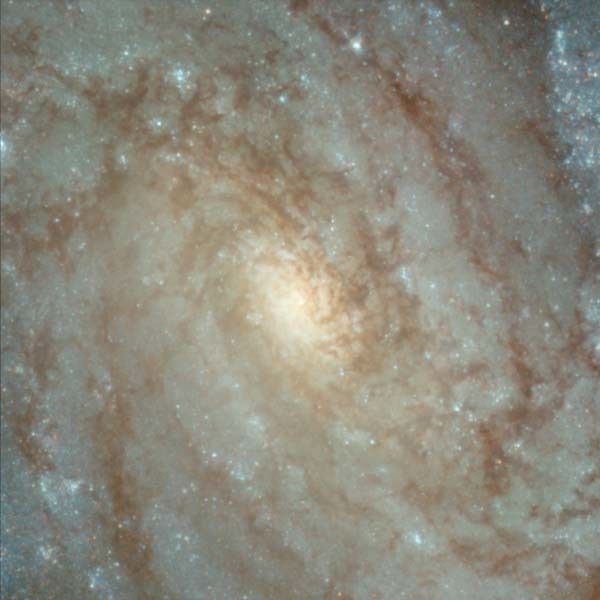
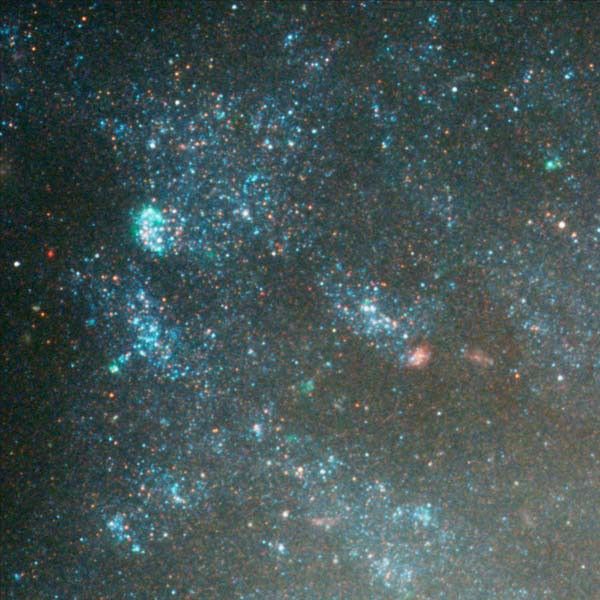
Amid a backdrop of far-off galaxies, the majestic dusty spiral, NGC 3370, looms in the foreground in this NASA Hubble Space Telescope image. Recent observations taken with the Advanced Camera for Surveys show intricate spiral arm structure spotted with hot areas of new star...
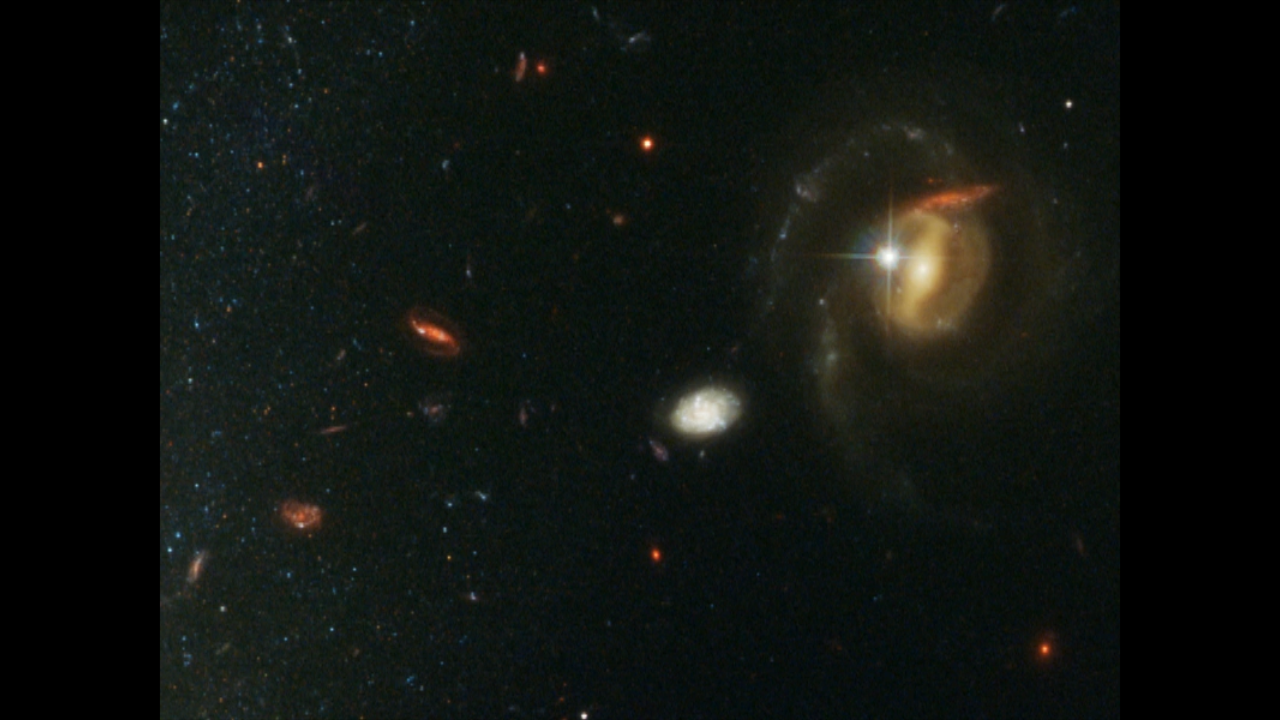

NGC 3370: Celestial Composition
Pan of the galaxy NGC 3370 taken by Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys in early 2003. Adam Riess, an astronomer at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Md., observed NGC 3370 a dozen times over the course of a month and has seen many Cepheid variables. These...
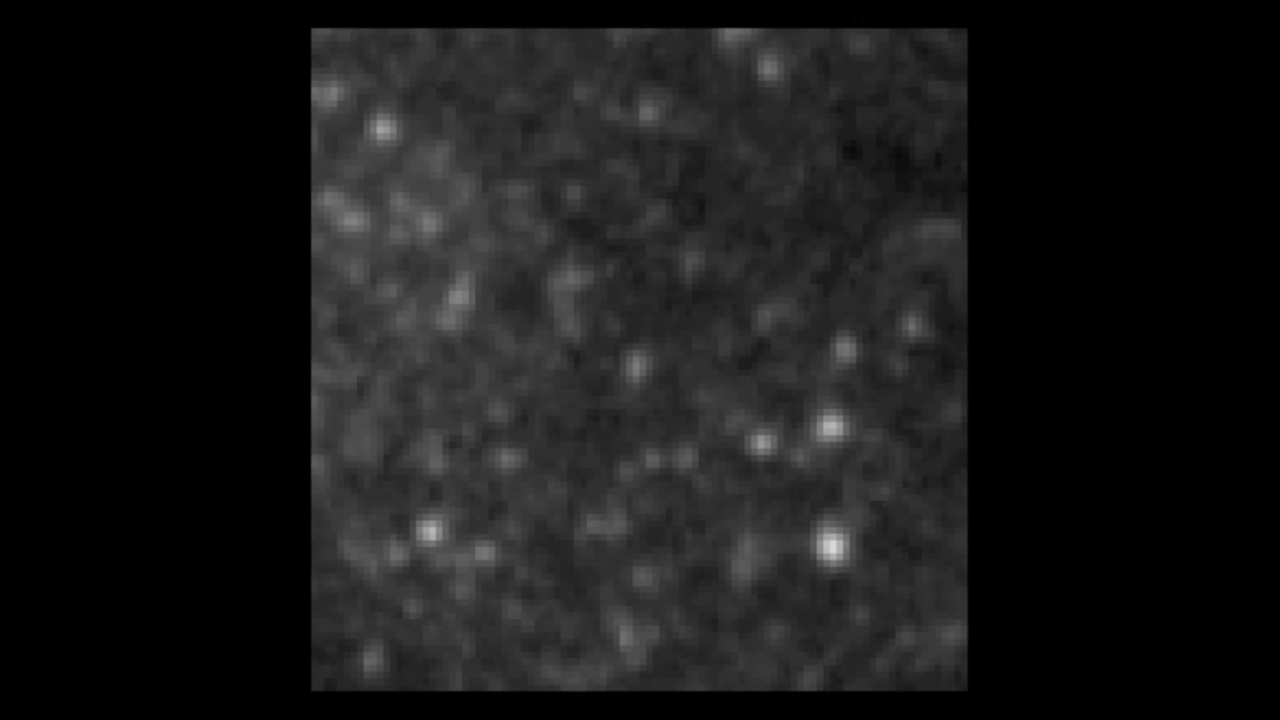
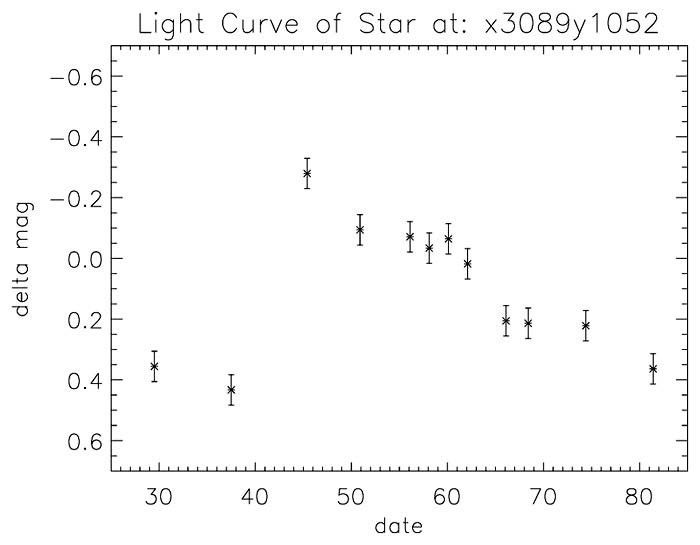
Cepheid Variable in NGC 3370
Here we see a "movie" of 12 consecutive epochs of a long period (~50 days) Cepheid variable. The Cepheid is in the center of a crowded region of stars. The resolution of HST is required to pick out the variable star from its neighbors. The star was caught initially fading before...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov