1 min read
Giant Starbirth Region in Neighboring Galaxy
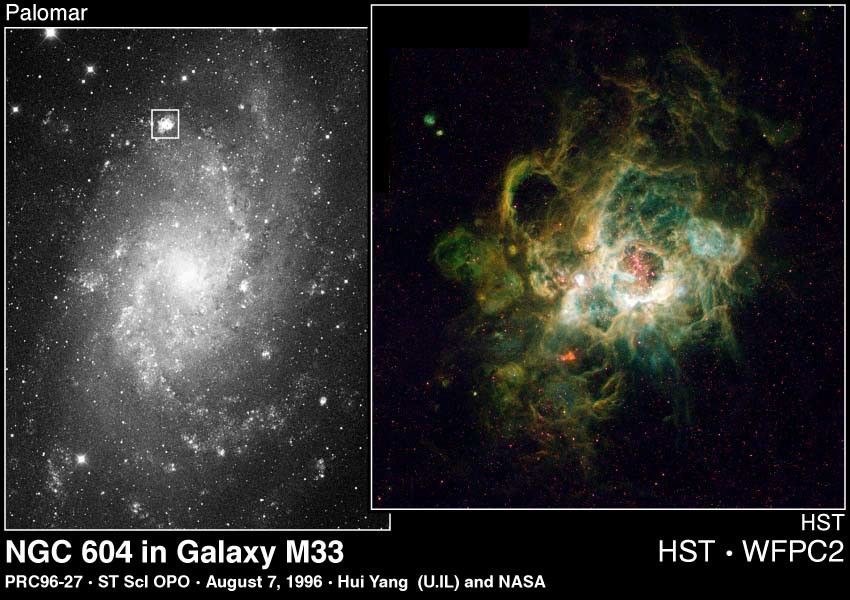
This is a Hubble Space Telescope image (right) of a vast nebula called NGC 604, which lies in the neighboring spiral galaxy M33, located 2.7 million light-years away in the constellation Triangulum.
This is a site where new stars are being born in a spiral arm of the galaxy. Though such nebulae are common in galaxies, this one is particularly large, nearly 1,500 light-years across. The nebula is so vast it is easily seen in ground-based telescopic images (left).
At the heart of NGC 604 are over 200 hot stars, much more massive than our Sun (15 to 60 solar masses). They heat the gaseous walls of the nebula making the gas fluoresce. Their light also highlights the nebula's three-dimensional shape, like a lantern in a cavern. By studying the physical structure of a giant nebula, astronomers may determine how clusters of massive stars affect the evolution of the interstellar medium of the galaxy. The nebula also yields clues to its star formation history and will improve understanding of the starburst process when a galaxy undergoes a "firestorm" of star formation.
The image was taken on January 17, 1995 with Hubble's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2. Separate exposures were taken in different colors of light to study the physical properties of the hot gas (17,000 degrees Fahrenheit, 10,000 degrees Kelvin).
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.01h 34m 33.79s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.30° 46' 59.0"
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.NGC 604, M33
- Release DateAugust 7, 1996
- Science ReleaseGiant Star Birth Region in Neighboring Galaxy
- CreditHui Yang (University of Illinois) and NASA
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov





























