1 min read
Ground-based Image of Globular Cluster NGC 6397

About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.17h 40m 41.35s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-53° 40' 25.29"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Ara
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.8,500 light-years (2.6 kiloparsecs)
About the Data
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.Antilhue Observatory
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.June 5, 2005
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.NGC 6397
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Globular Cluster
- Release DateDecember 4, 2007
- Science ReleaseHow White Dwarfs Get Their ‘Kicks’
- CreditD. Verschatse (Antilhue Observatory, Chile)
Related Images & Videos
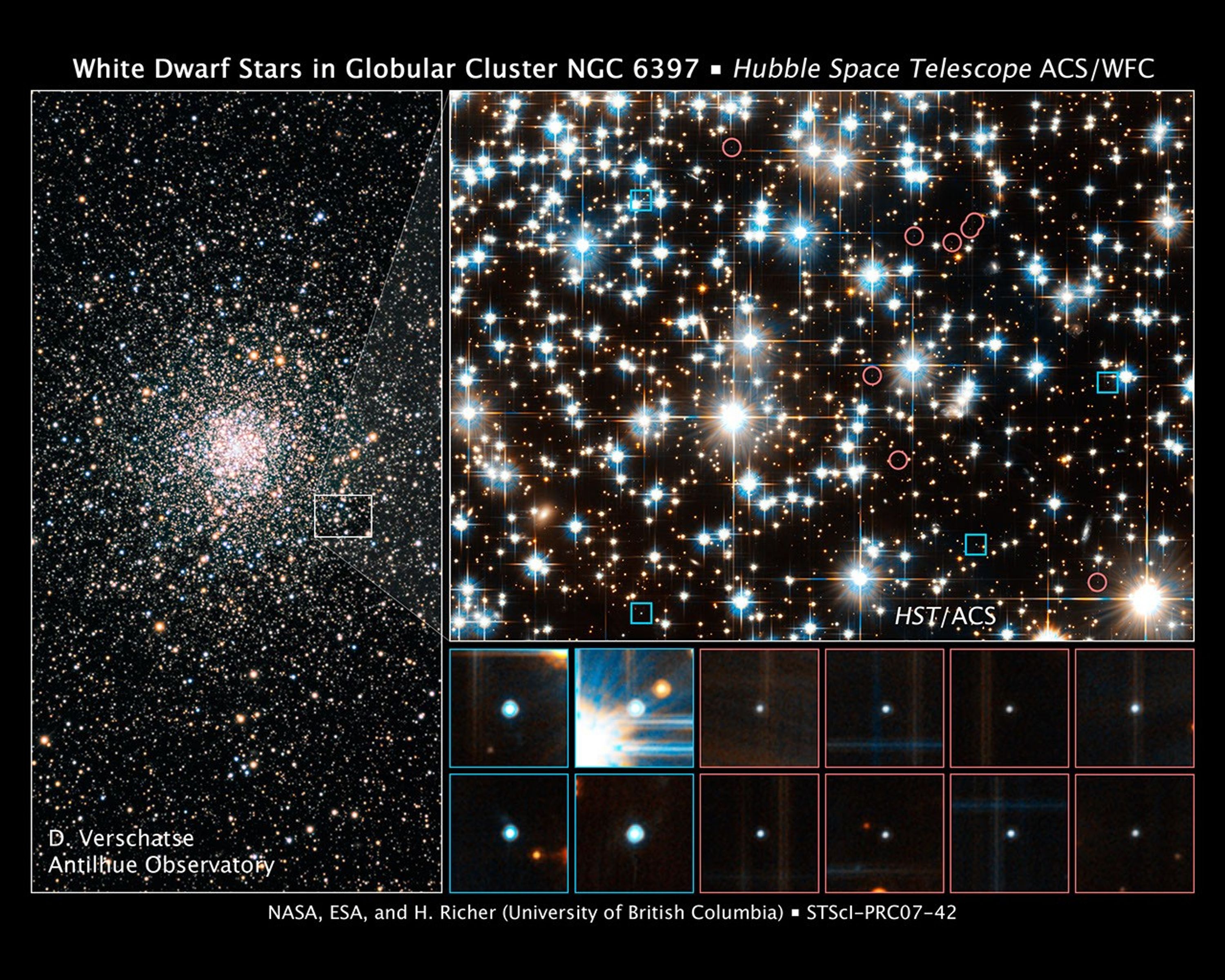
Hubble Finds Young White Dwarfs on the Fast Track
These images show young and old white dwarf stars – the burned-out relics of normal stars – in the ancient globular star cluster NGC 6397. The image at left, taken by a ground-based telescope, shows the dense swarm of hundreds of thousands of stars that make up the globular...
Share
Details
Last Updated
Aug 17, 2025
Contact
Media
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov