1 min read
HH 30 — 2000

About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.04h 31m 37.6s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.18° 12' 25.99"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Taurus
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.Disk diameter: 450 AU Astronomical Units
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.Disk diameter: 450 AU Astronomical Units. Magnitude: V19.5 mags
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.A Variable Asymmetry in the Circumstellar Disk of HH 30: Stapelfeldt, et. al., ApJ 516 L95 (1999) - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>WFPC2
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.February 2000
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.R band (F675W)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.HH 30
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Herbig-Haro Object
- Release DateSeptember 21, 2000
- Science ReleaseMovies from Hubble Show the Changing Faces of Infant Stars
- CreditNASA, Alan Watson (Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico, Mexico), Karl Stapelfeldt (Jet Propulsion Laboratory), John Krist (Space Telescope Science Institute) and Chris Burrows (European Space Agency/ Space Telescope Science Institute)
Related Images & Videos
Movies from Hubble Show the Changing Faces of Infant Stars
Time-lapse movies made from a series of pictures taken by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope are showing astronomers that young stars and their surroundings can change dramatically in just weeks or months. As with most children, a picture of these youngsters taken today won't look...

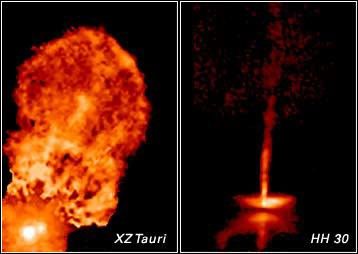
Hot Gas Bubble Ejected by Young Binary Star System XZ Tauri
These images taken with the Hubble Space Telescope's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 reveal the evolution of bubbles of glowing gas being blown out from the young binary star system XZ Tauri. Gas from an unseen disk around one or both of the stars is channeled through magnetic...

Young Star HH30's Dynamic Disk and Jets
These images of HH 30 show changes over only a five-year period in the disk and jets of this newborn star, which is about half a million years old. The pictures were taken between 1995 and 2000 with the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 aboard NASA's Hubble Space Telescope....
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov





























