1 min read
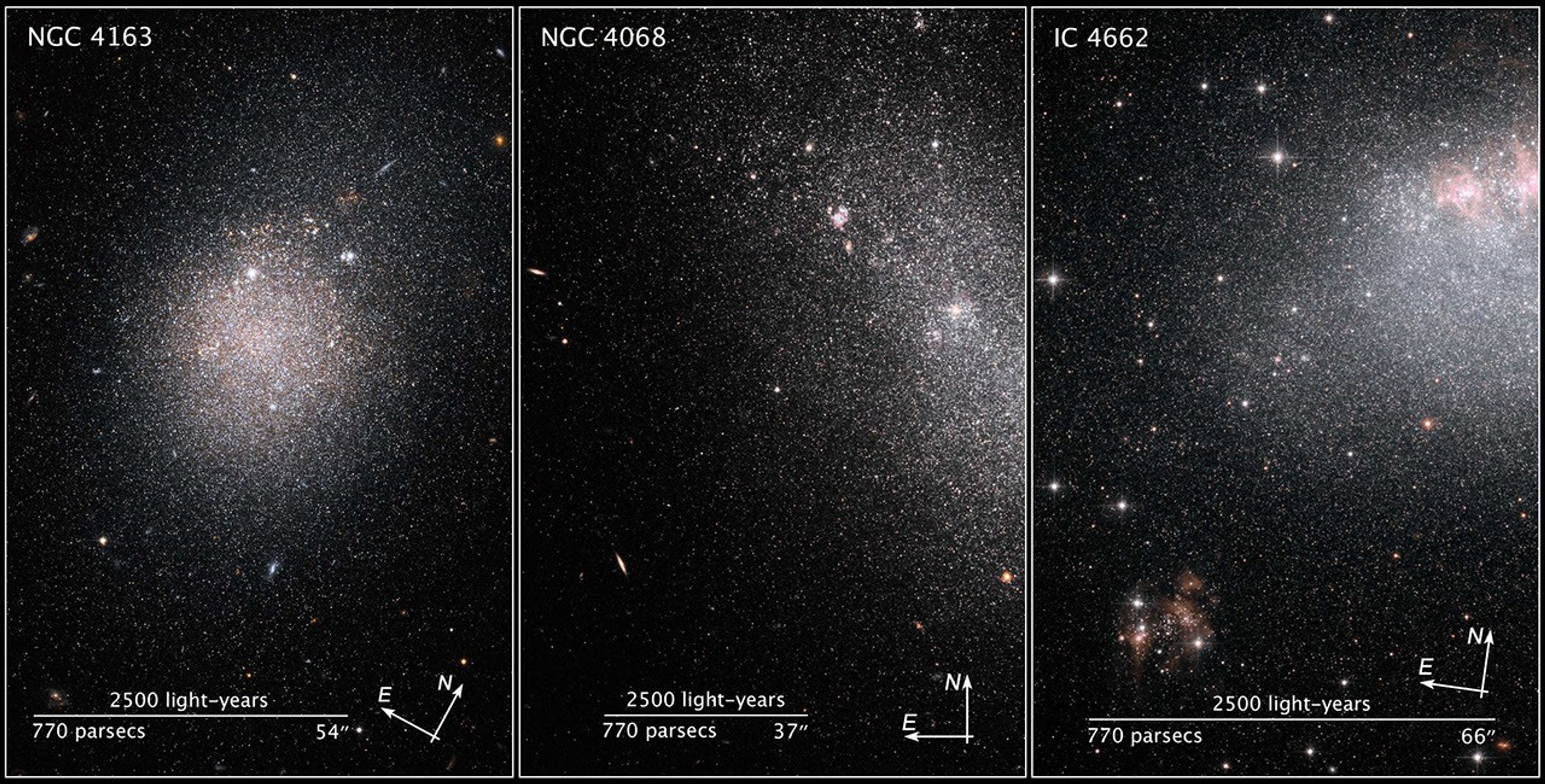
Hubble ACS Image of NGC 4068

About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.12h 4m 0.79s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.52° 35' 17.99"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Ursa Major
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.14 million light-years or 4.3 megaparsecs
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.92 arcseconds (6,300 light- years or 1,900 parsecs) wide
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The image was created from Hubble data from proposal 9771: I. Karachentsev (Russian Academy of Sciences, Special Astrophysical Observatory), B. Tully (University of Hawaii), V. Karachentseva (Kyiv University), A. Dolphin (Raytheon Company), S. Sakai (University of California, Los Angeles), E. Shaya (University of Maryland), and M. Sharina, L. Makarova, and D. Makarov (Russian Academy of Sciences, Special Astrophysical Observatory). The science team comprises: K. McQuinn and E. Skillman (University of Minnesota, Minneapolis), J. Cannon (Macalester College, MN), J. Dalcanton (University of Washington, Seattle), A. Dolphin (Raytheon Company), and D. Stark and D. Weisz (University of Minnesota, Minneapolis). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.July 10, 2004, Exposure Time: 35 minutes
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F606W (R) and F814W (I)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.NGC 4068
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Starburst Galaxy
- Release DateApril 30, 2009
- Science ReleaseStarbursts in Dwarf Galaxies are a Global Affair
- Credit

These images are composites of several separate exposures made by the ACS instrument on the Hubble Space Telescope. Two filters were used to sample broad wavelength ranges for each image. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic image. In this case, the assigned colors are orange/yellow for the I-band (F814W) and cyan/blue for the wide V-band (F606W) filter. The images have been further adjusted so the colors more closely resemble their true visual appearance, particularly the red hydrogen emission of the star-forming regions. Cyan: F606W (R) Yellow: F814W (I)

Related Images & Videos
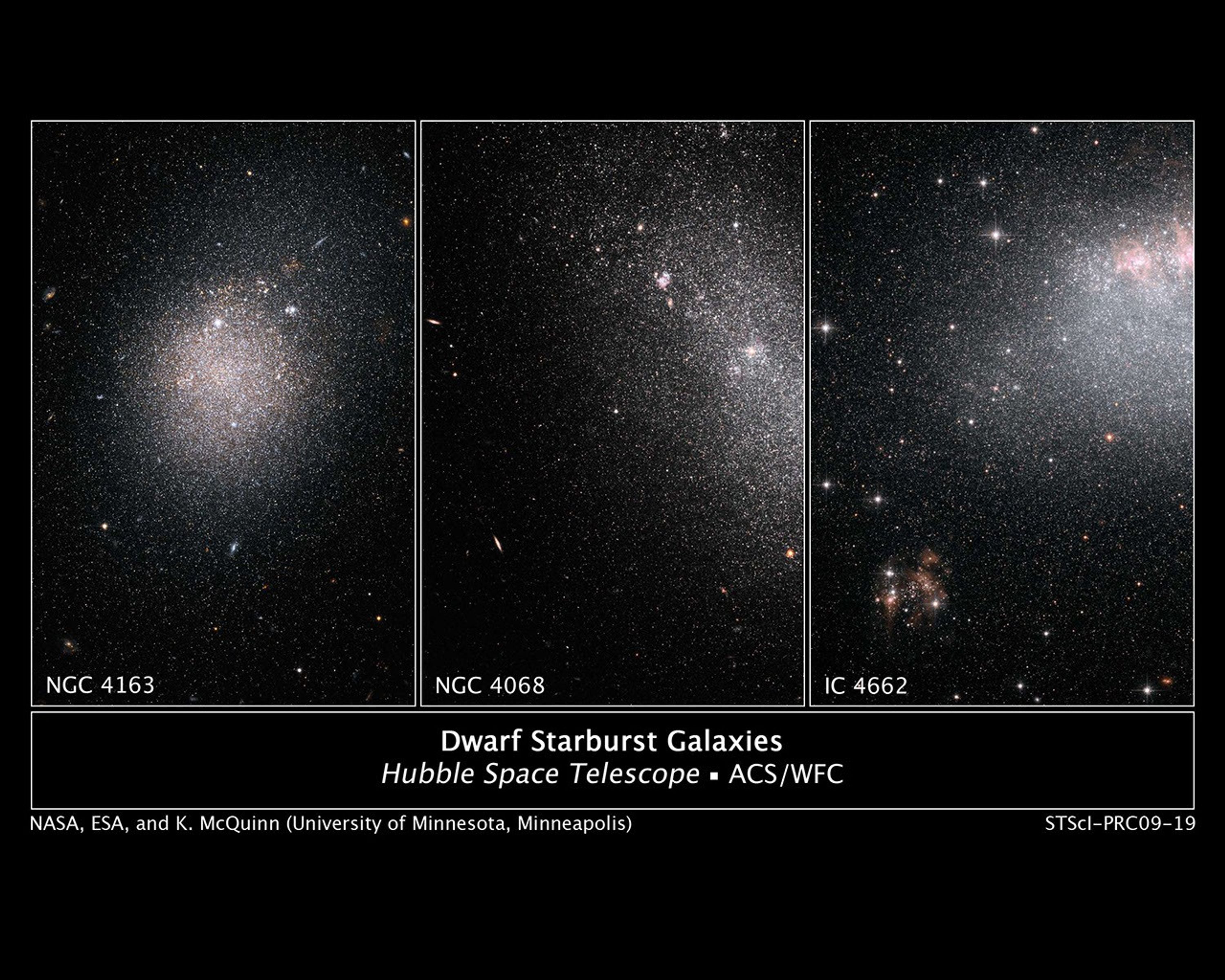

Hubble Spies a Frenzy of Star Birth in Dwarf Galaxies
These images, taken by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, show myriad stars residing in the central regions of the three dwarf galaxies NGC 4163, NGC 4068, and IC 4662. The bluish dots are younger stars; the reddish dots, older stars. The irregularly shaped red blobs in the images...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov