1 min read
Hubble Optical Image of Hercules A (3C 348)

About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.16h 51m 8.14s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.04° 59' 33.32"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Hercules
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.2.1 billion light-years (637 million parsecs or redshift z = 0.156)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The image was created from Hubble data from proposal 13065: S. Baum and C. O'Dea (Rochester Institute of Technology) and J. Stoke and F. Lo (Associated Universities, Inc.). Notes:The VLA data are from the National Radio Astronomy Observatory observation project TDEM0011: R. Perley, W. Cotton, and U. Rao (NRAO/AUI/NSF). These data were taken August 2010 through September 2011. Frequencies 4-9 GHz were measured. - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>WFC3/UVIS
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.October 8, 2012, Exposure Time: 1 hour
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F606W (V) and F814W (I)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Hercules A, Herc A, 3C 348
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Active Galaxy
- Release DateNovember 29, 2012
- Science ReleaseA Multi-Wavelength View of Radio Galaxy Hercules A
- Credit

This image is a composite of separate exposures acquired by Hubble's WFC3 instrument. Several filters were used to sample various wavelengths/frequencies. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Orange: F814W (I) Blue: WFC3/UVIS F606W (V)
Related Images & Videos

A Multi-Wavelength View of Radio Galaxy Hercules A
Spectacular jets powered by the gravitational energy of a supermassive black hole in the core of the elliptical galaxy Hercules A illustrate the combined imaging power of two of astronomy's cutting-edge tools, the Hubble Space Telescope's Wide Field Camera 3, and the recently...
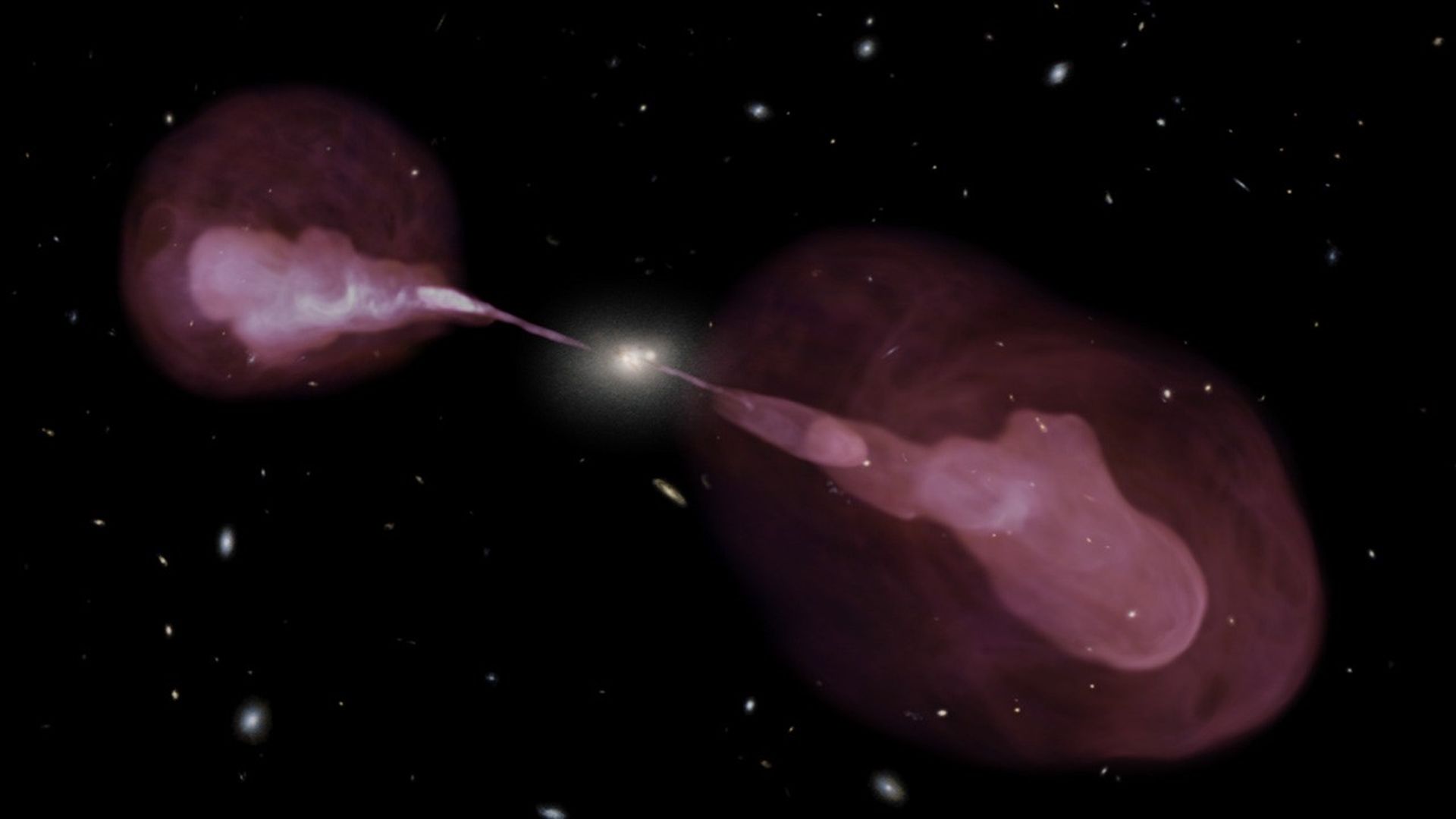

A 3-D Perspective on Hercules A
This video envisions a three-dimensional look at the combined visible light and radio emission from the active galaxy Hercules A. Unusually, this giant elliptical galaxy is not found in a large cluster of galaxies, but rather within a comparatively small group of galaxies. The...
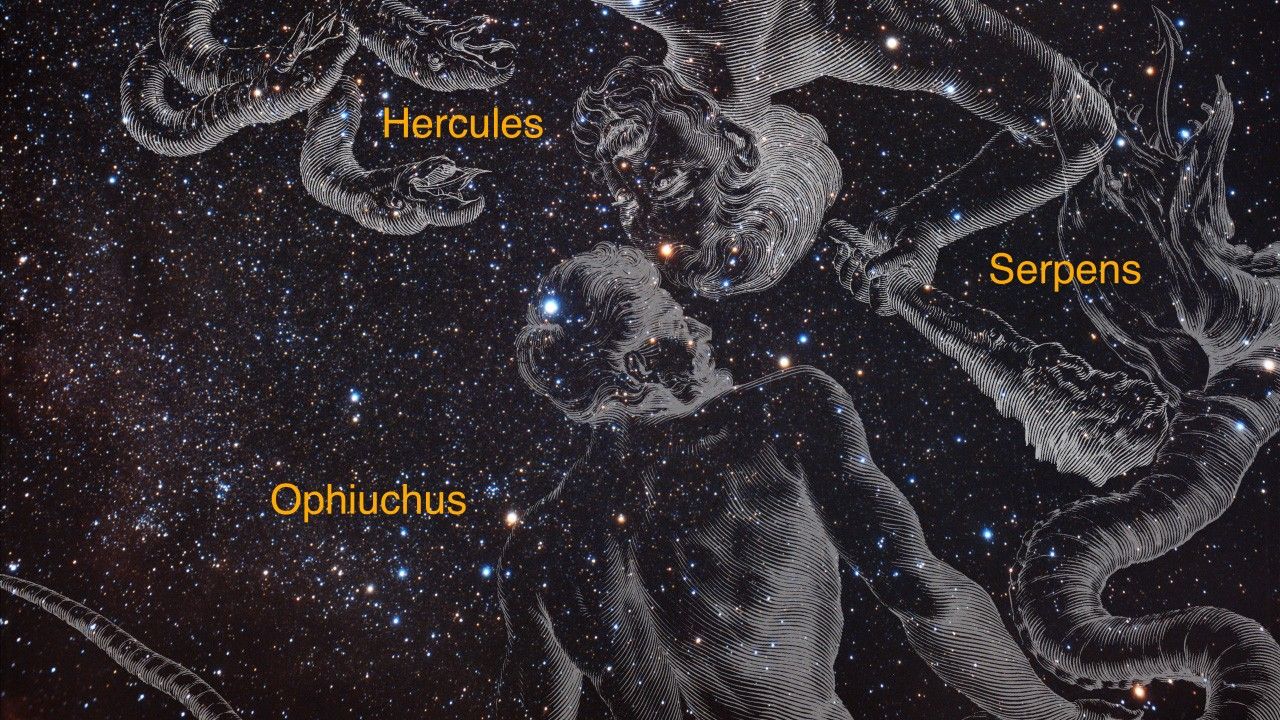
Hercules A Zoom Sequence (Annotated)
This video zooms in on the active radio galaxy Hercules A. Spectacular jets powered by the gravitational energy of a supermassive black hole in the core of the elliptical galaxy Hercules A illustrate the combined imaging power of two of astronomy's cutting-edge tools, the Hubble...

Hercules A Zoom Sequence
This video zooms in on the active radio galaxy Hercules A. Spectacular jets powered by the gravitational energy of a supermassive black hole in the core of the elliptical galaxy Hercules A illustrate the combined imaging power of two of astronomy's cutting-edge tools, the Hubble...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov






























