1 min read
Hubble Photographs Boulders Flung Off Asteroid Dimorphos

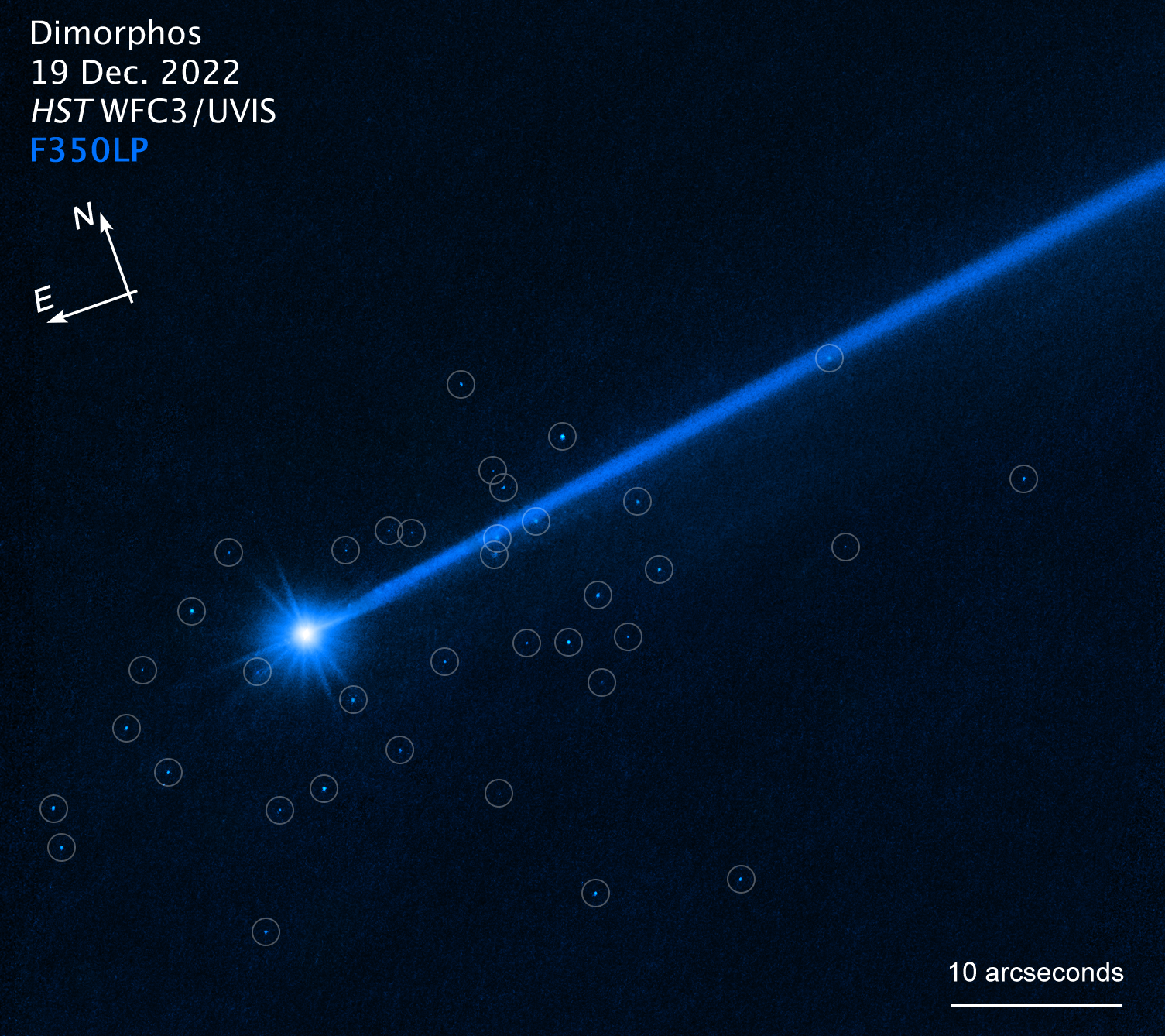
This Hubble Space Telescope image of the asteroid Dimorphos was taken on December 19, 2022, nearly four months after the asteroid was impacted by NASA's DART mission (Double Asteroid Redirection Test). Hubble's sensitivity reveals a few dozen boulders knocked off the asteroid by the force of the collision. These are among the faintest objects Hubble has ever photographed inside the solar system. The free-flung boulders range in size from three feet to 22 feet across, based on Hubble photometry. They are drifting away from the asteroid at a little more than a half-mile per hour. The discovery yields invaluable insights into the behavior of a small asteroid when it is hit by a projectile for the purpose of altering its trajectory.
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created with Hubble data from proposal: 17289 (D. Jewitt)
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.WFC3/UVIS
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.19 Dec 2022
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F350LP
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Dimorphos
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Asteroid boulder field
- Release DateJuly 20, 2023
- Science ReleaseHubble Sees Boulders Escaping from Asteroid Dimorphos
- CreditNASA, ESA, David Jewitt (UCLA); Image Processing: Alyssa Pagan (STScI)

This image is acquired by the WFC3 instrument on the Hubble Space Telescope. The color results from assigning a blue hue to a monochromatic (grayscale) image.
Related Images & Videos

Hubble Photographs Boulders Flung Off Asteroid Dimorphos (Compass Image)
Image of the asteroid Dimorphos, with compass arrows, scale bar, and color key for reference. The north and east compass arrows show the orientation of the image on the sky. Note that the relationship between north and east on the sky (as seen from below) is flipped relative to...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov





























