1 min read
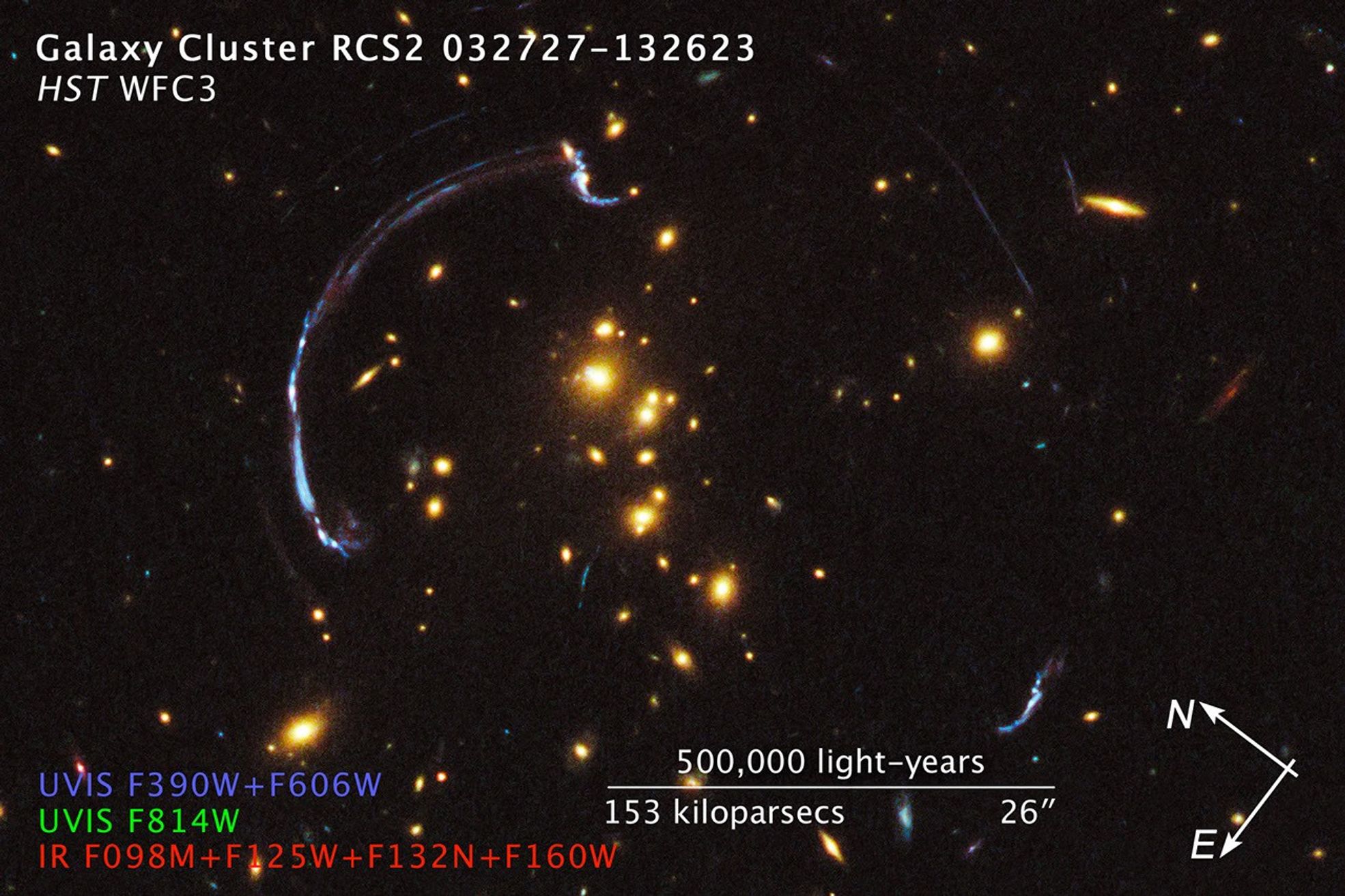
Hubble WFC3 Image of Core of RCS2 032727-132623 and Reconstruction of RCSGA 032727-132609

About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.03h 27m 27.09s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-13° 26' 22.8"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Eridanus
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.z = 1.701 (background galaxy RCSGA 032727-132609) and z = 0.564 (foreground galaxy cluster RCS2 032727-132623)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The image was created from Hubble data from proposal 12267: J. Rigby (NASA Goddard Space Flight Center) et al. - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>WFC3/UVIS and HST>WFC3/IR
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.March 1, 2011, Exposure Time: 2.7 hours
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.WFC3/UVIS: F390W (U), F606W (V), and F814W (I) WFC3/IR: F098M (blue grism), F125W (J), F132N (Paschen β), and F160W (H)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.RCS2 032727-132623, RCSGA 032727-132609
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Galaxy Cluster and Gravitational Lens System
- Release DateFebruary 2, 2012
- Science ReleaseHubble Zooms in on a Magnified Galaxy
- Credit

This image is a composite of separate exposures acquired by the WFC3 instrument on HST. Several filters were used to sample broad wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: F390W (U) + F606W (V) Green: F814W (I) Red: F098M (blue grism) + F125W (J) + F132N (Paschen β) + F160W (H)

Related Images & Videos

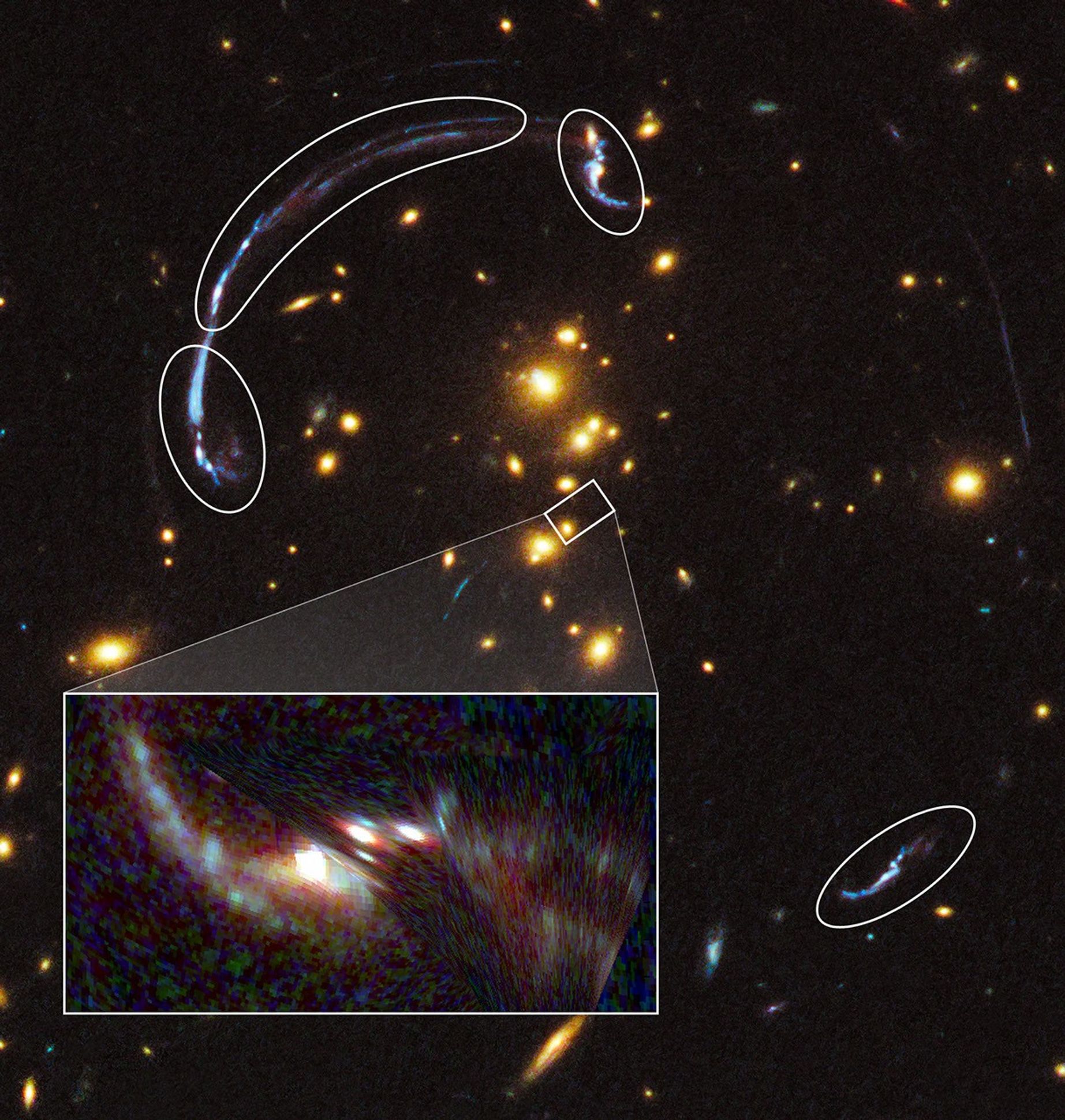
Hubble Sees Giant Lensed Galaxy Arc
Thanks to the presence of a natural "zoom lens" in space, this is a close-up look at the brightest distant "magnified" galaxy in the universe known to date. It is one of the most striking examples of gravitational lensing, where the gravitational field of a foreground galaxy...
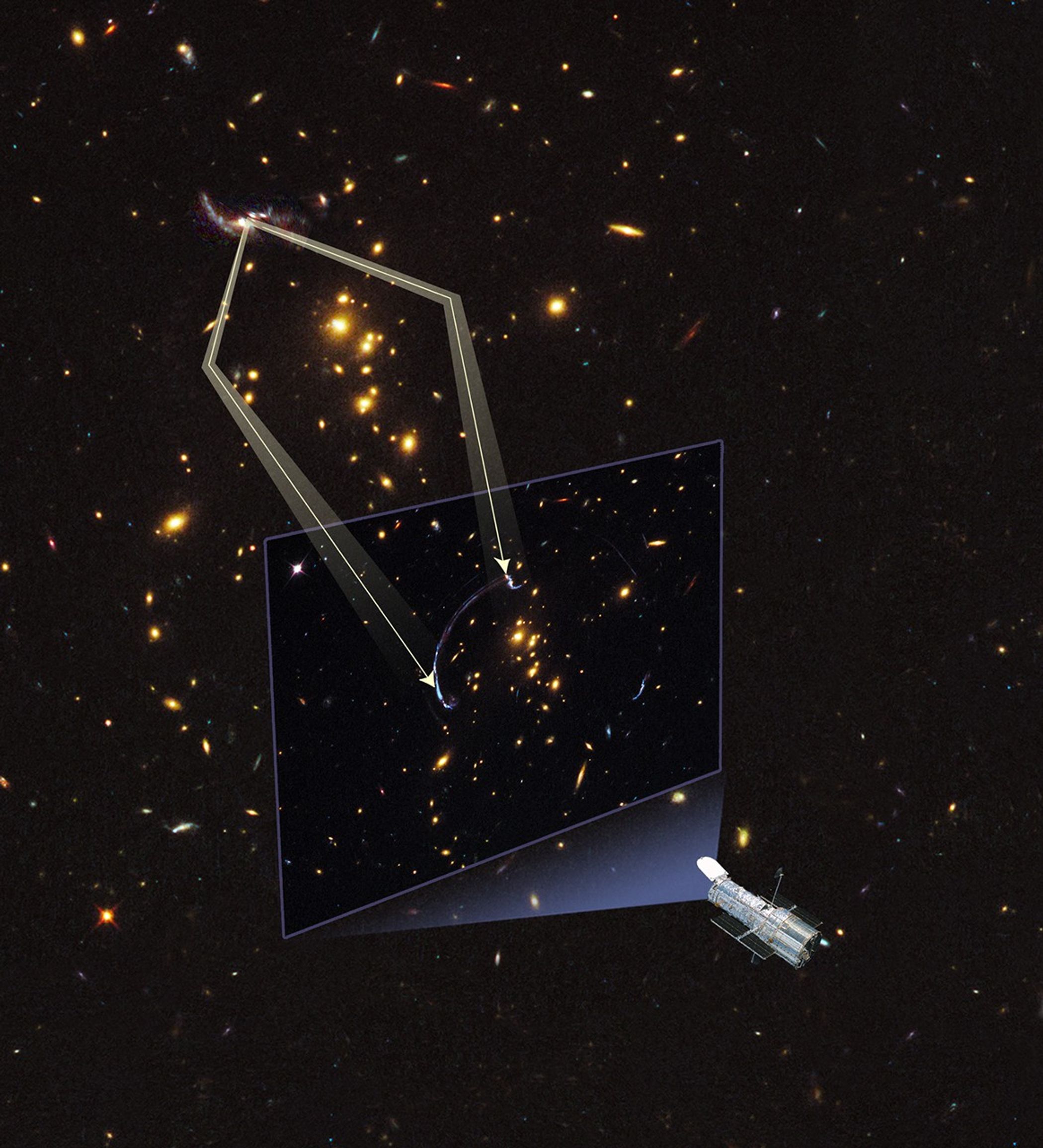

Gravitational Lens Forms Giant Arc
This illustration shows how an image of a background galaxy is distorted and magnified by the gravitational field of a foreground galaxy. In this alignment gravity acts as a lens in space by warping space like a funhouse mirror. The image of a distant galaxy is stretched into a...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov