1 min read
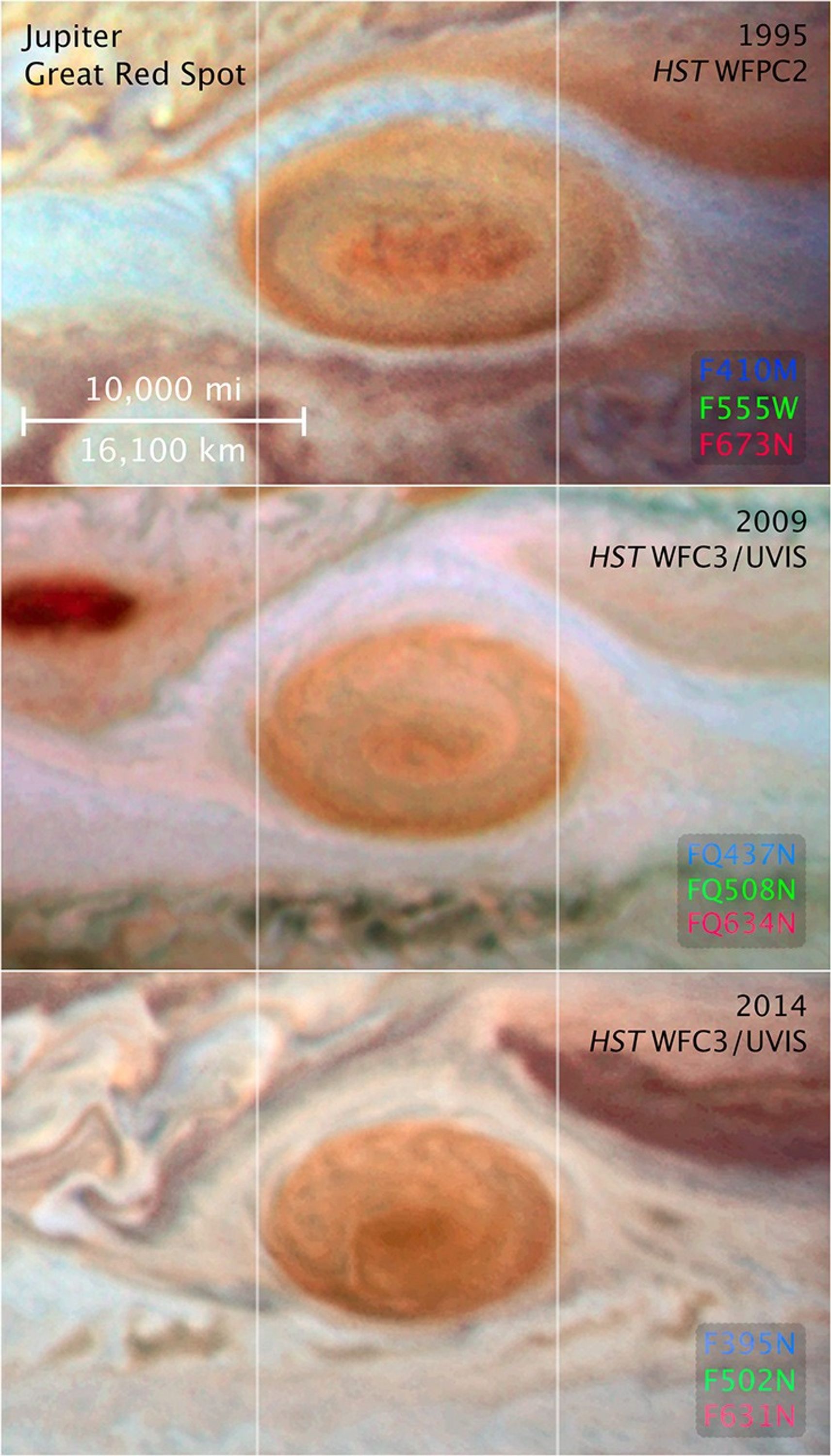
Jupiter’s Great Red Spot (1995, WFPC2)

About the Object
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.The semi-major axis of Jupiter's orbit about the Sun is 5.2 astronomical units (483 million miles or 778 million km).
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.The planet has a diameter of roughly 88,789 miles (142,984 km) at the equator.
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The Jupiter image is from HST proposals 5313 PI: R. Beebe (New Mexico State University), M. Belton (NOAO/AURA), C. Cunningham (Institute for Space and Terrestrial Science), P. Gierasch (Cornell University), A. Ingersoll (Caltech), G. Orton (NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory), J. Pollack (NASA Ames Research Center), and K. Rages (SETI Institute)
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>WFPC2
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.1995
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F410M, F555W, and F673N
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Jupiter
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Planet
- Release DateMay 15, 2014
- Science ReleaseHubble Shows that Jupiter’s Great Red Spot Is Smaller than Ever Seen Before
- Credit

Blue: F410MGreen: F555WRed: F673N
Related Images & Videos
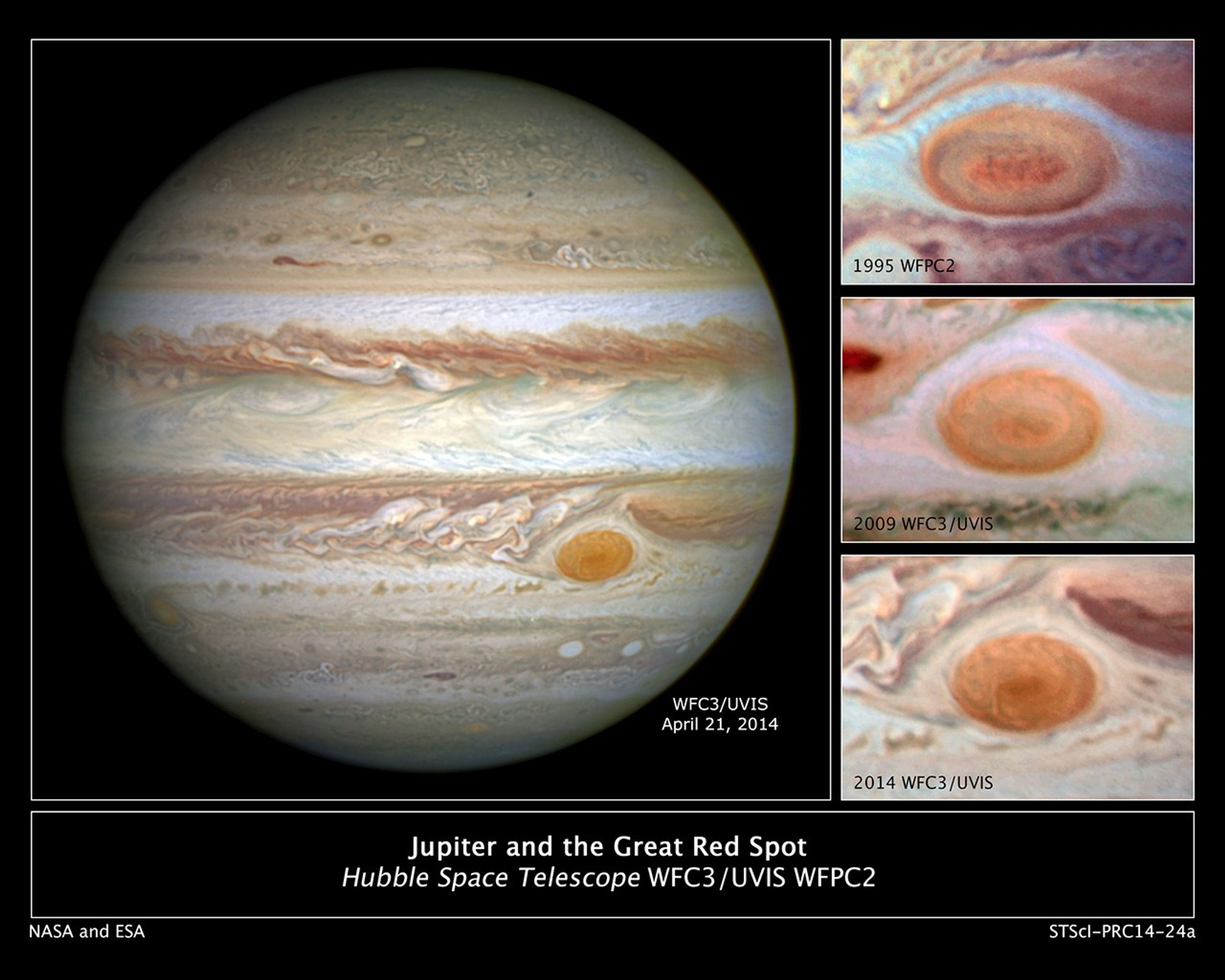
Jupiter and the Great Red Spot
Jupiter's trademark Great Red Spot – a swirling anticyclonic storm feature larger than Earth – has shrunken to the smallest size ever measured. Astronomers have followed this downsizing since the 1930s. "Recent Hubble Space Telescope observations confirm that the Great Red Spot...
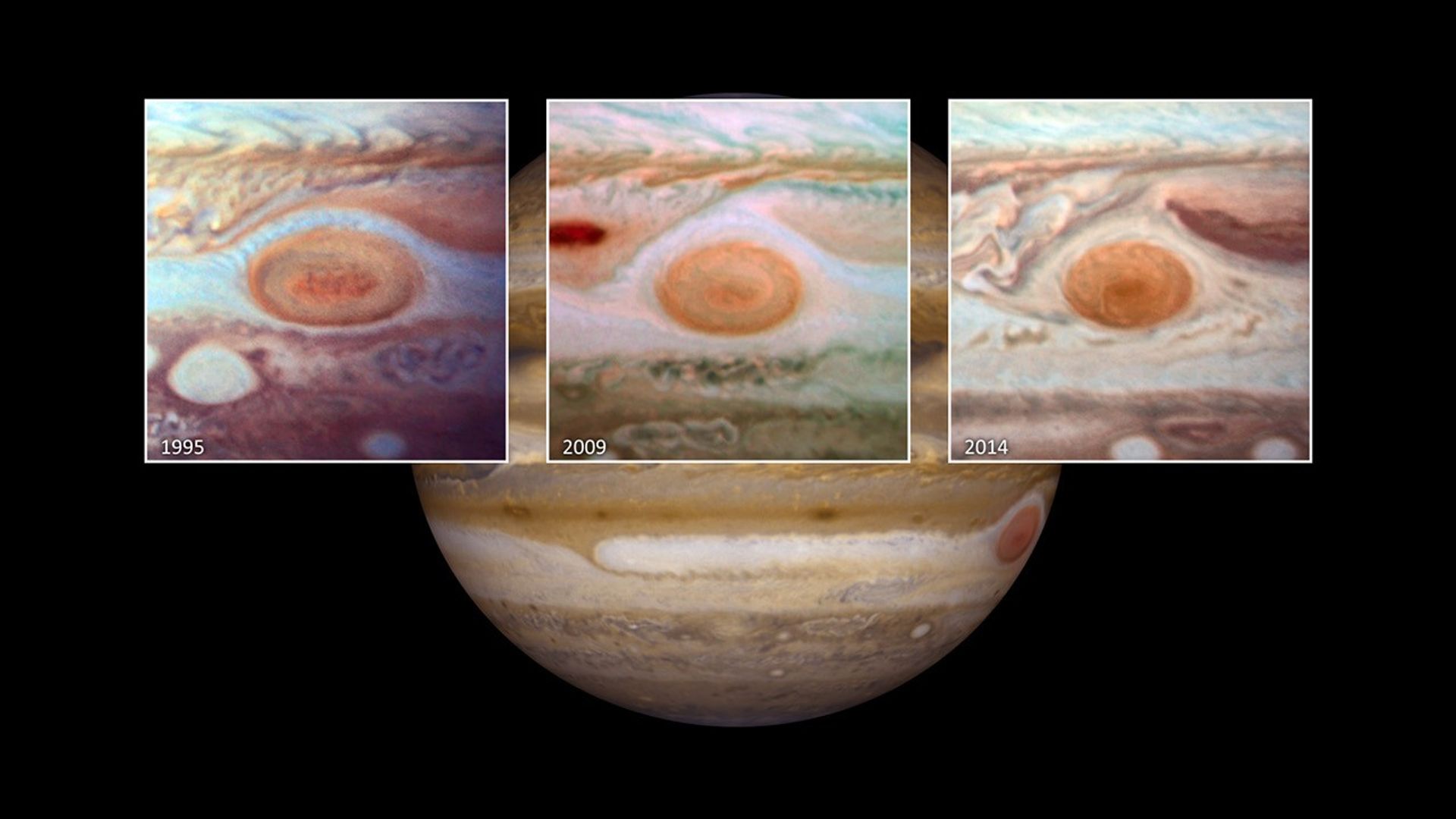

Jupiter's Shrinking Great Red Spot (Narrated)
Narration Transcript: Located nearly 500 million miles away, the planet Jupiter is best known for its Great Red Spot. The spot is really a huge storm… big enough to swallow Earth. This series of Hubble Space Telescope photos spanning nearly two decades shows the Great Red Spot...
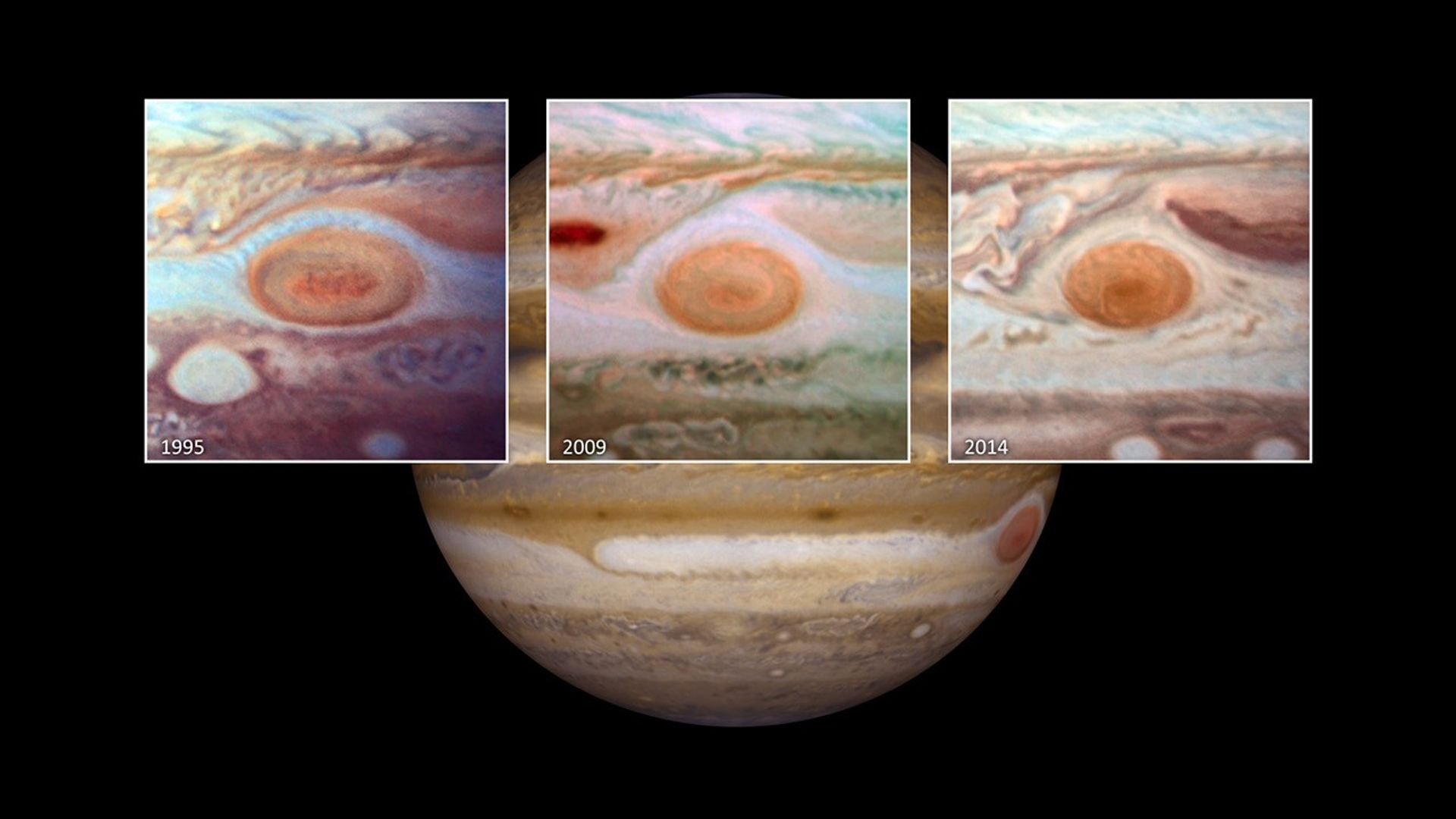

Jupiter's Shrinking Great Red Spot (Unnarrated)
Located nearly 500 million miles away, the planet Jupiter is best known for its Great Red Spot. The spot is really a huge storm… big enough to swallow Earth. This series of Hubble Space Telescope photos spanning nearly two decades shows the Great Red Spot shrinking to the...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov