1 min read
Mars Near Opposition 2024
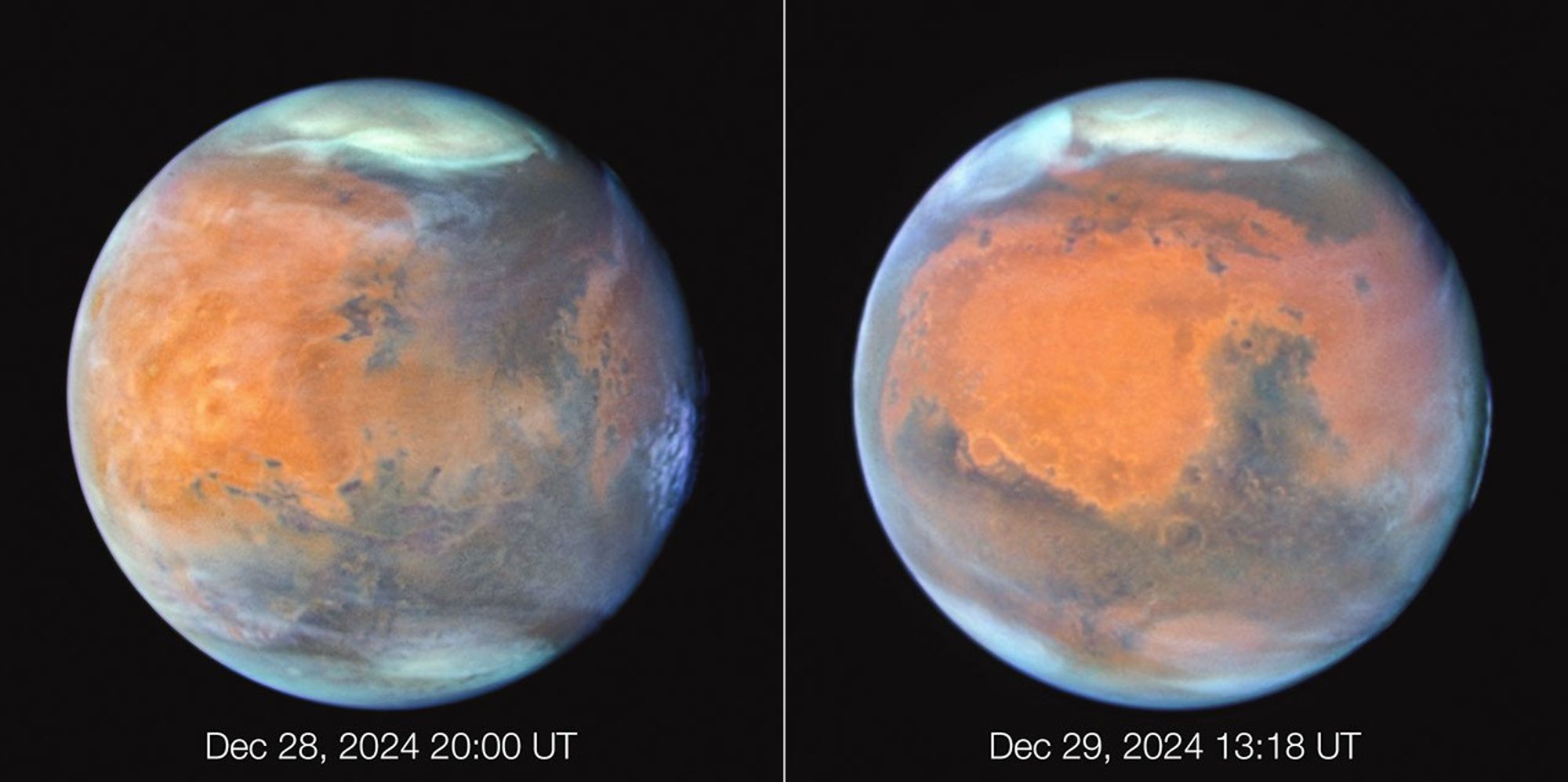
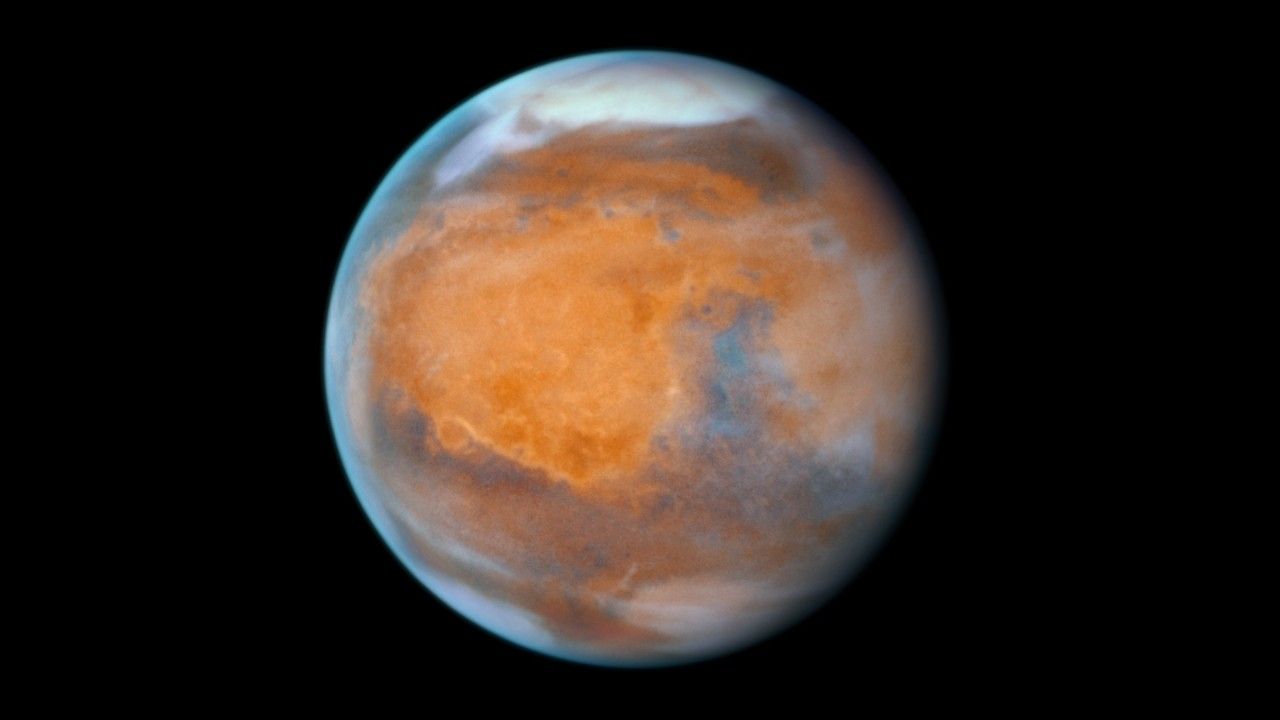
This is a combination of Hubble Space Telescope images of Mars taken from December 28th to 30th, 2024. At the midpoint of the observations, Mars was approximately 61 million miles from Earth. Thin water-ice clouds that are apparent in ultraviolet light give the Red Planet a frosty appearance. The icy northern polar cap was experiencing the start of Martian spring. In the left image, the bright orange Tharsis plateau is visible with its chain of dormant volcanoes. The largest volcano, Olympus Mons, pokes above the clouds at the 10 o’clock position near the northwest limb. At an elevation of 70,000 feet, it is 2.5 times the height of Mt. Everest above sea level. Valles Marineris, Mars’ 2,500-mile-long canyon system, is a dark, linear, horizontal feature near center left. In the right image, high-altitude evening clouds can be seen along the planet’s eastern limb. The 1,400-mile-wide Hellas basin, an ancient asteroid impact feature, appears far to the south. Most of the hemisphere is dominated by the classical “shark fin” feature, Syrtis Major.
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The HST observations include those from program 17879 (C. Britt)
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.WFC3/UVIS
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.28-30 December 2024
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F275W, F410M, F502N, F673N
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Mars
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Planet
- Release DateApril 23, 2025
- Science ReleaseEye on Infinity: NASA Celebrates Hubble’s 35th Year in Orbit
- CreditImage: NASA, ESA, STScI; Image Processing: Joseph DePasquale (STScI)
Downloads

These images were acquired by the WFC3 Instrument on the Hubble Space Telescope. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to a monochromatic (grayscale) image. In this case, the assigned colors are: Violet: F275W, Blue: F410M, Green: F502N, Red: F673N

Related Images & Videos

Mosaic of Hubble 35th Anniversary Targets
A selection of photogenic space targets to celebrate the 35th anniversary of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. Upper left: Mars. Upper right: planetary nebula NGC 2899. Lower left: a small portion of the Rosette Nebula. Lower right: barred spiral galaxy NGC 5335.

Rosette Nebula Context Image
The Rosette Nebula is a vast star-forming region, 100 light-years across, that lies at one end of a giant molecular cloud. The background image is from the Digitized Sky Survey, while the inset is a small portion of the nebula as photographed by the Hubble Space Telescope.
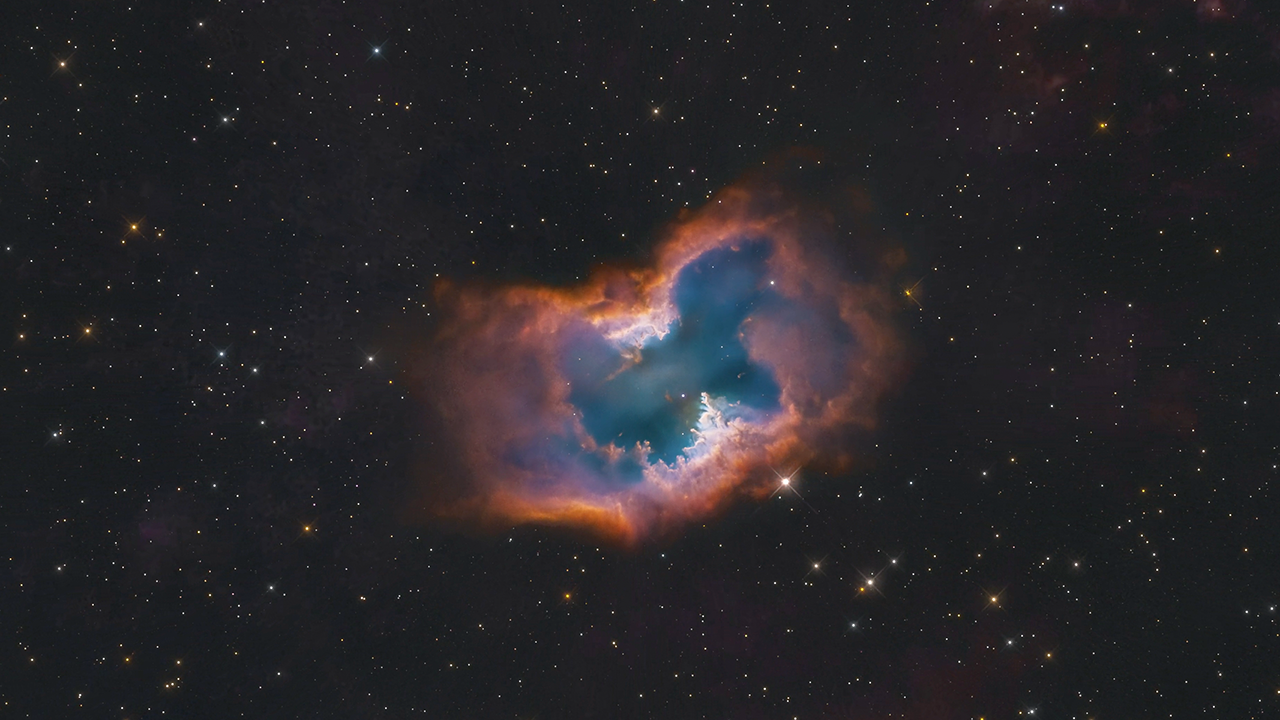

Planetary Nebula NGC 2899
This video zooms across 6,500 light-years through a star-studding field to visit the planetary nebula NGC 2899, as photographed by the Hubble Space Telescope. The nebula has a diagonal bipolar structure formed by a cylindrical-shaped outflow of hot gasses and radiation from the c...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov




































