1 min read
NGC 1275 (Perseus A) Multi-wavelength Composite

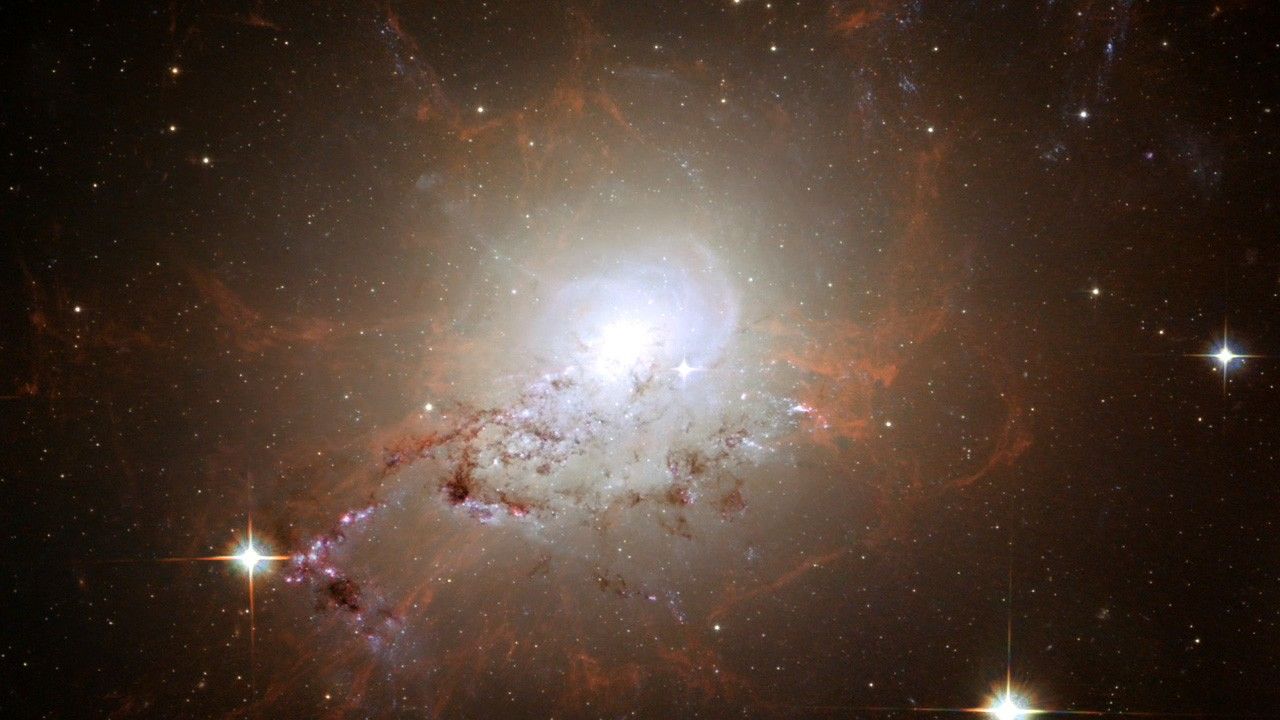
The active galaxy NGC 1275 is also a well-known radio source (Perseus A) and a strong emitter of X-rays due to the presence of a black hole in the center of the galaxy. The behemoth also lies at the center of the cluster of galaxies known as the Perseus Cluster. By combining multi-wavelength images into a single composite, the dynamics of the galaxy are more easily visible. Detail and structure from radio, optical and radio wavelengths combine for an aesthetically pleasing, but nonetheless violent depiction of events going on at the heart of the galaxy.
X-ray data from the Chandra's Advanced CCD Imaging Spectrometer and radio data from NRAO's Very Large Array were combined with optical wavelengths in the red, green and blue from Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys. In the composite image, the X-ray data contribute to the soft violet shells around the outside of the center. The pinkish lobes toward the center of the galaxy are from radio frequencies. The radio emission, tracing jets from the black hole, fills the X-ray cavities. Dust lanes, star-forming regions, hydrogen filaments, foreground stars, and background galaxies are contributions from the Hubble optical data.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.03h 19m 48.15s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.41° 30' 42.09"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Perseus
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.About 230 million light-years (70 Megaparsecs)
About the Data
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS/WFC, CXO>ACIS and NARO>VLA
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.NGC 1275, Perseus A, 3C 84
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Active Galaxy
- Release DateAugust 20, 2008
- Science ReleaseHubble Sees Magnetic Monster in Erupting Galaxy
- CreditImage: NASA, ESA, and L. Frattare (STScI); Science: X-ray: NASA/CXC/IoA/A.Fabian et al.; Radio: NRAO/VLA/G. Taylor; Optical: NASA, ESA, the Hubble Heritage (STScI/AURA)-ESA/Hubble Collaboration, and A. Fabian (Institute of Astronomy, University of Cambridge, UK)
Related Images & Videos

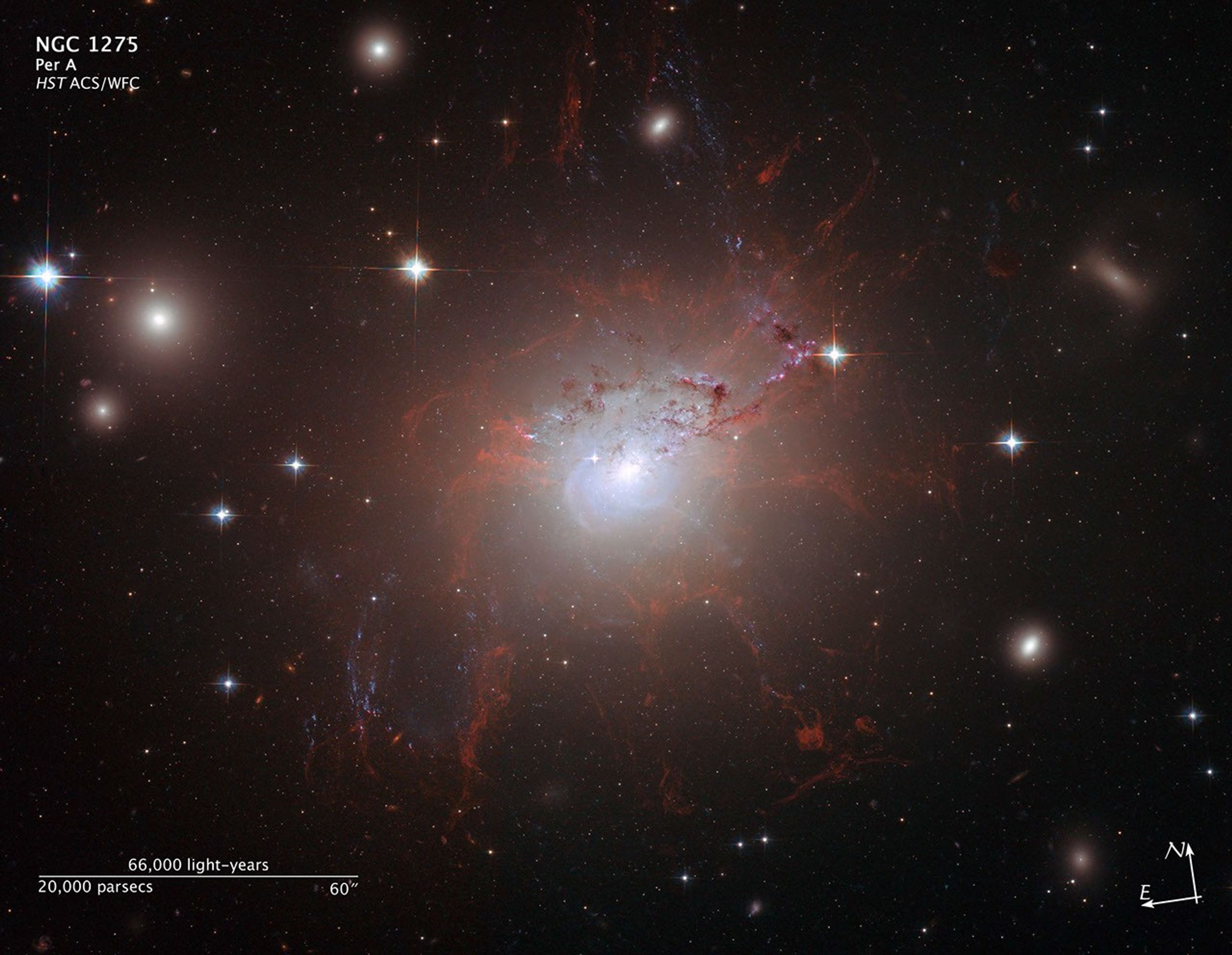
Hubble ACS image of NGC 1275
This Hubble Space Telescope image of galaxy NGC 1275 reveals the fine, thread-like filamentary structures in the gas surrounding the galaxy. The red filaments are composed of cool gas being suspended by a magnetic field, and are surrounded by the 100-million-degree Fahrenheit...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov