1 min read
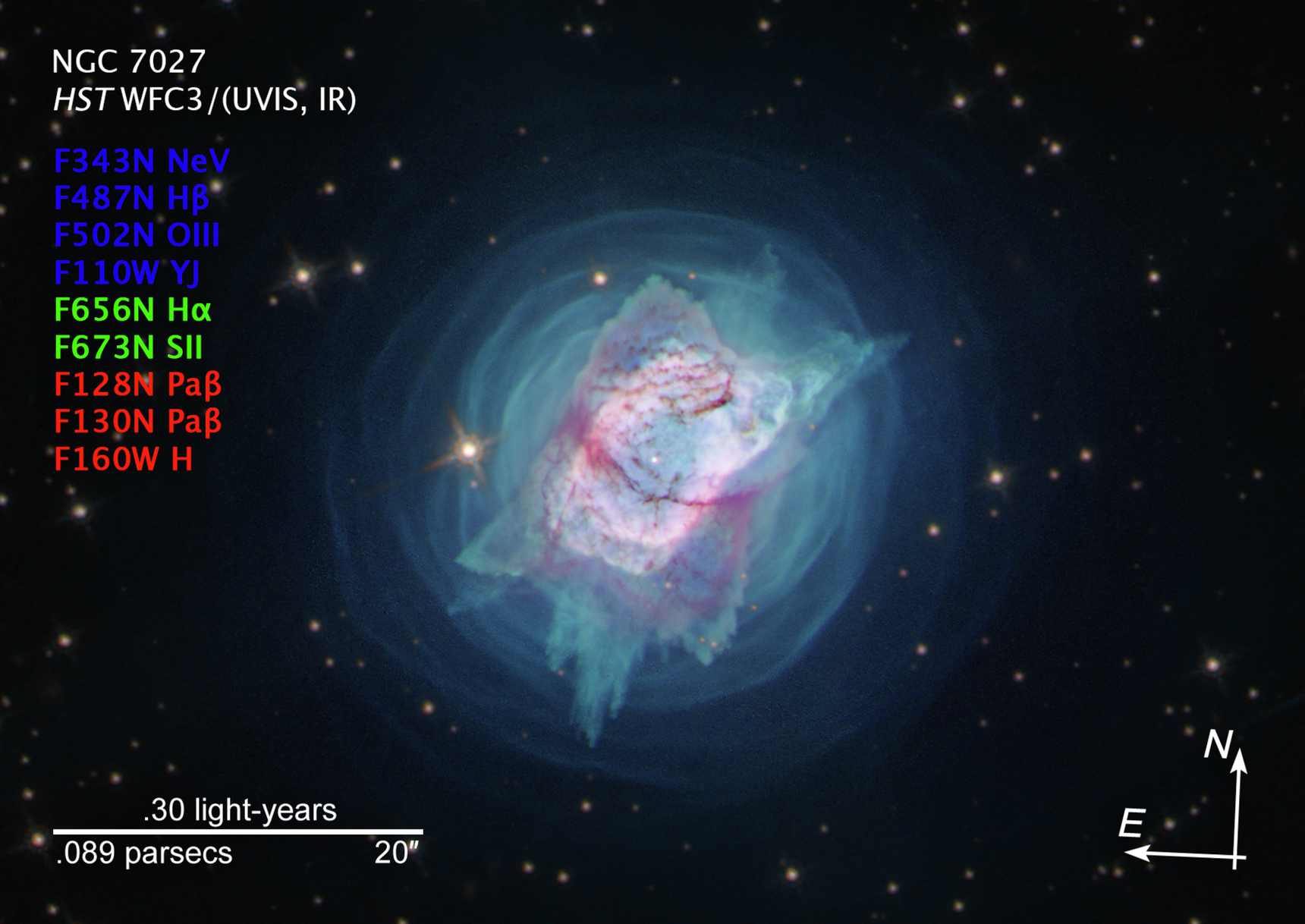
NGC 7027
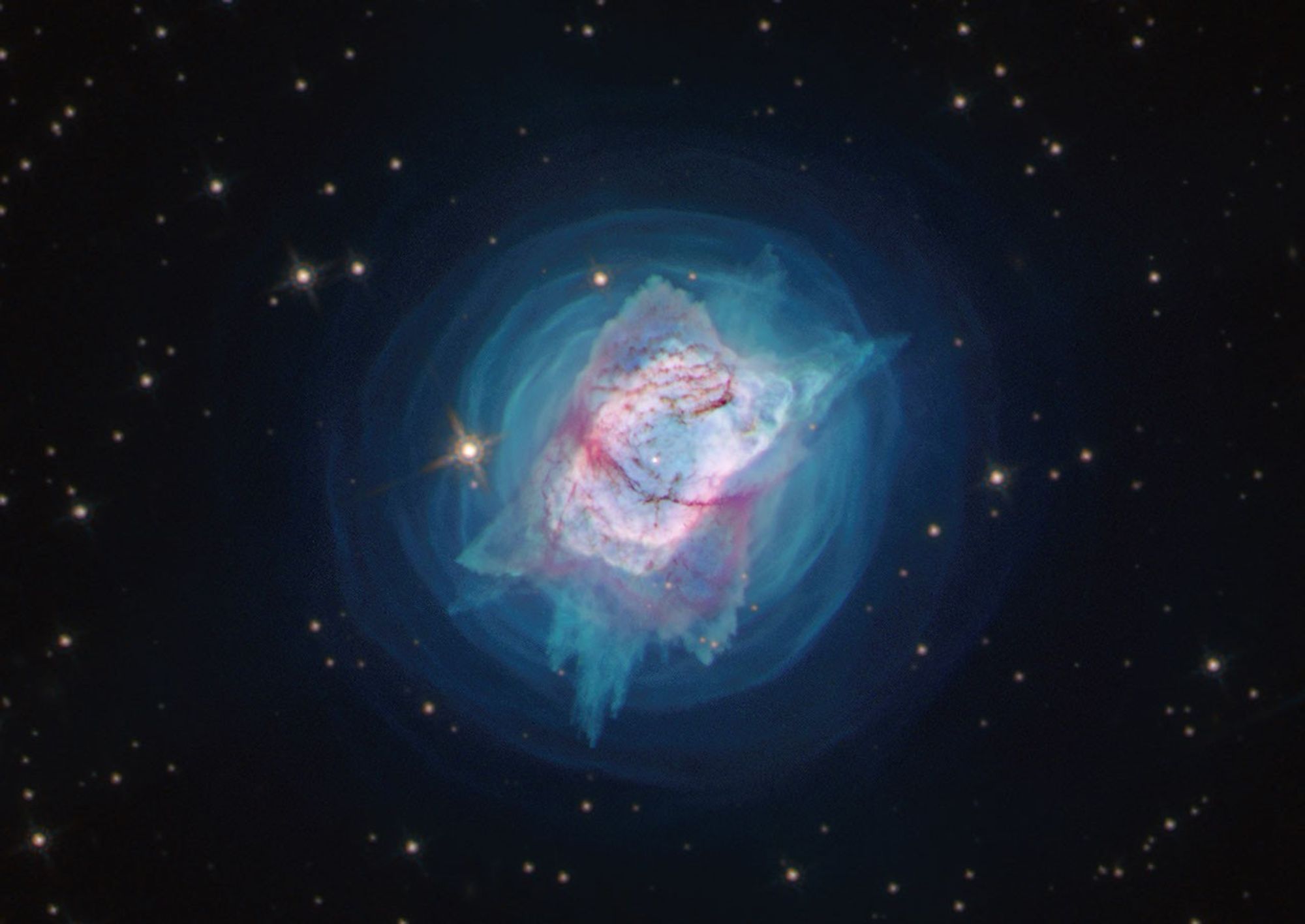

Recently, NGC 7027's central star was identified in a new wavelength of light — near-ultraviolet — for the first time by using Hubble's unique capabilities. The near-ultraviolet observations will help reveal how much dust obscures the star and how hot the star really is.
This object, which resembles a colorful jewel bug, is a visibly diffuse region of gas and dust that may be the result of ejections by closely orbiting binary stars that were first slowly sloughing off material over thousands of years, and then entered a phase of more violent and highly directed mass ejections. Hubble first looked at this planetary nebula in 1998. By comparing the old and new Hubble observations, researchers now have additional opportunities to study the object as it changes over time.
Planetary nebulas are expanding shells of gas created by dying stars that are shedding their outer layers. When new ejections encounter older ejections, the resulting energetic collisions shape the nebula. The mechanisms underlying such sequences of stellar mass expulsion are far from fully understood, but researchers theorize that binary companions to the central, dying stars play essential roles in shaping them.
NGC 7027 is approximately 3,000 light-years away in the constellation Cygnus.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.21:07:01.7
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.+42:14:11
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Cygnus
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.3000 light-years
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.Image is 116 arcmin across (about 1 light-year)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The HST observations include those from programs 15953 (J. Kastner) - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.WFC3/UVIS and IR
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.30 observations between Nov 2019 and Apr 2020
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F343N, F487N, F502N, F656N, F658N, F673N, F110W, F128N, F130N, F160W, F164N
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.NGC 7027
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Planetary Nebula
- Release DateJune 18, 2020
- Science ReleaseHubble Provides Holistic View of Stars Gone Haywire
- CreditNASA, ESA, Joel Kastner (RIT)

These images are a composite of separate exposures acquired by the WFC3/UVIS and WFC3/IR instruments on the Hubble Space Telescope. Several filters were used to sample narrow wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: F343N, F487N, F502N, F110W Green: F656N, F673N Red: F128N, F130N, F160W
Related Images & Videos

Two Planetary Nebulas: NGC 6302 and NGC 7027
Hubble was recently retrained on NGC 6302, known as the "Butterfly Nebula," to observe it across a more complete spectrum of light, from near-ultraviolet to near-infrared, helping researchers better understand the mechanics at work in its technicolor "wings" of gas. The...

NGC 6302: The "Butterfly Nebula"
Hubble was recently retrained on NGC 6302, known as the "Butterfly Nebula," to observe it across a more complete spectrum of light, from near-ultraviolet to near-infrared, helping researchers better understand the mechanics at work in its technicolor "wings" of gas. The...

Compass Image for NGC 6302
Image of planetary nebula NGC 6302, with compass arrows, scale bar, and color key for reference. The north and east compass arrows show the orientation of the image on the sky. Note that the relationship between north and east on the sky (as seen from below) is flipped relative...

Compass Image for NGC 7027
Image of planetary nebula NGC 7027, with compass arrows, scale bar, and color key for reference. The north and east compass arrows show the orientation of the image on the sky. Note that the relationship between north and east on the sky (as seen from below) is flipped relative...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov




























