1 min read
Quasar 3C 273 Compass Image
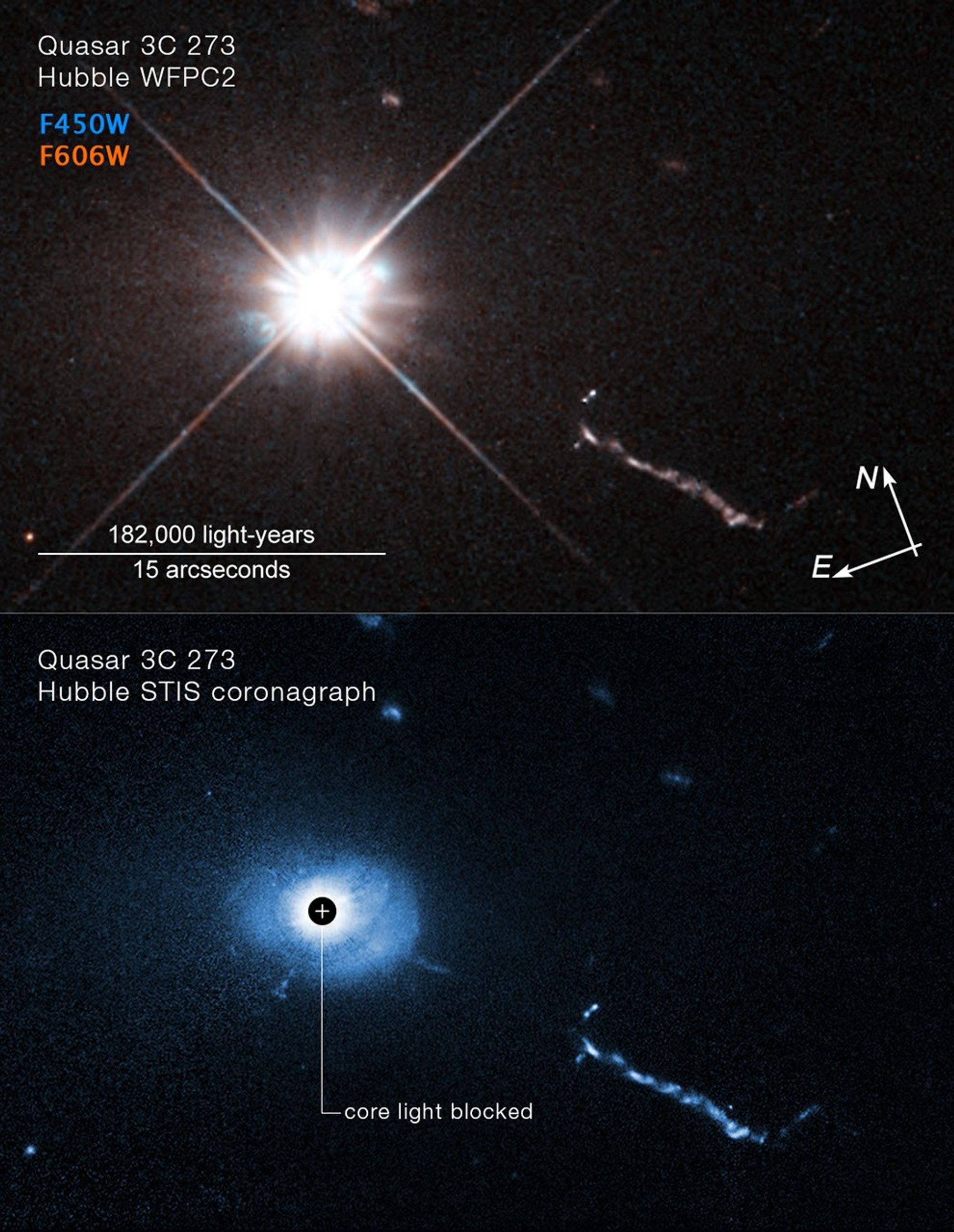

A two-panel image of quasar 3C 273, taken by different Hubble instruments. The top panel is a WFPC2 image of 3C 273. It looks like a bright white car headlight. There’s a linear orange-white smoke-like feature stretching to the 4 o’clock position, an extragalactic jet launched from the quasar in the center of the black hole of an unseen galaxy. Below the title is a color key showing which filters were used to create the image and which color is assigned to each filter: F450W is blue, F606W is orange. Compass arrows at bottom right corner show the orientation of the image on the sky; north arrow points in the 11 o'clock direction; east arrow points toward 8 o'clock. A scale bar at bottom left corner is labeled "182,000 light-years" over "15 arc seconds." The STIS coronagraph image in the bottom panel is roughly the same as the WFPC2 image, but in blue shades. A black circle blocks the glare of the quasar. Blue-colored filamentary material can be seen near the black hole. The extragalactic jet is still visible.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.12:29:06.7
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.02:03:09.0
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Virgo
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.About 2.5 billion light-years
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.Image is 0.7 arcmin across (about 500,000 light-years)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The image was created from Hubble data from the following proposals: 05099 (J. Bachall) and 16715 (B. Ren)
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.WFPC2; STIS
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.June 1995 and September 2022
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.WFPC2: F450W and F606W; STIS: 50CORON
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.3C 273
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Quasar
- Release DateDecember 5, 2024
- Science ReleaseNASA’s Hubble Takes the Closest-Ever Look at a Quasar
- CreditNASA, ESA, Bin Ren (Université Côte d’Azur/CNRS)

These images were acquired by the WFPC2 and STIS instrument on the Hubble Space Telescope. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to a monochromatic (grayscale) image. For WFPC2, the assigned colors are: Cyan: F450W, Orange: F606W and for STIS, a blue hue was assigned to the image.
Related Images & Videos
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov
John Bahcall (IAS)
Joseph DePasquale (STScI)