1 min read
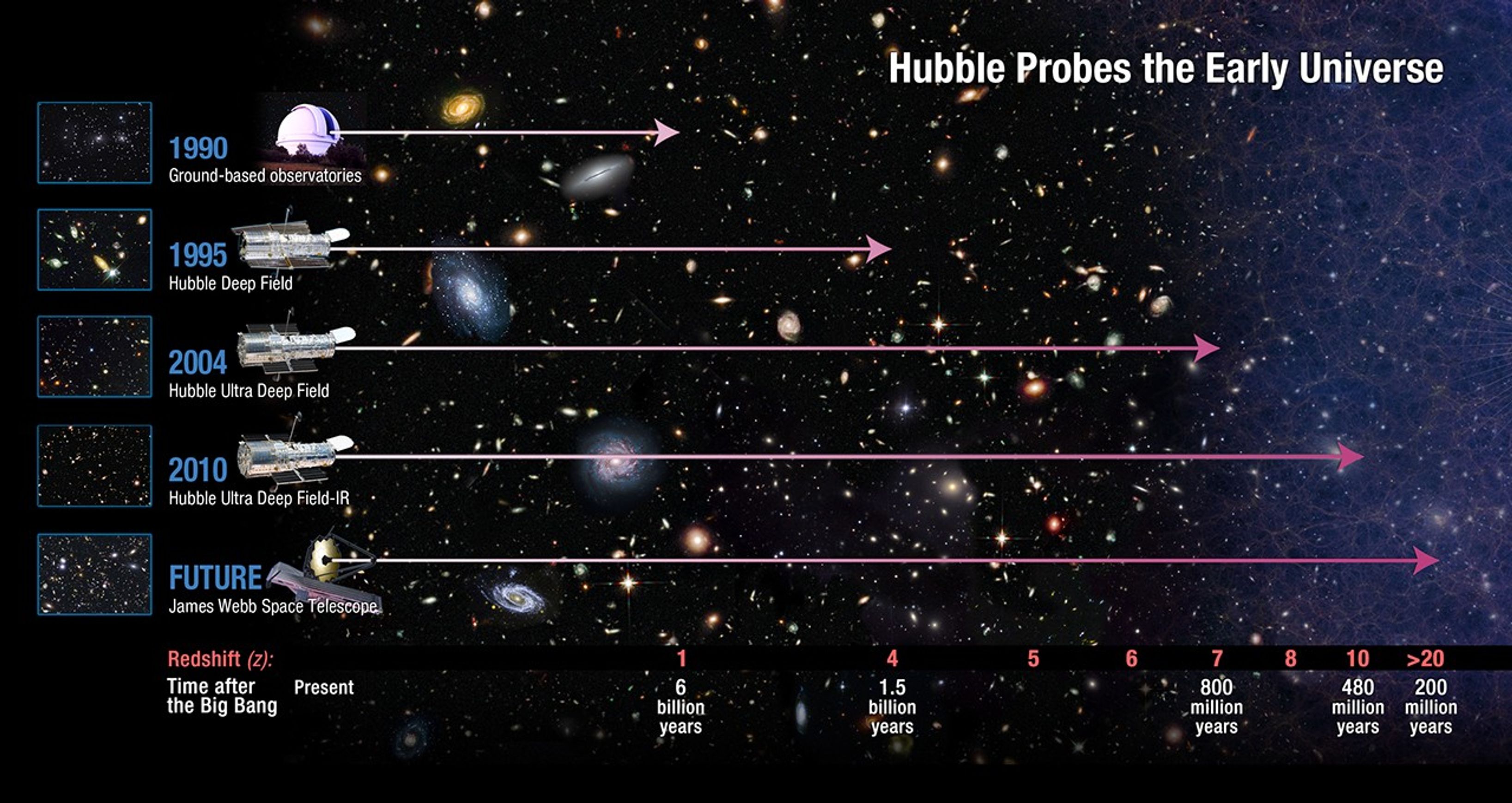
Rate of Star Birth in the Early Universe
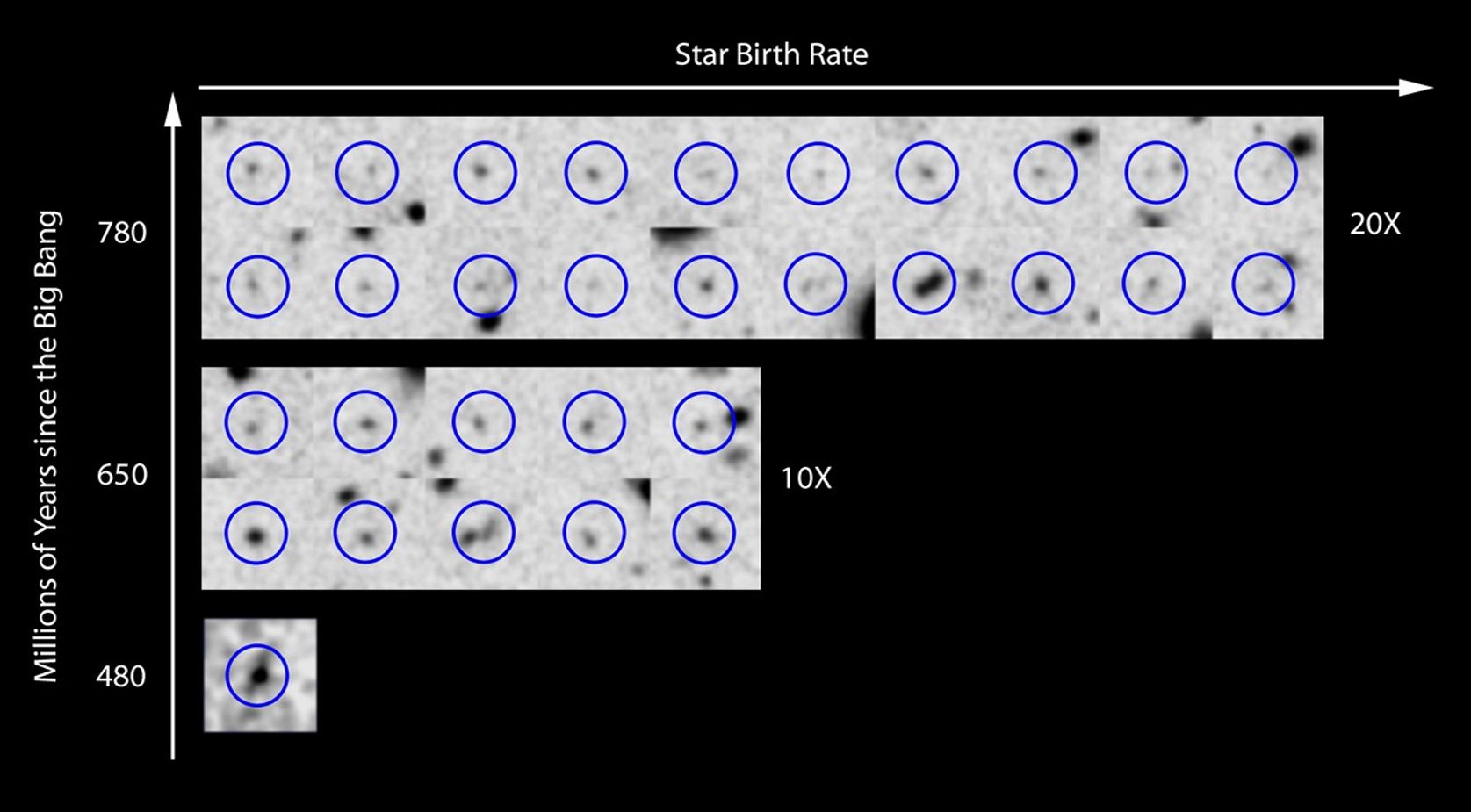
The new Hubble Space Telescope results show that the rate of star birth changed dramatically in the universe over just 170 million years, increasing by ten times from 480 million years after the Big Bang to 650 million years, and doubling again in the next 130 million years. The astonishing 10 times increase in star birth happened in a period that is just 1 percent of the current age of the universe. This is shown schematically in this figure that shows the new galaxy at 480 million years and comparable galaxies from the epoch at 650 million years and at 780 million years after the Big Bang to represent the relative amounts of star birth in galaxies at different times.
- Release DateJanuary 26, 2011
- Science ReleaseNASA’s Hubble Finds Most Distant Galaxy Candidate Ever Seen in Universe
- Credit
Related Images & Videos
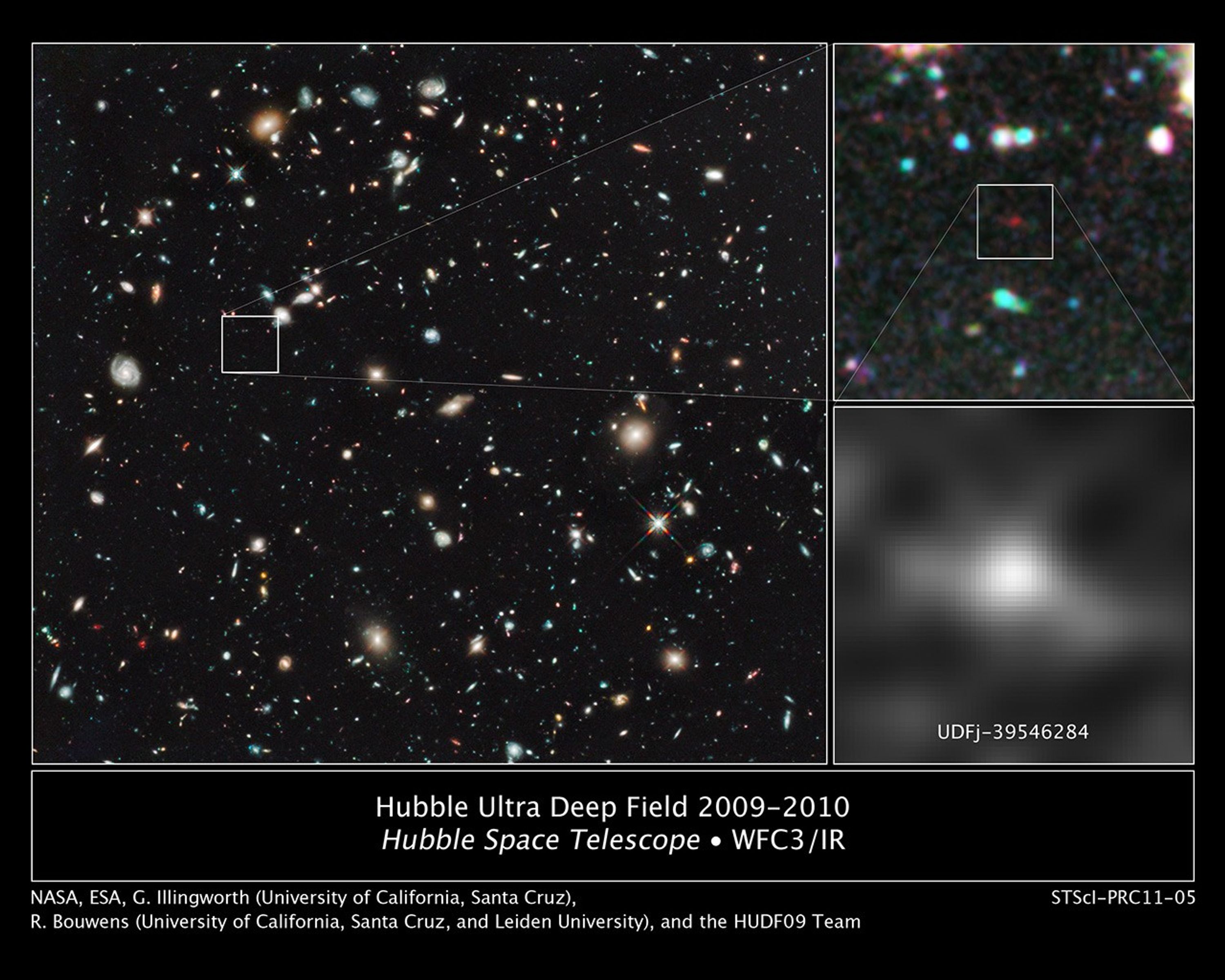

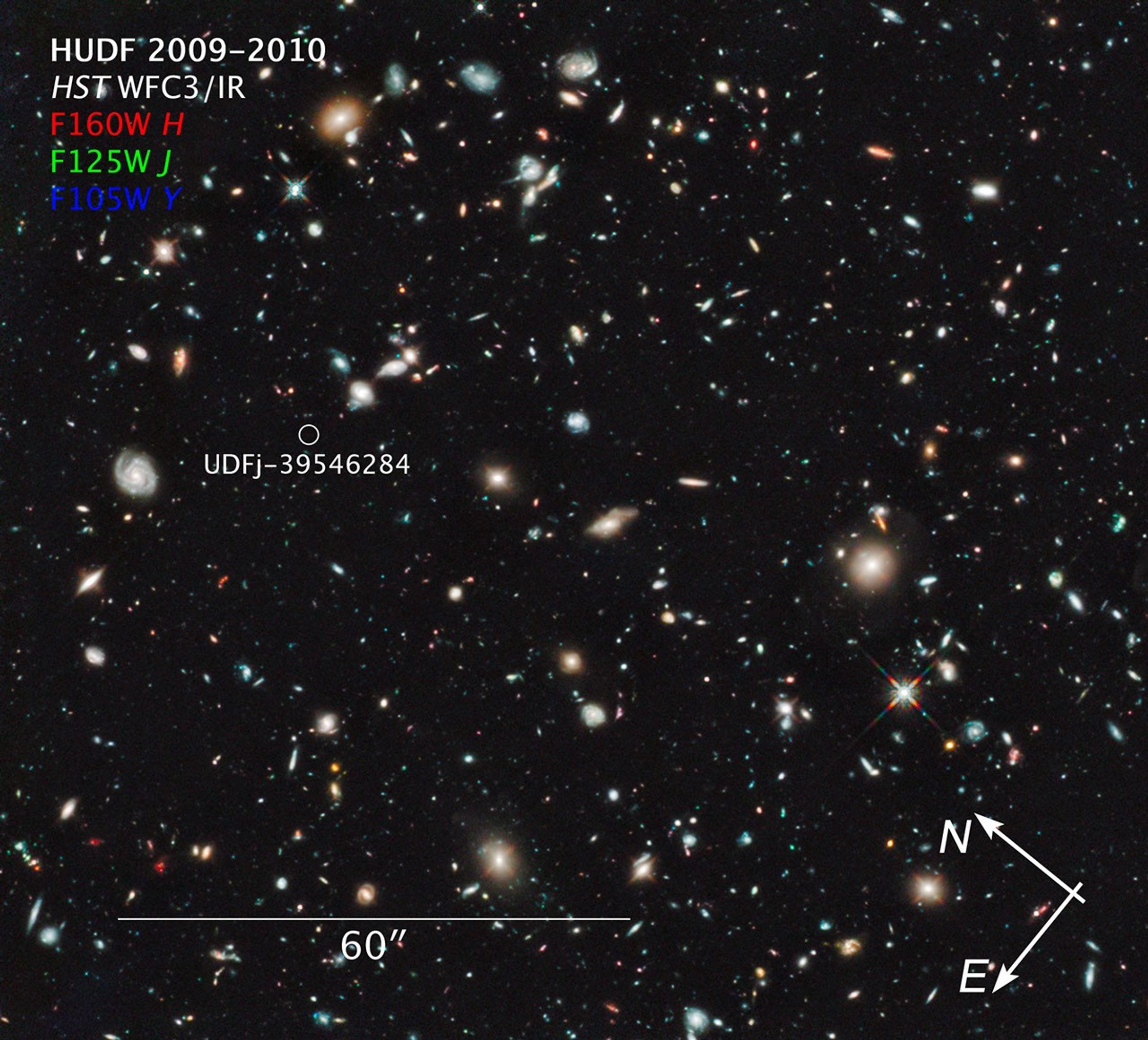
Hubble Ultra Deep Field 2009-2010 and UDFj-39546284
The farthest and one of the very earliest galaxies ever seen in the universe appears as a faint red blob in this ultra-deep-field exposure taken with NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. This is the deepest infrared image taken of the universe. Based on the object's color, astronomers...
Zoom into Infrared Hubble Ultra Deep Field and Object UDFj-39546284
This video is a zoom into the Hubble Space Telescope infrared Ultra Deep Field, first taken in 2009. It is a very small patch of sky in the southern constellation Fornax. Several thousand galaxies at various distances fill Hubble's field of view. The zoom centers on the farthest...
Share
Details
Last Updated
Aug 17, 2025
Contact
Media
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov