1 min read
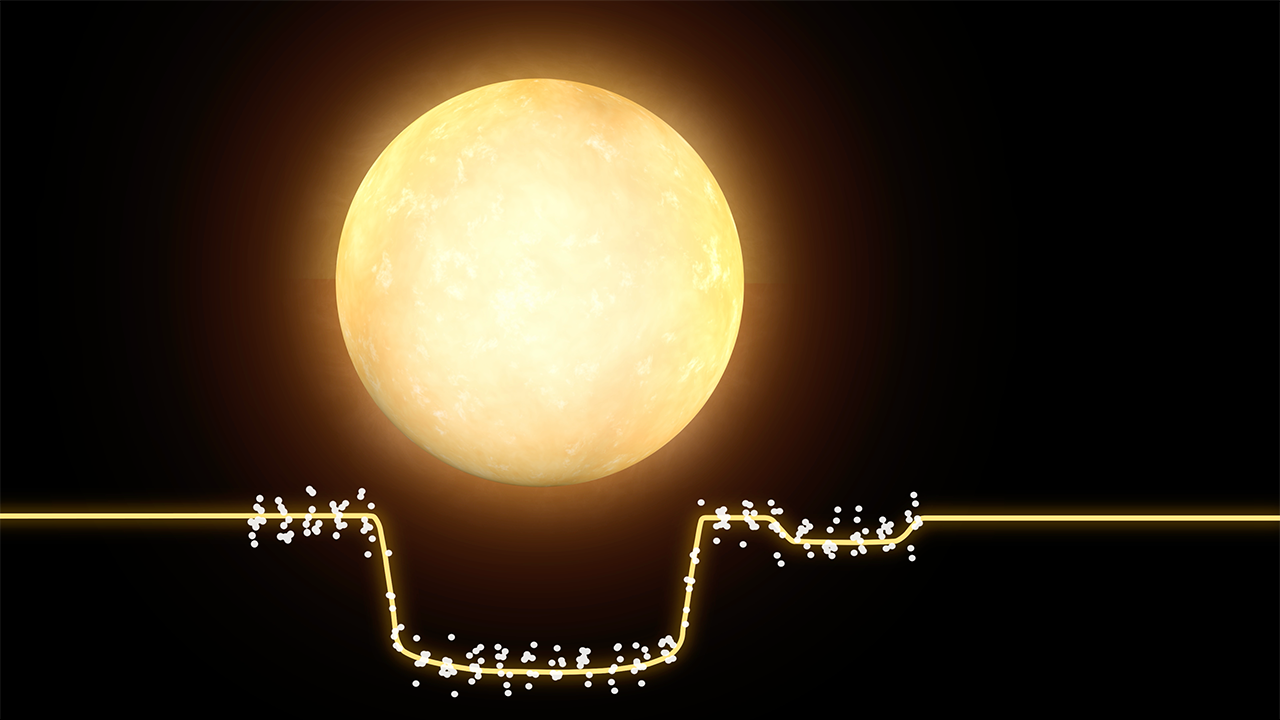
Transit of Kepler-1625b and Suspected Moon

This diagram represents Hubble Space Telescope photometric observations of the planet Kepler-1625b passing in front of its parent star — called a transit. The planet blocks a small fraction of the star's light and this is recorded on a light curve (bottom green line) as a slight dip in the star’s brightness. After the planet's 19-hour-long transit was completed, astronomers noted a second, smaller dip in the light curve about three and a half hours later (panel 4). (Due to observing constraints Hubble was not able to record the full event.) The second dip is interpreted as the signature of a moon trailing the planet. The moon is estimated to be as big as the planet Neptune. The inclination of the candidate moon's orbit is just one of a broad range of possible inclinations that are consistent with the data. Astronomers hope to repeat this observation to confirm the moon's existence. If follow-up observations are successful, this would be the first moon discovered outside of our solar system.
- Release DateOctober 3, 2018
- Science ReleaseAstronomers Find First Evidence of Possible Moon Outside Our Solar System
- Credit
Related Images & Videos

Artist's Illustration of Kepler-1625 System
Artist's Illustration of Possible Moon Outside Our Solar System This is an artist's illustration of the gas giant planet Kepler-1625b and a suspected accompanying moon. Estimated to be as big as the planet Neptune, the moon is unlike anything found inside our solar system. It...
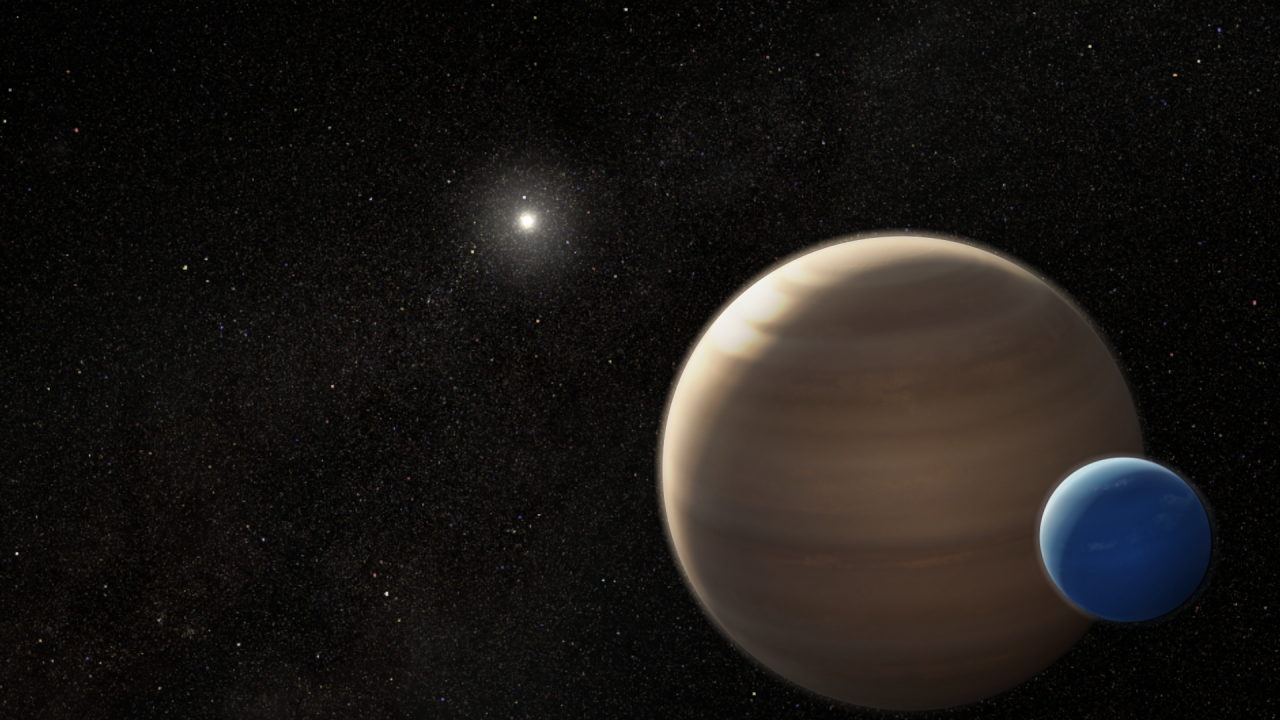

Possible Moon Outside Our Solar System (Artist's Interpretation)
This is an artist's interpretation of the gas giant planet Kepler-1625b and a suspected accompanying moon. Estimated to be as big as the planet Neptune, the moon is unlike anything found inside our solar system. The planet and moon orbit the Sun-like star Kepler-1625, located...

Did the Hubble Telescope Confirm the First Exomoon?
The Hubble and Kepler space telescopes found evidence for what could be a giant moon accompanying a gas-giant planet that orbits the star Kepler-1625, located 8,000 light-years away in the constellation Cygnus. The moon may be as big as Neptune and it orbits a planet several...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov