1 min read
Video News Release: The Hubble Deep Field South
EMBARGOED UNTIL 3:00 PM November 23, 1998 The Space Telescope Science Institute, Baltimore Maryland Ray Villard, Public Affairs Officer
[00:1:55:00] Edited
VIDEO NEWS RELEASE 2:24 VIDEO NEWS RELEASE ELEMENTS
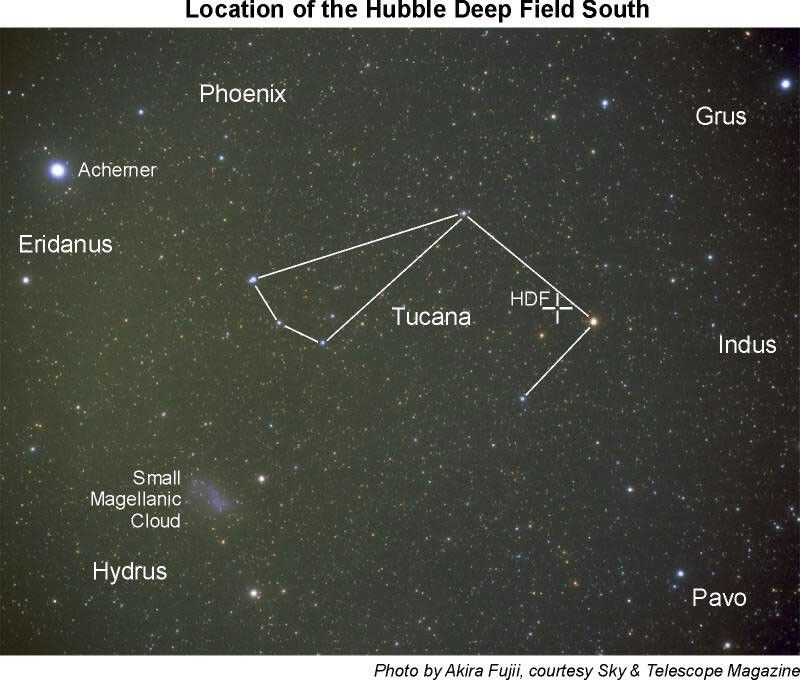
[00:04:42:00] Pointing Animation :15 The Hubble Space Telescope is pointing north at a blank patch of sky above the Big Dipper. Next, shown in orbit, Hubble is slewing to point at the southern skies in the direction of the constellation Tucana, near the south celestial pole.
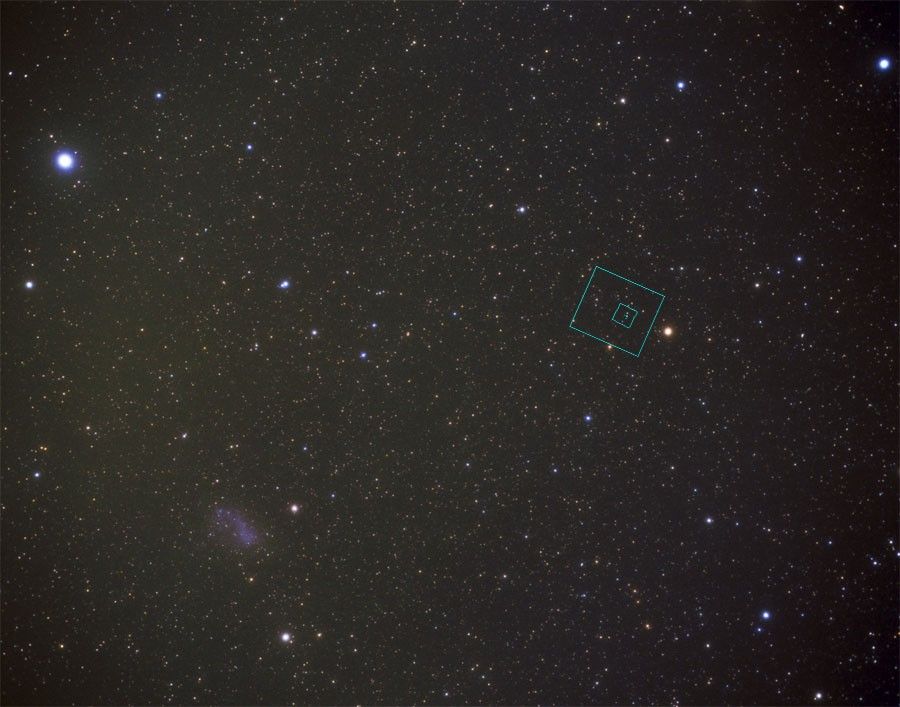
[00:05:32:00] The Hubble Deep Field South ZOOMS :16 and :14 The Hubble Deep Field South penetrates deep into a very small patch of the sky near the southern constellation Tucana. The ZOOM represents the Hubble looking at the distant universe to uncover thousands of never-before-seen galaxies.
[00:06:26:00] Animation of Birth of a Quasar :22 Light from a quasar, a bright, active core of a distant galaxy, will travel three quarters of the way across the universe and provide a beacon on the universe's hidden structure.
[00:07:21:00] Graphic of Quasar and Clouds Observation Light coming to earth from a distant quasar passes through gas clouds. The STIS instrument on Hubble is used to determine the distances and chemical composition of the invisible clouds.
[00:07:55:00] B ROLL Hubble Deep Field Team Members 2:07 Hubble Deep Field South team members at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Maryland get a first look at the processed images from the Hubble Space Telescope's observation of the Deep Field South.
HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPE IMAGES from the Hubble Deep Field South
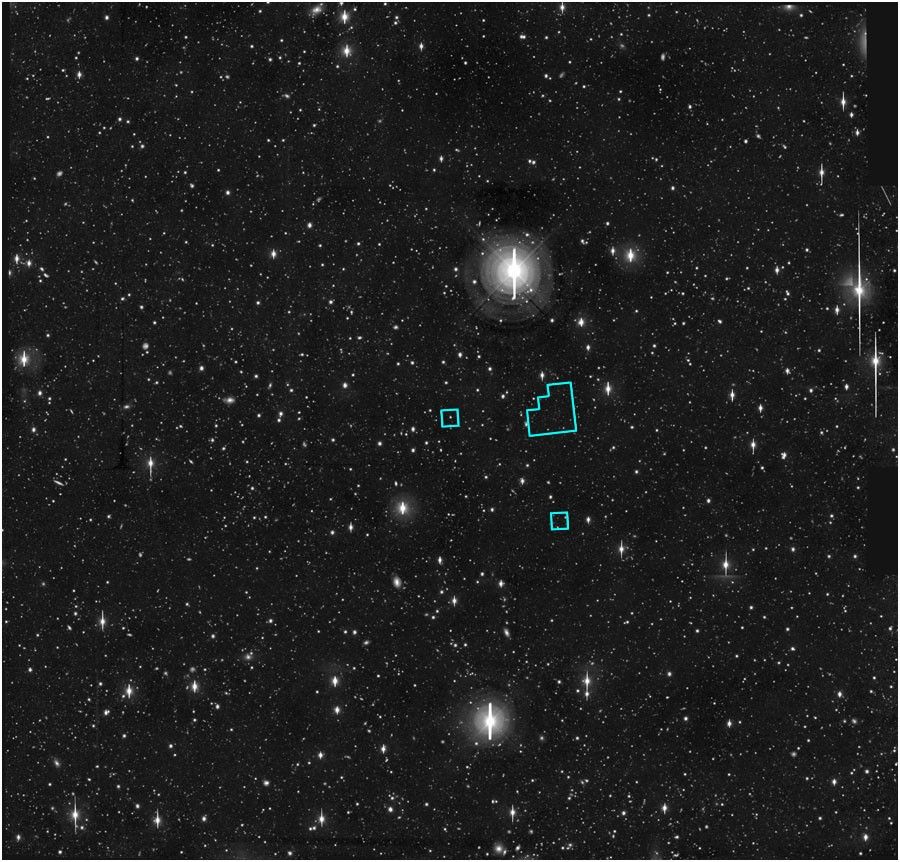
[00:10:23:00:00] Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC 2) The Deep Field South observed in October 1998 complements the deep field taken in 1995. It reveals another host of galaxies of various ages and shapes to add to the story of the universe: pin-wheel-shaped spirals; peculiar ones from collisions; reddish ellipticals; blue ones with hot, young stars; and red ones that may have older stars.
[00:10:55:00] Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS) The STIS instrument has taken the deepest visible/ultraviolet light image of the universe ever. The quasar to be used as a beacon for studying invisible clouds is at center. [00:11:27:00] Near Infrared and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) NICMOS captures the light hidden in dusty galaxies and far away galaxies that are seen only in infrared.
INTERVIEW CLIPS
[00:11:59:00] Harry Ferguson, Astronomer, The Space Telescope Science Institute Gives one reason for making a second deep field observation. :28
[00:12:53:00] Harry Ferguson, Astronomer, The Space Telescope Science Institute Describes the use of the quasar for information about the evolution of the universe. :14
[00:13:33:00] Harry Ferguson Astronomer, The Space Telescope Science Institute Comments on the good resolution of the STIS instrument. :26
- Release DateNovember 23, 1998
- Science ReleaseThe Universe “Down Under” is the Latest Target for Hubble’s Latest Deep-View
- CreditAnimation: Greg Bacon, Walt Feimer, Ed Weibe, and Zolt Levay (STScI) Images: Akira Fujii (Sky and Telescope Magazine), Digitized Sky Survey (STScI), Anglo-Australian Telescope Board, J. Gardner (NOAO), Cerro-Tololo Interamerican Observatory, R. Williams (STScI), HDF-South Team, and NASA; Illustration: Bryan Preston (STScI)
Related Images & Videos

Hubble Deep Field South Unveils Myriad Galaxies
A NASA Hubble Space Telescope view down a 12 billion light-year long corridor of space loaded with a dazzling assortment of thousands of never-before seen galaxies. This picture is the culmination of a 10-day-long observation called the Hubble Deep Field South (HDF-S) which was...
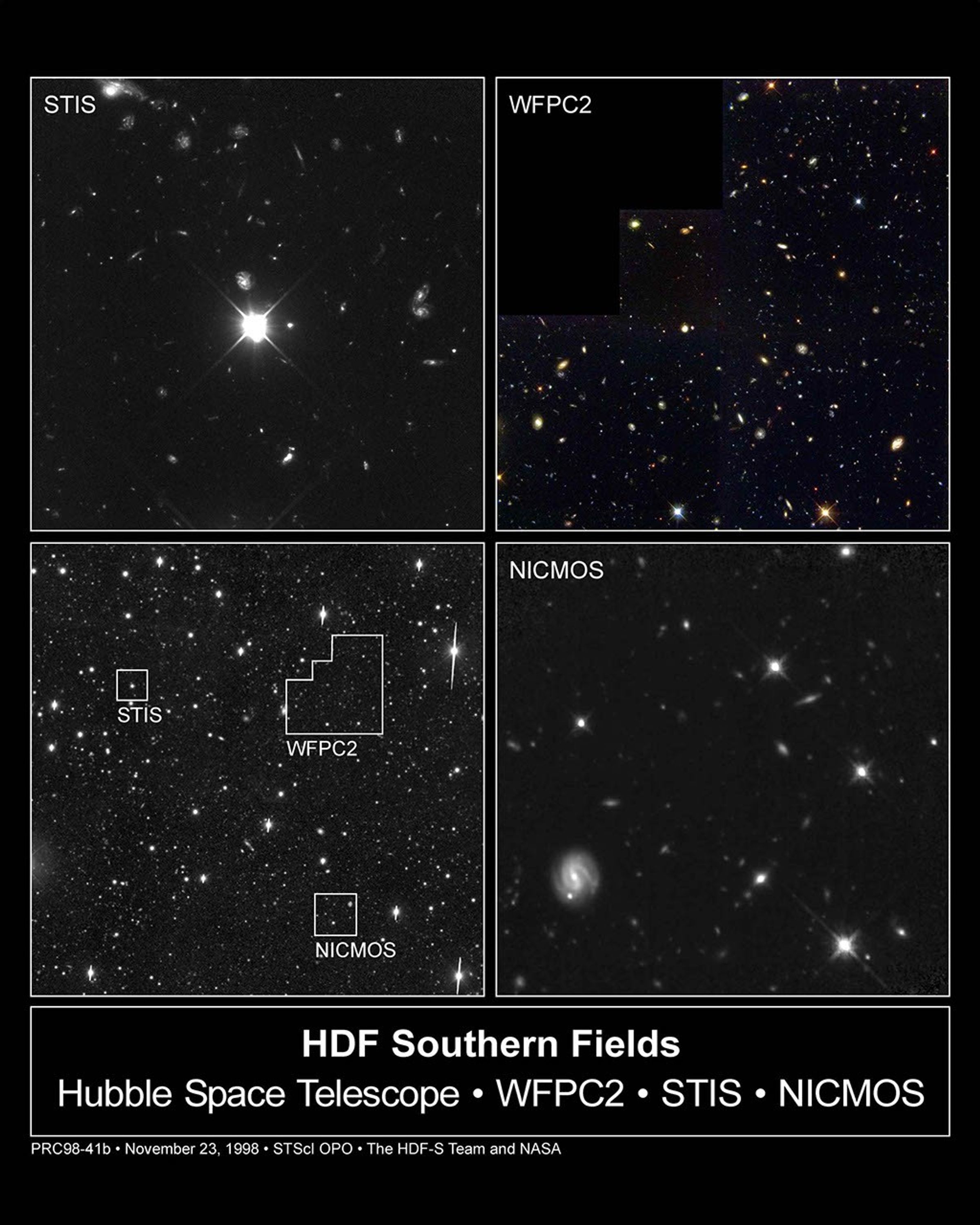

Hubble Deep Field South – Multiple Windows on the Universe
Peering at a small patch of sky near the south celestial pole, NASA's Hubble Space Telescope used its full array of instruments to look nearly all the way across the universe. Called the Hubble Deep Field South (HDF-S), this new far-look complements the original Hubble "deep...
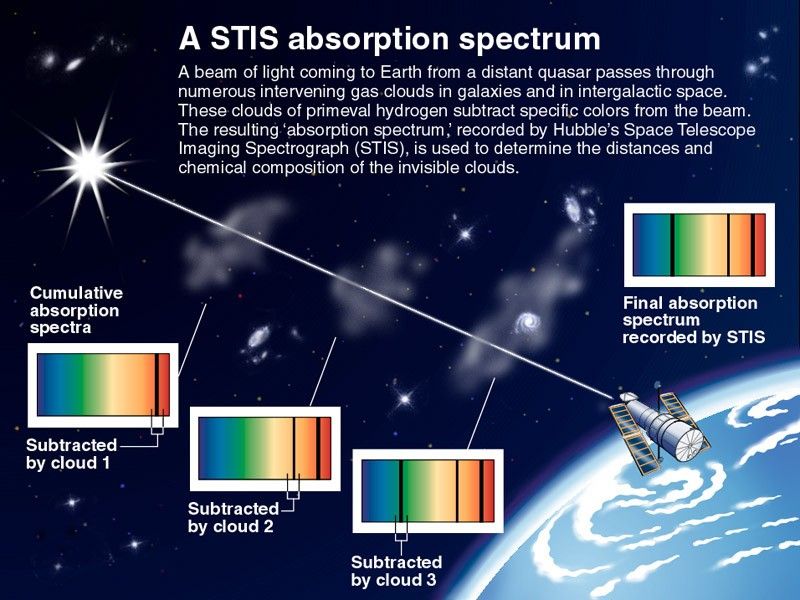
A STIS Absorption Spectrum
A beam of light coming to Earth from a distant quasar passes through numerous intervening gas clouds in galaxies and in intergalactic space. These clouds of primeval hydrogen subtract specific colors from the beam. The resulting "absorption spectrum," recorded by Hubbles Space...

Hubble Space Telescope Telescope Pointing at HDF North and South Targets
The Hubble Space Telescope is pointing north at a blank patch of sky above the Big Dipper. Next, shown in orbit, Hubble is slewing to point at the southern skies in the direction of the constellation Tucana, near the south celestial pole.
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov