1 min read
Atmospheric Methane of Brown Dwarfs W1935 and W2220 (NIRSpec)
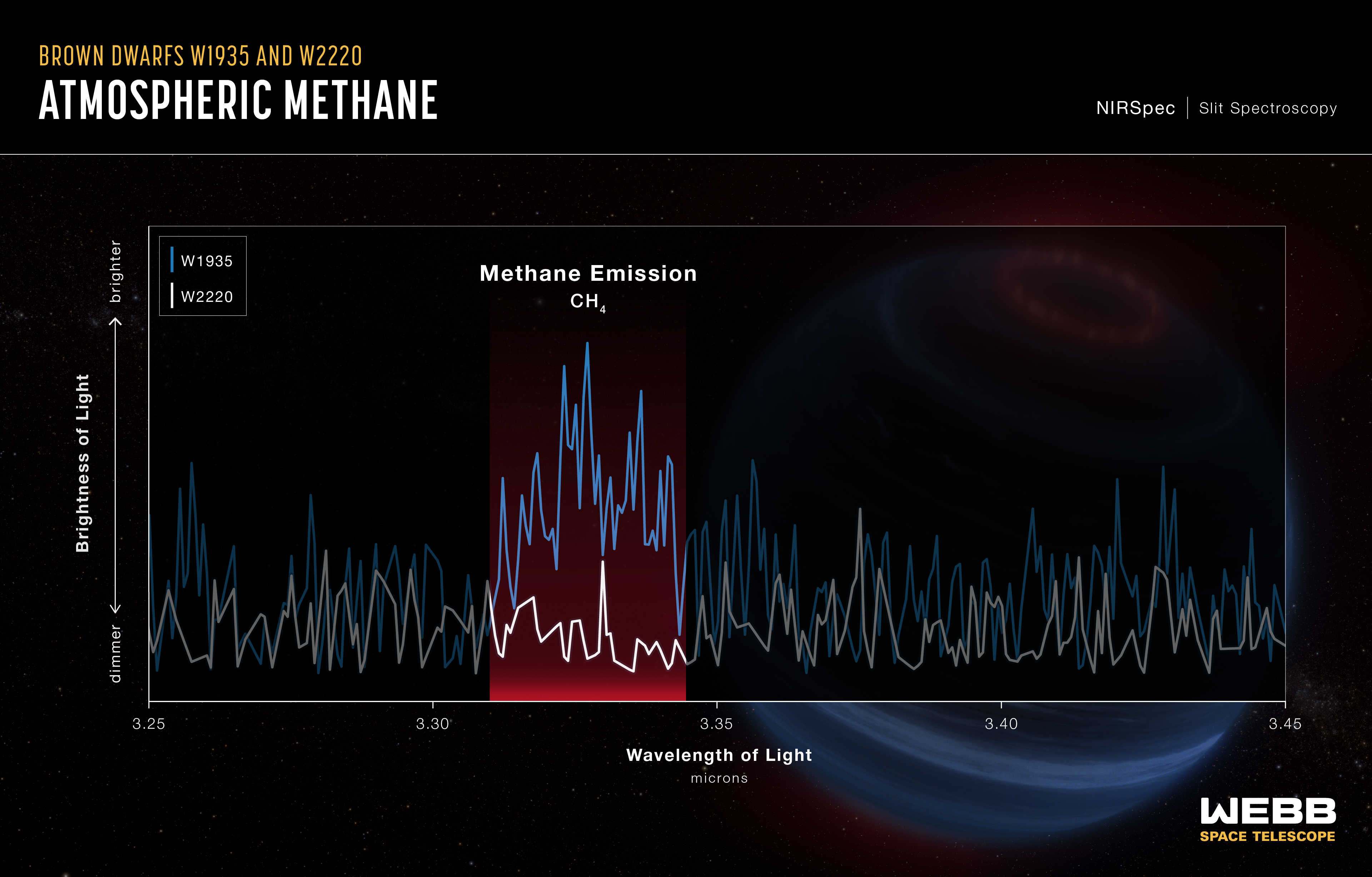
Astronomers used NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope to study 12 cold brown dwarfs. Two of them – W1935 and W2220 – appeared to be near twins of each other in composition, brightness, and temperature. However, W1935 showed emission from methane, as opposed to the anticipated absorption feature that was observed toward W2220. The team speculates that the methane emission may be due to processes generating aurorae.
- Release DateJanuary 9, 2024
- Science ReleaseNASA’s Webb Finds Signs of Possible Aurorae on Isolated Brown Dwarf
- CreditIllustration: NASA, ESA, CSA, Leah Hustak (STScI)
Related Images & Videos

Brown Dwarf W1935 (Artist Concept)
This artist concept portrays the brown dwarf W1935, which is located 47 light-years from Earth. Astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope found infrared emission from methane coming from W1935. This is an unexpected discovery because the brown dwarf is cold and lacks a...
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov
NASA, ESA, CSA, Leah Hustak (STScI)