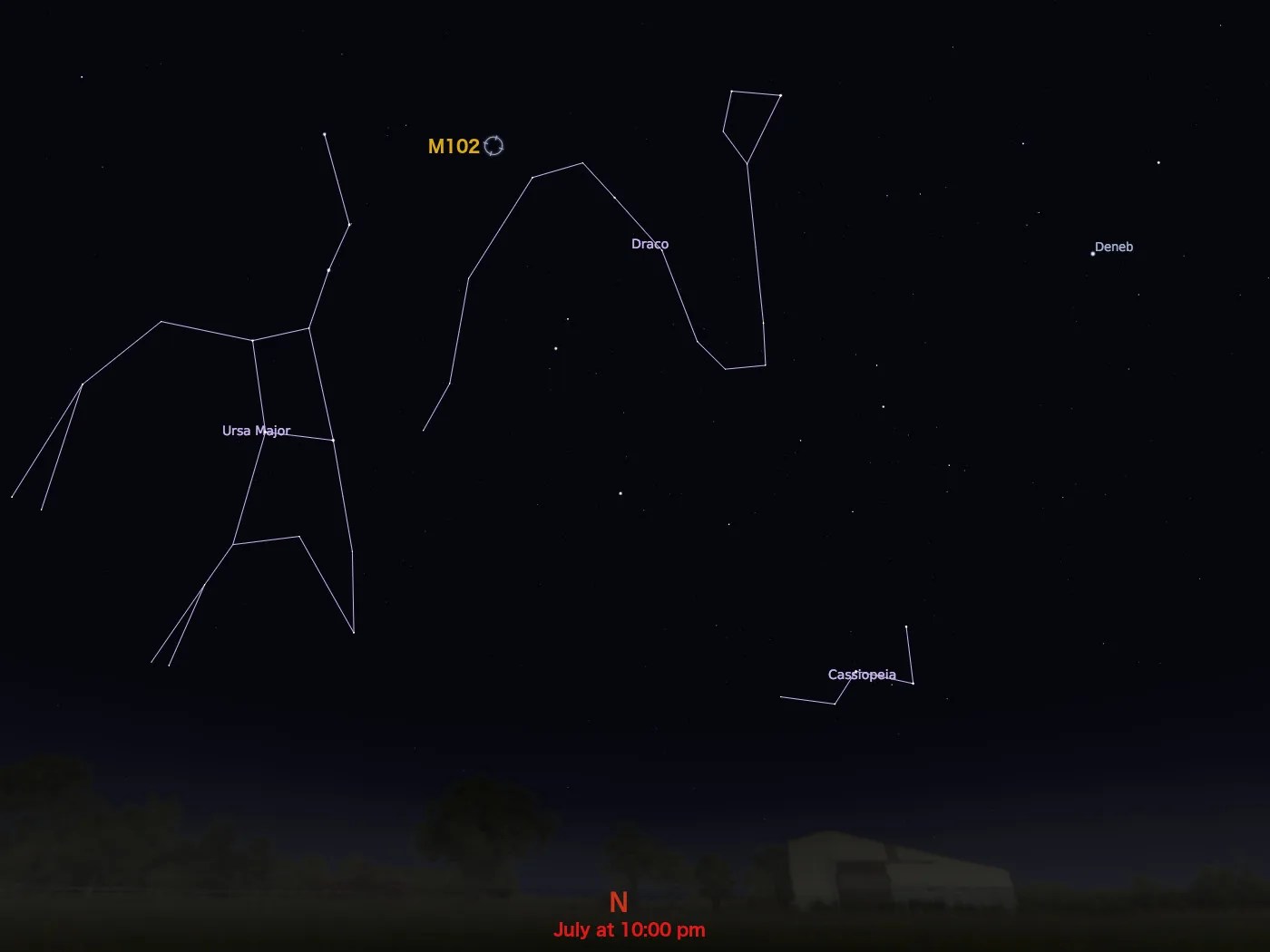
Messier 102
Hubble was able to resolve details in the dust lanes of Messier 102.
Distance
44 million light-years
Apparent Magnitude
10.7
constellation
Draco
object type
Lenticular Galaxy
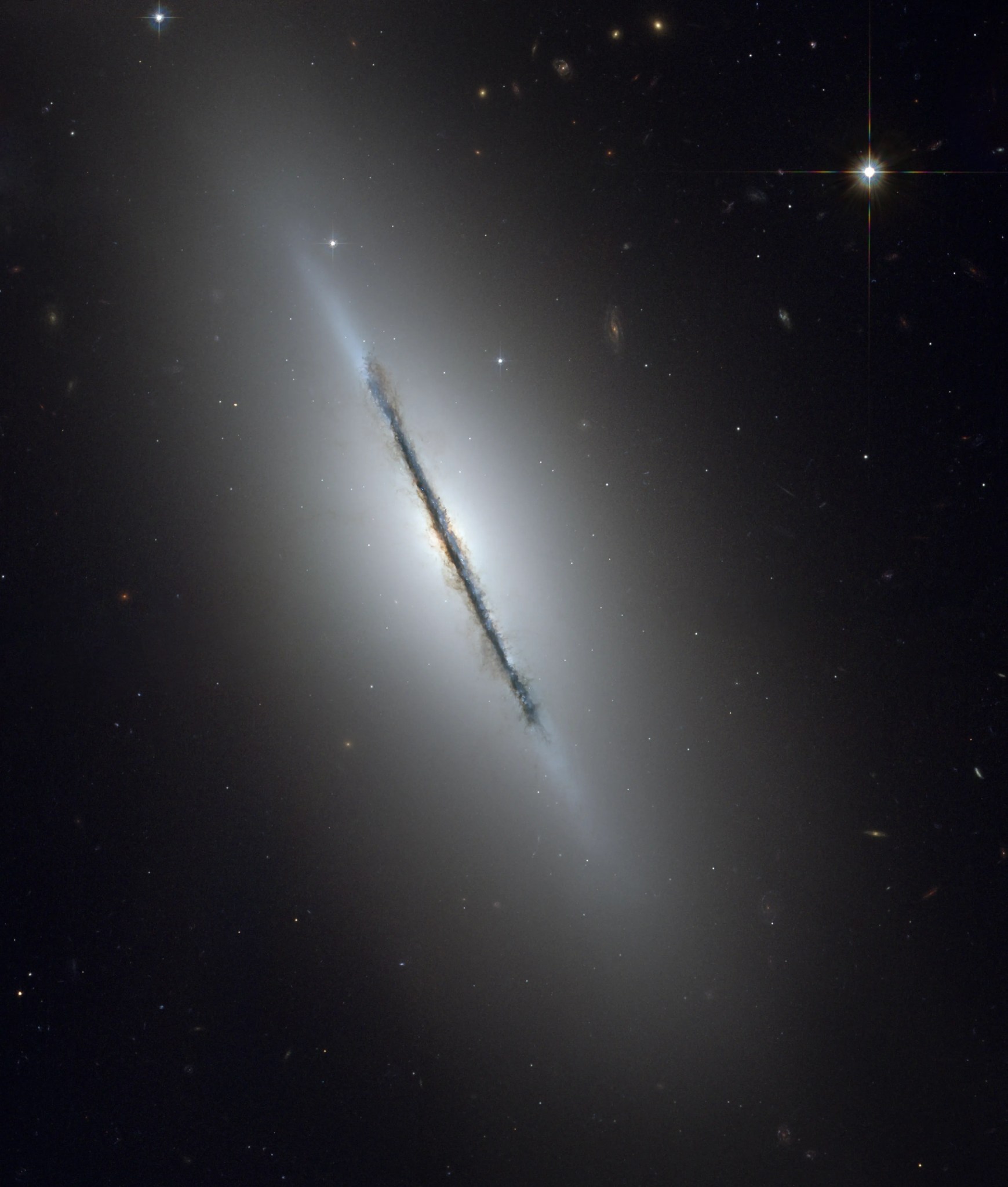

Hubble’s sharp vision reveals a crisp dust lane dividing M102, also known as the Spindle galaxy, into two halves. The dust lane is slightly warped compared to the disk of starlight. This warp indicates that the galaxy might have experienced gravitational tidal disturbances in the distant past. These disturbances were likely caused by an interaction with a nearby galaxy, as M102 is the largest member of a small cluster of galaxies.
Some faint, wispy trails of dust can be seen meandering away from the disk out into the bulge and inner halo of the galaxy. The outer halo is dotted with numerous globular star clusters, gravitationally bound clusters of nearly a million stars each. Background galaxies that are millions to billions of light-years farther away than M102 are also seen through its halo.
Pierre Méchain, a French astronomer and colleague of Charles Messier, discovered the Spindle galaxy in 1781 — the same year that he discovered the first two of his eight comets. M102 is located 44 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Draco and has an apparent magnitude of 10.7. It can be observed using a small telescope and is most easily spotted during June.
For more information about Hubble’s observations of M102, see:
- Previous: Messier 101 (Pinwheel Galaxy) | Next: Messier 104 (Sombrero Galaxy)
- Back to Hubble's Messier Catalog
Explore Hubble's Messier Catalog
The following pages contain some of Hubble’s best images of Messier objects.

Overview The Messier catalog, begun by astronomer Charles Messier in the 18th Century and revised over the years, includes some…
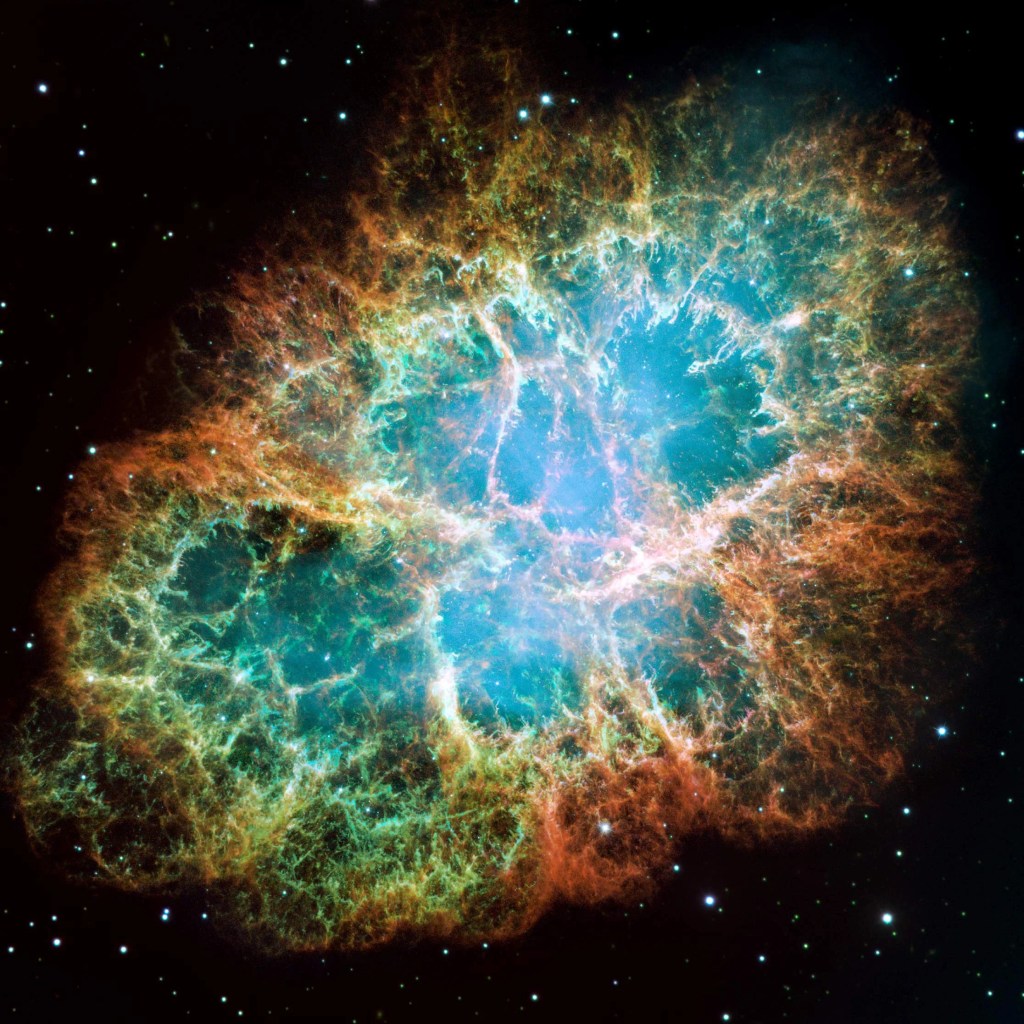

Better known as the Crab Nebula, Charles Messier originally mistook Messier 1 for Halley’s Comet, which inspired him to create…

Hubble's image of Messier 2 is comprised of visible and infrared wavelengths of light.