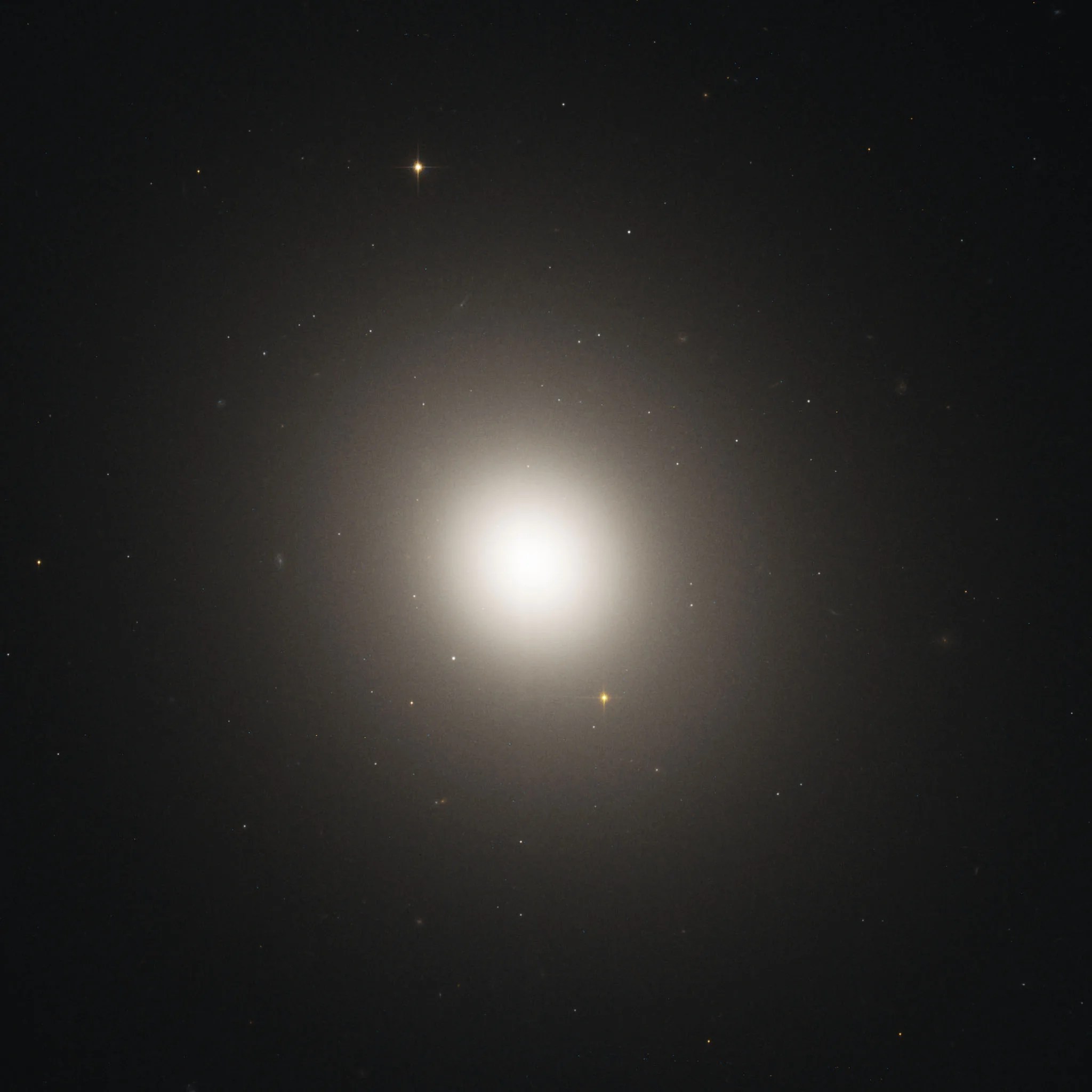
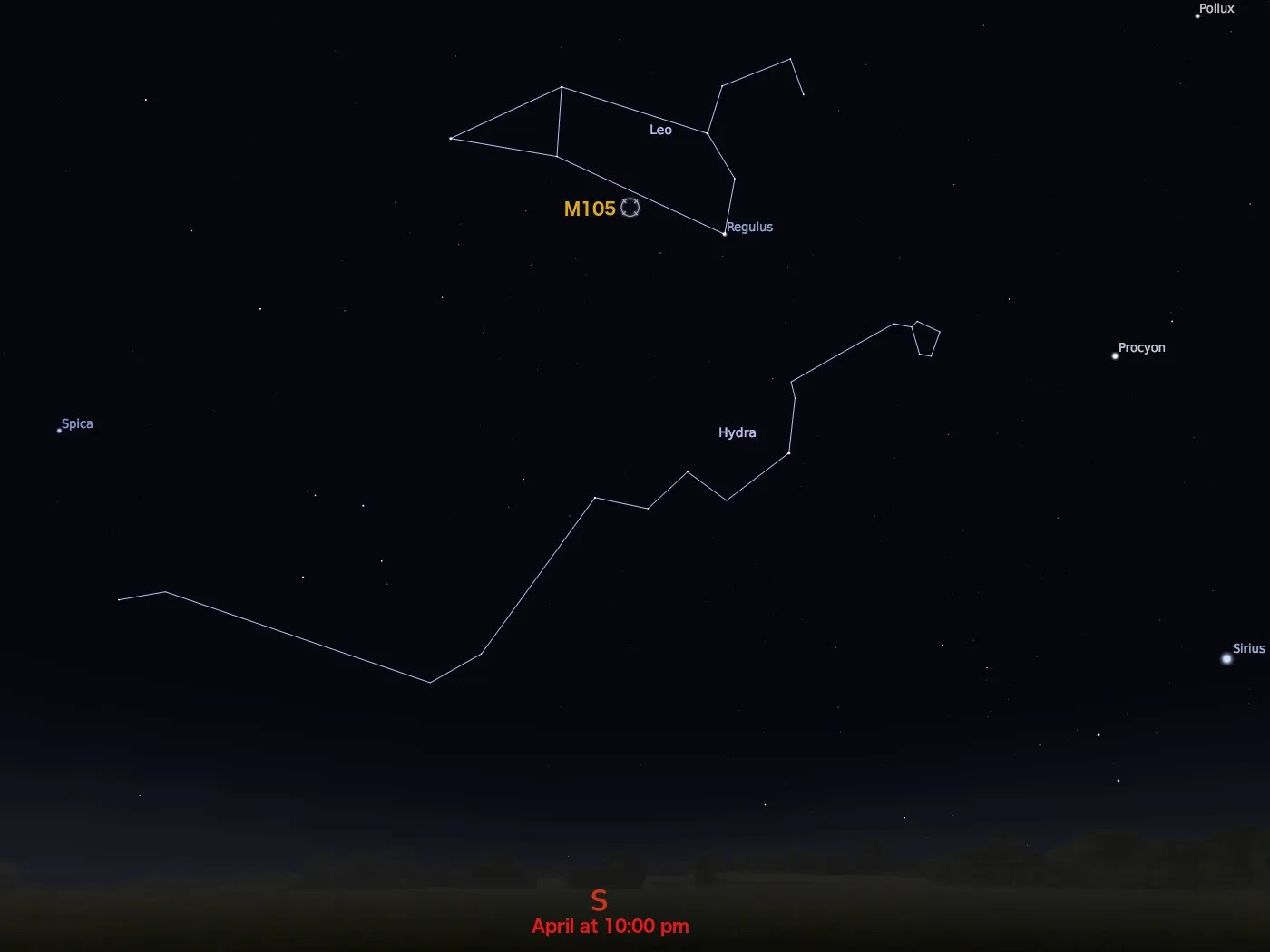
Messier 105
Messier 105 is the largest elliptical galaxy in the Messier catalog.
Distance
32 million light-years
Apparent Magnitude
10.2
constellation
Leo
object type
Elliptical Galaxy
Messier 105 (M105) is an elliptical galaxy 32 million light-years away in the constellation Leo. It is the largest elliptical in the Messier catalog that is not a member of the Virgo cluster of galaxies. M105 does, however, belong to the M96 (or Leo I) Group, which includes neighbors M95 and M96 as well as several other fainter galaxies. Charles Messier’s colleague Pierre Méchain discovered M105 in 1781 just a few days after locating M95 and M96. Yet M105 was not originally included in Messier’s catalog. It was added in 1947 after astronomer Helen S. Hogg found a letter written by Méchain describing the galaxy.
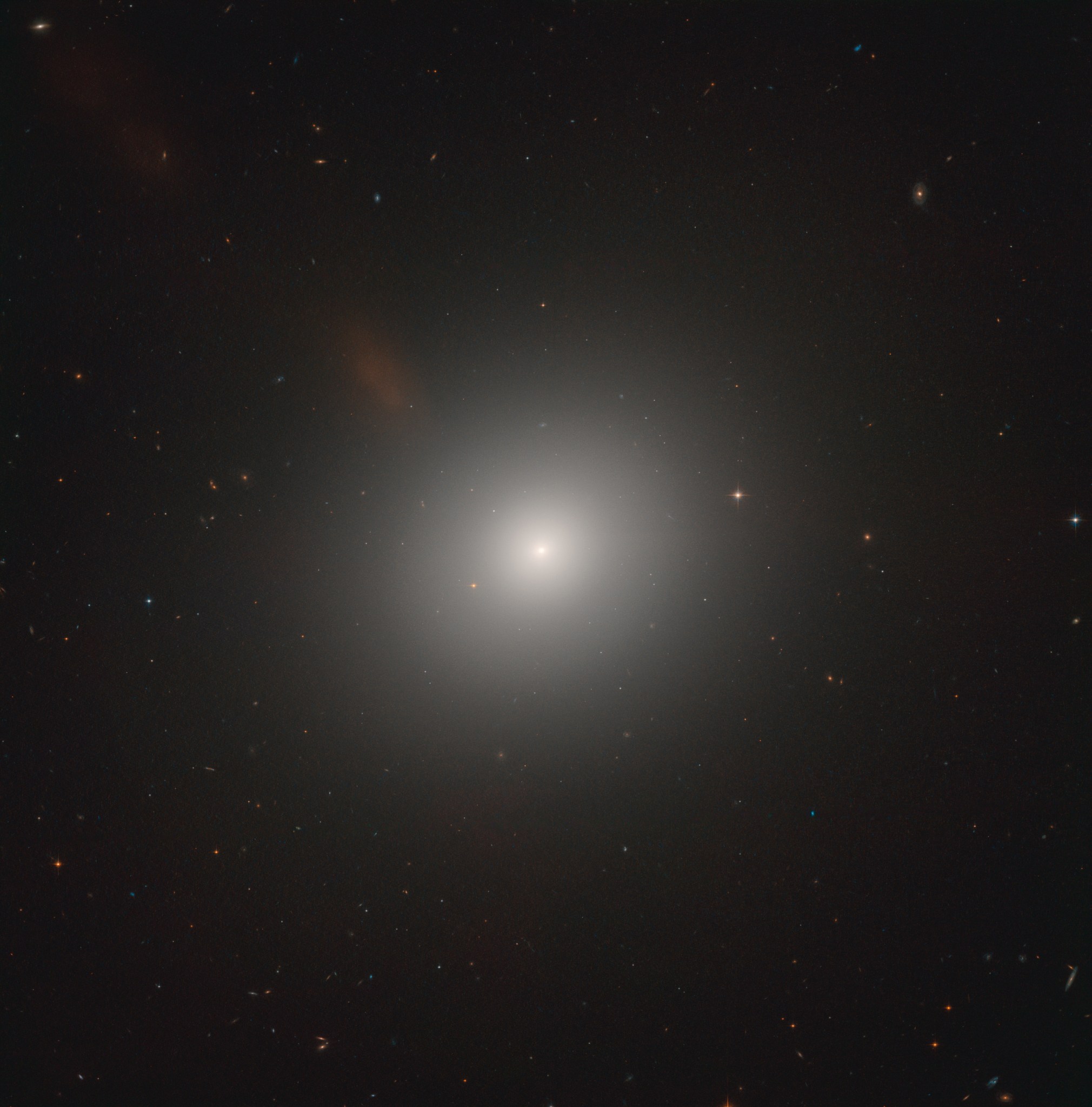
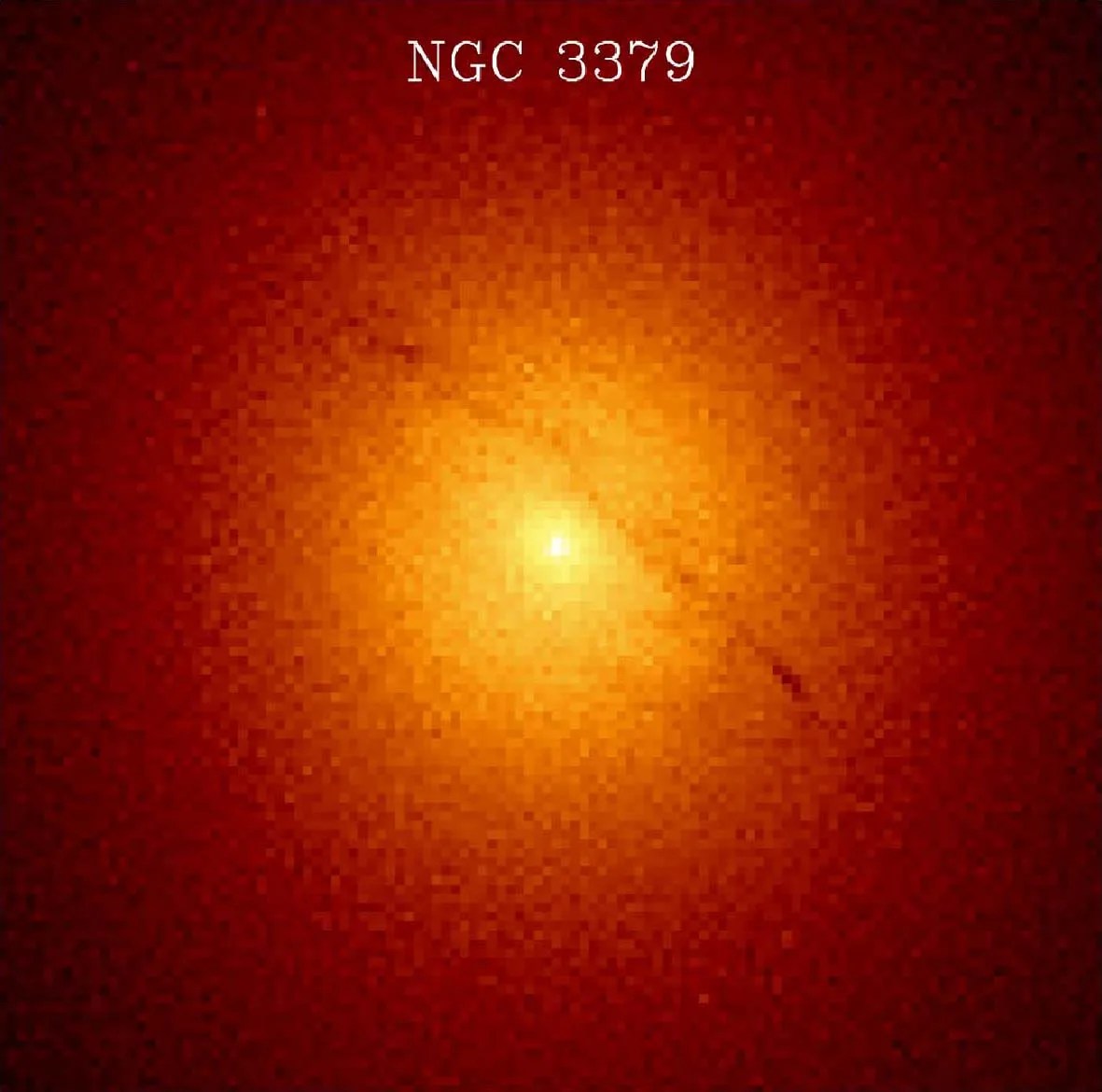


This Hubble image of M105 was taken in near-infrared and visible light. Like most elliptical galaxies it appears rather featureless and inactive. However, Hubble observations surprised astronomers by revealing young stars and star clusters in M105, indicating that star formation is still taking place in what was thought to be a “dead” galaxy no longer capable of giving birth to new stars. Other Hubble observations measured the speeds of stars moving around the center of the galaxy, which demonstrated that a supermassive black hole resides at M105’s core.
Best observed in April, M105 has an apparent magnitude of 10.2 and can be spotted with a small telescope. Large telescopes will uncover two fainter galaxies (NGC 3384 and NGC 3389) close to the bright elliptical.
For more information about Hubble’s observations of M105, see:
Explore Hubble's Messier Catalog
The following pages contain some of Hubble’s best images of Messier objects.

Overview The Messier catalog, begun by astronomer Charles Messier in the 18th Century and revised over the years, includes some…
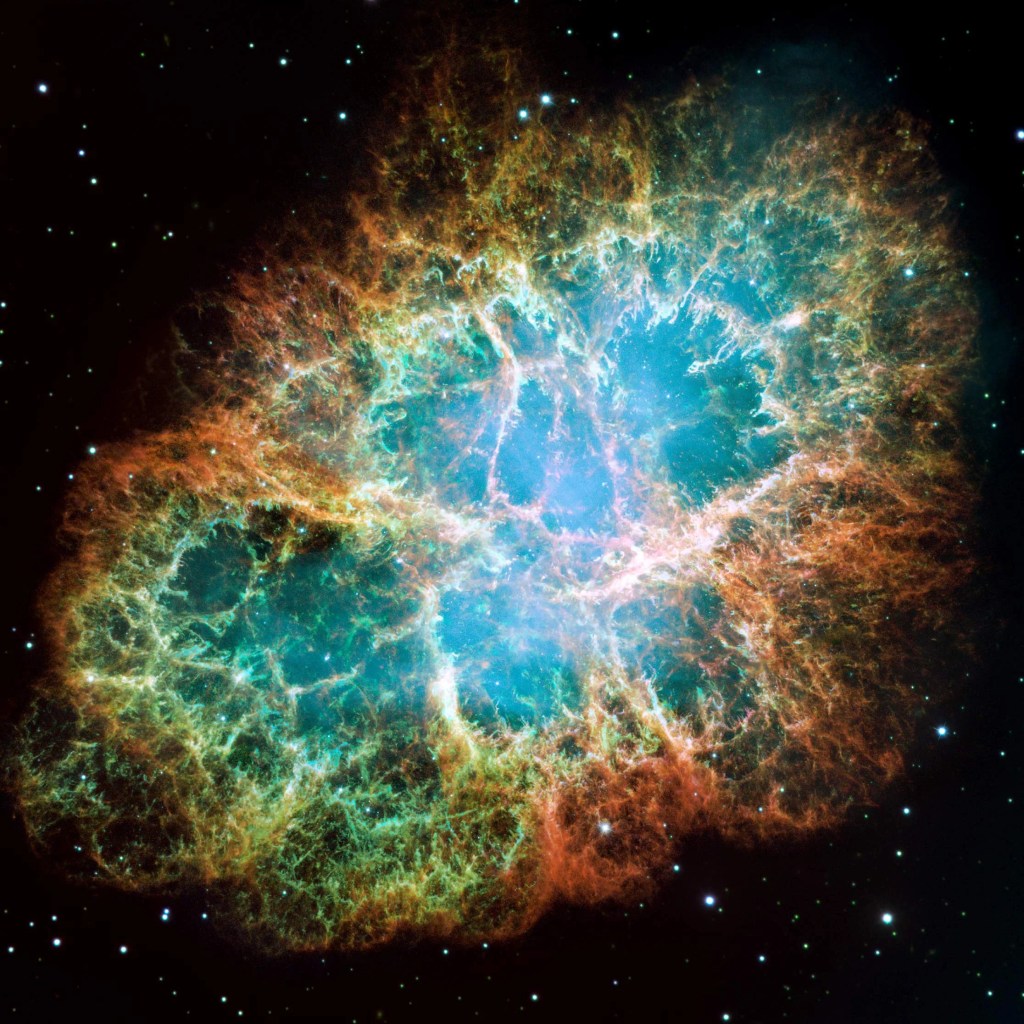

Better known as the Crab Nebula, Charles Messier originally mistook Messier 1 for Halley’s Comet, which inspired him to create…

Hubble's image of Messier 2 is comprised of visible and infrared wavelengths of light.