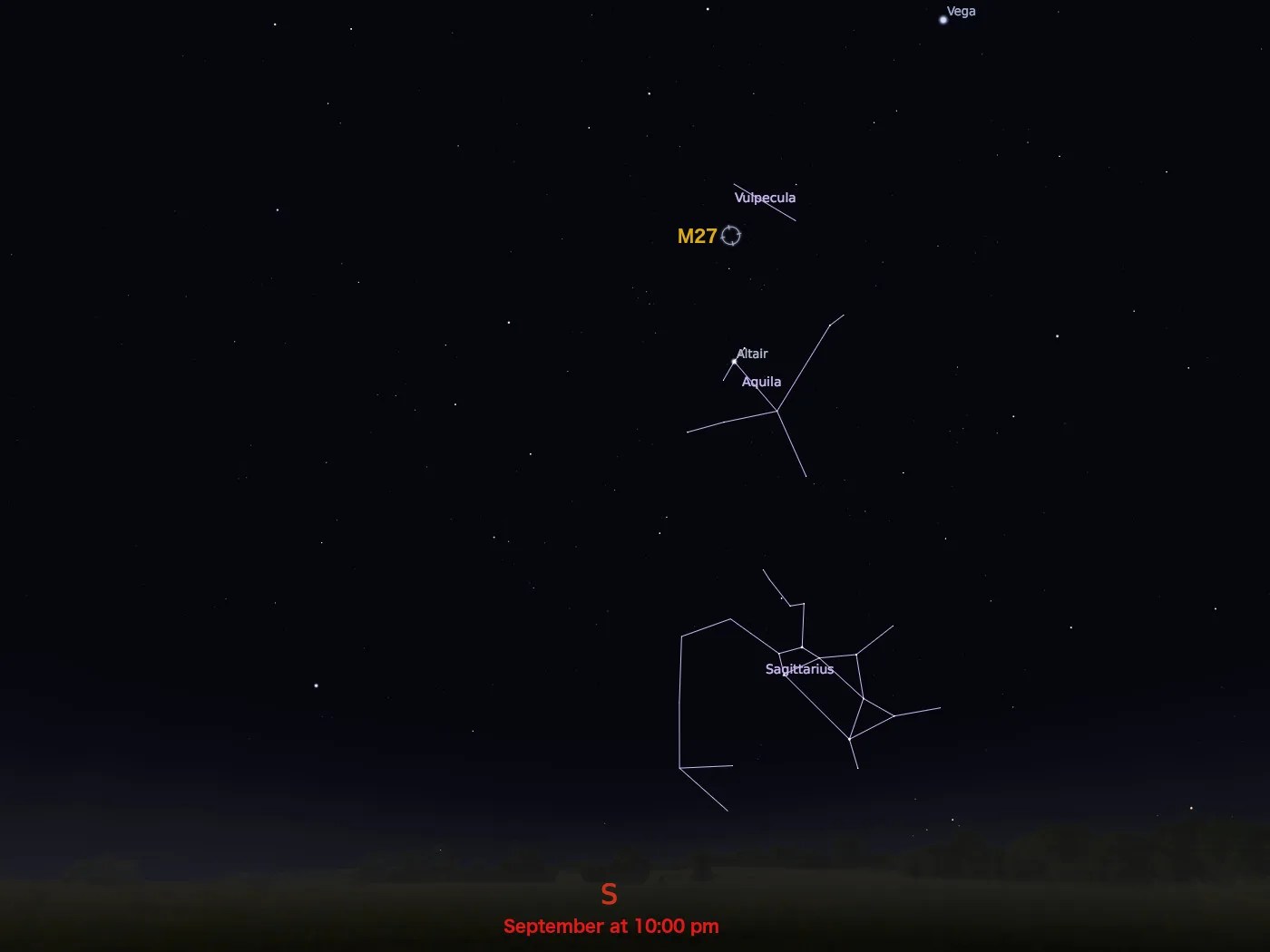
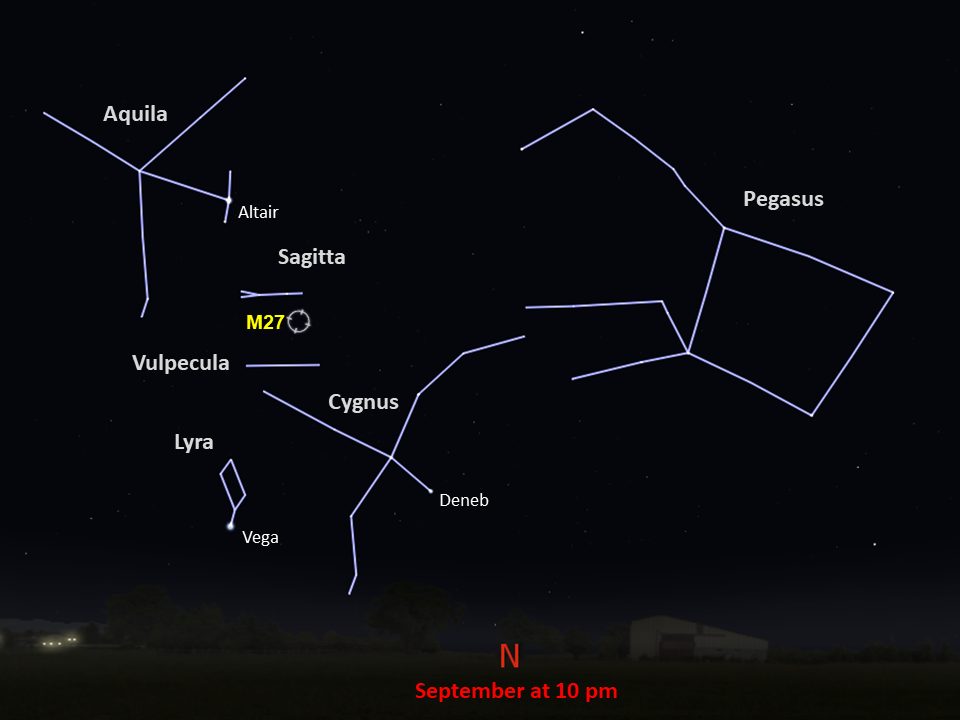
Messier 27
Through backyard telescopes, Messier 27 has two bright lobes making it look like a dumbbell, and is commonly called the Dumbbell Nebula.
Distance
1,200 light-years
Apparent Magnitude
7.5
constellation
Vulpecula
object type
Planetary Nebula
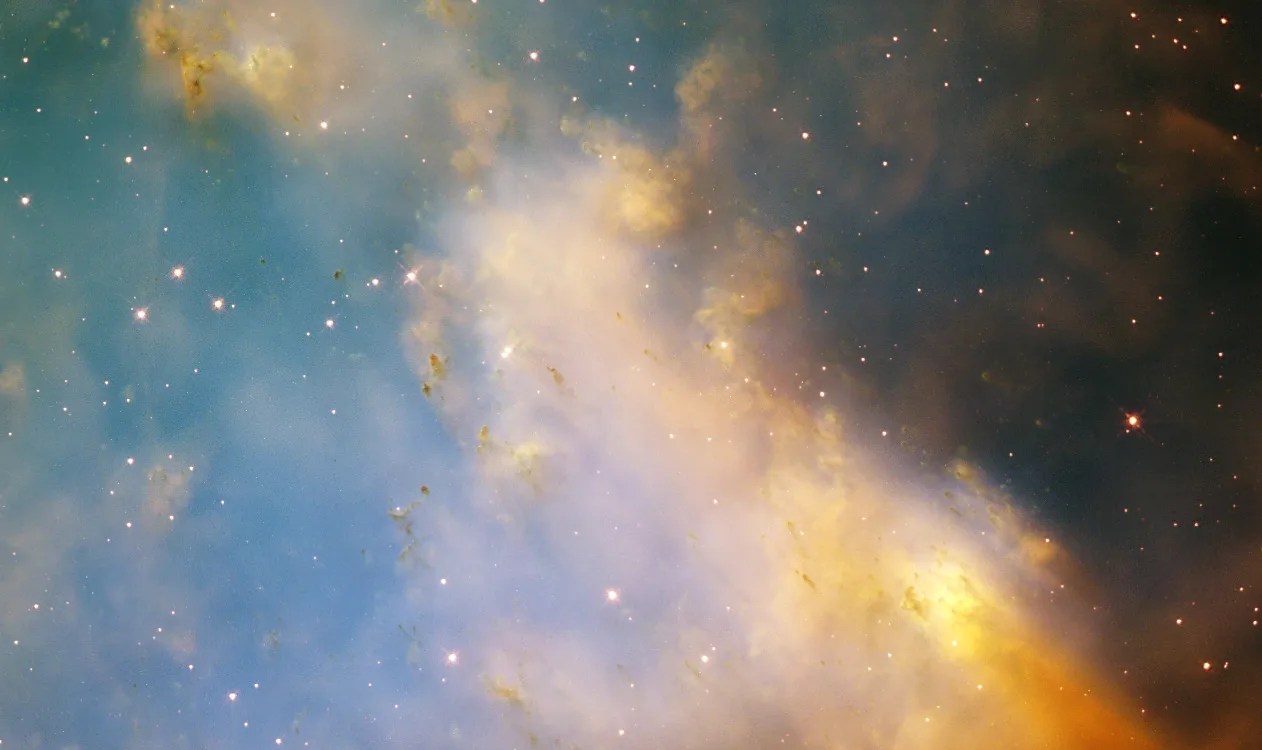

Spotted by Charles Messier in 1764, Messier 27, also referred to as the Dumbbell Nebula, was the first planetary nebula ever discovered. The term “planetary nebula” is a bit of a misnomer based on the nebula’s round, planet-like appearance when viewed through smaller telescopes. The nebula is the result of an old, dying star that shed its outer layers in a glowing display of color.
M27 hosts many knots of gas and dust. As this Hubble image reveals, some look like fingers pointing at the central star, located out of the field of view to the upper left of the image; others are isolated clouds, some with and some without tails. Their sizes typically range from 17 billion to 56 billion kilometers, which is several times larger than the distance from the Sun to Pluto. Each contains as much mass as three Earths.
These dense knots of gas and dust seem to be a natural part of the evolution of planetary nebulae. They form when the stellar winds are not powerful enough to blow away a larger clump of matter but are able to blow away smaller particles, creating a trail behind the clump. The shapes of these knots change as the nebula expands. Similar knots are also found in other nearby planetary nebulae that are all part of the same evolutionary scheme.
M27 resides more than 1,200 light-years away in the constellation Vulpecula. With an apparent magnitude of 7.5, the nebula is visible with a small telescope most easily in September.
NASA and L. Barranger (STScI/AVL)
For more information about Hubble’s observations of M27, see:
Explore Hubble's Messier Catalog
The following pages contain some of Hubble’s best images of Messier objects.

Overview The Messier catalog, begun by astronomer Charles Messier in the 18th Century and revised over the years, includes some…
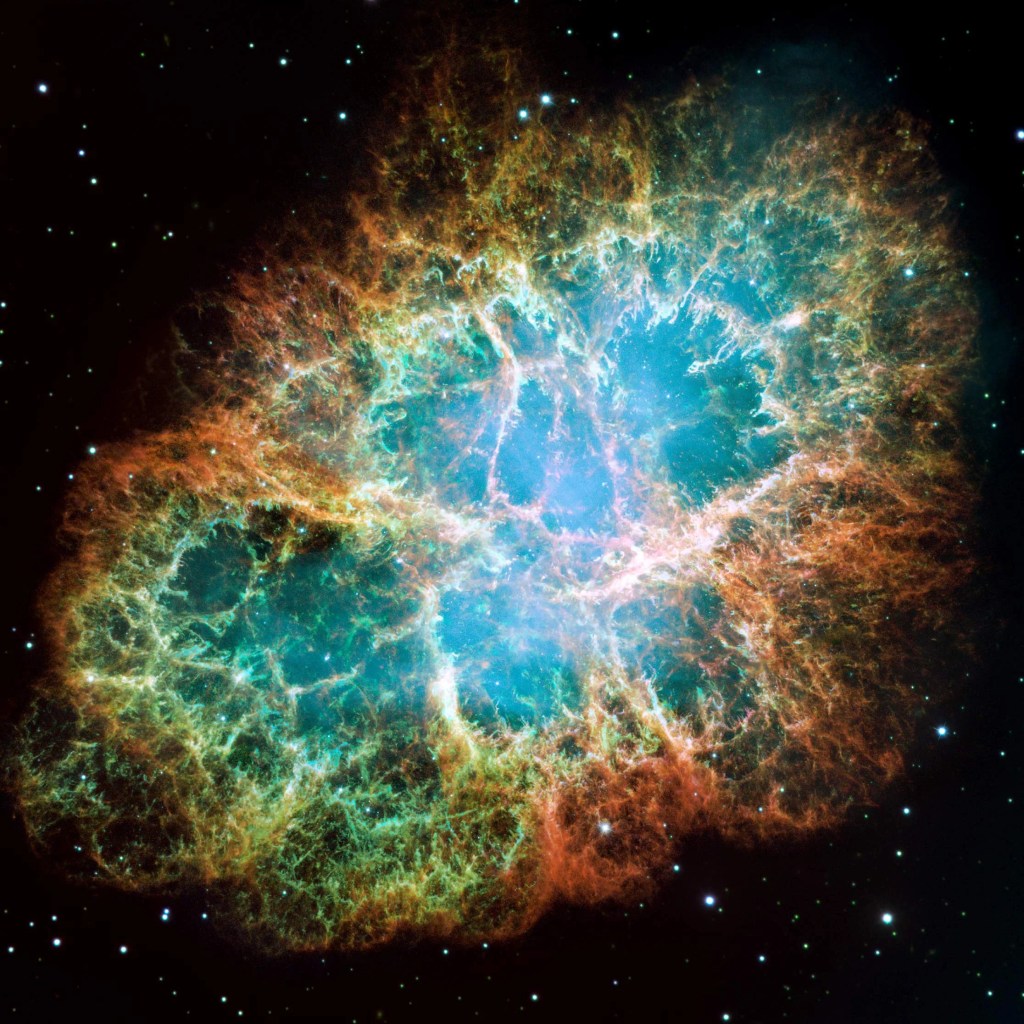

Better known as the Crab Nebula, Charles Messier originally mistook Messier 1 for Halley’s Comet, which inspired him to create…

Hubble's image of Messier 2 is comprised of visible and infrared wavelengths of light.