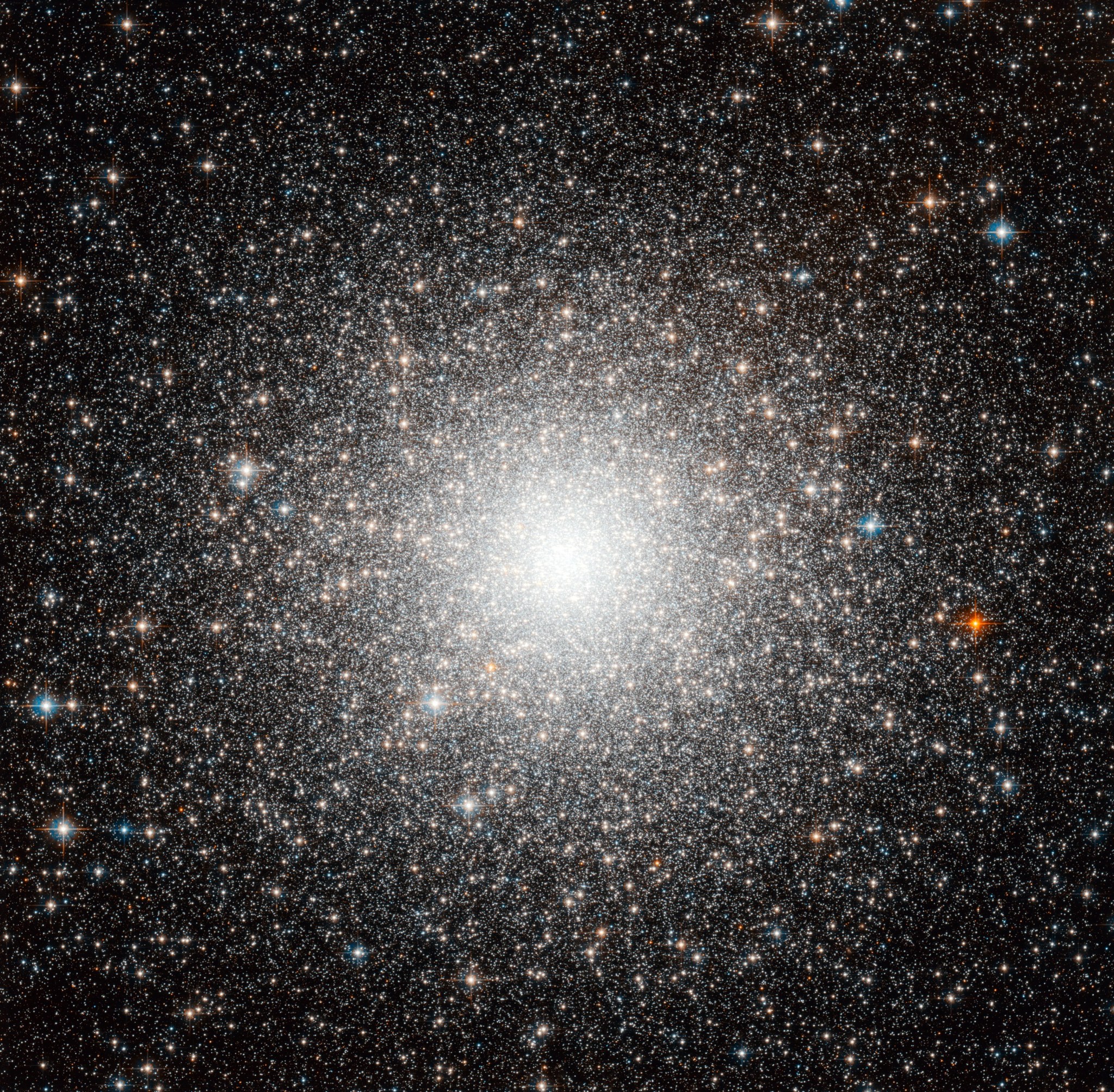
Messier 54
Messier 54 belongs to a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way.
Distance
90,000 light-years
Apparent Magnitude
8.4
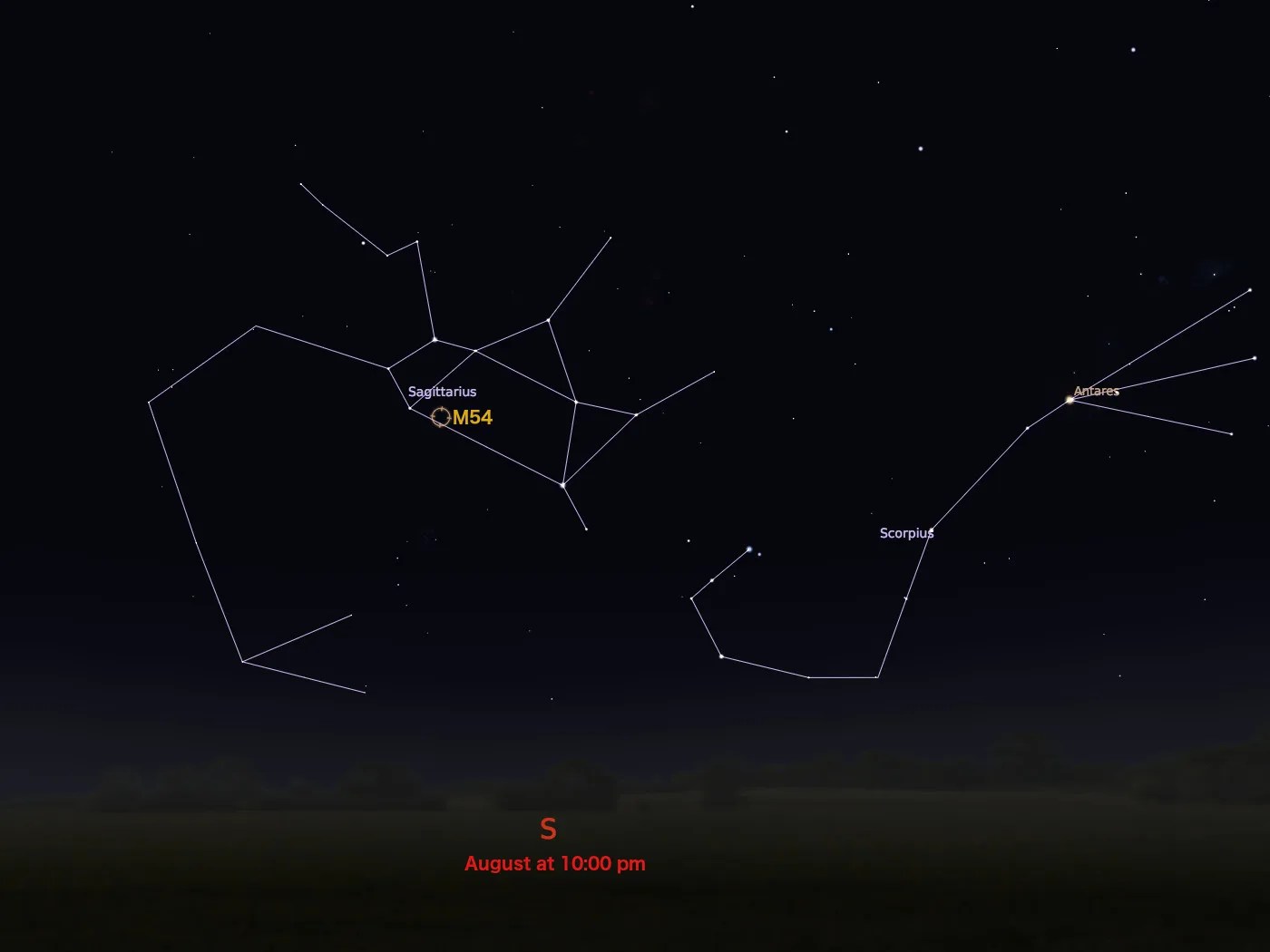
constellation
Sagittarius
object type
Globular Cluster
This beautiful visible and infrared Hubble image shows what could be just another globular cluster, but this dense group of stars known as M54 was the first globular cluster found outside our galaxy. M54 belongs to a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way called the Sagittarius Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy. When Charles Messier discovered M54 in 1778, he did not know that the cluster belonged to another galaxy.
Even though M54 is now understood to lie outside the Milky Way, it will become part of our galaxy in the future. The strong gravitational pull of our large galaxy is slowly engulfing the Sagittarius dwarf galaxy, which will eventually merge with the Milky Way to create one larger galaxy.
M54 is located roughly 90,000 light-years from Earth. It has an apparent magnitude of 8.4 and can be spotted in the constellation Sagittarius most easily during August. Binoculars will resolve a small patch of light in the sky, but larger telescopes are needed to resolve individual stars.
For more information about Hubble’s observations of M54, see:
Explore Hubble's Messier Catalog
The following pages contain some of Hubble’s best images of Messier objects.

Overview The Messier catalog, begun by astronomer Charles Messier in the 18th Century and revised over the years, includes some…
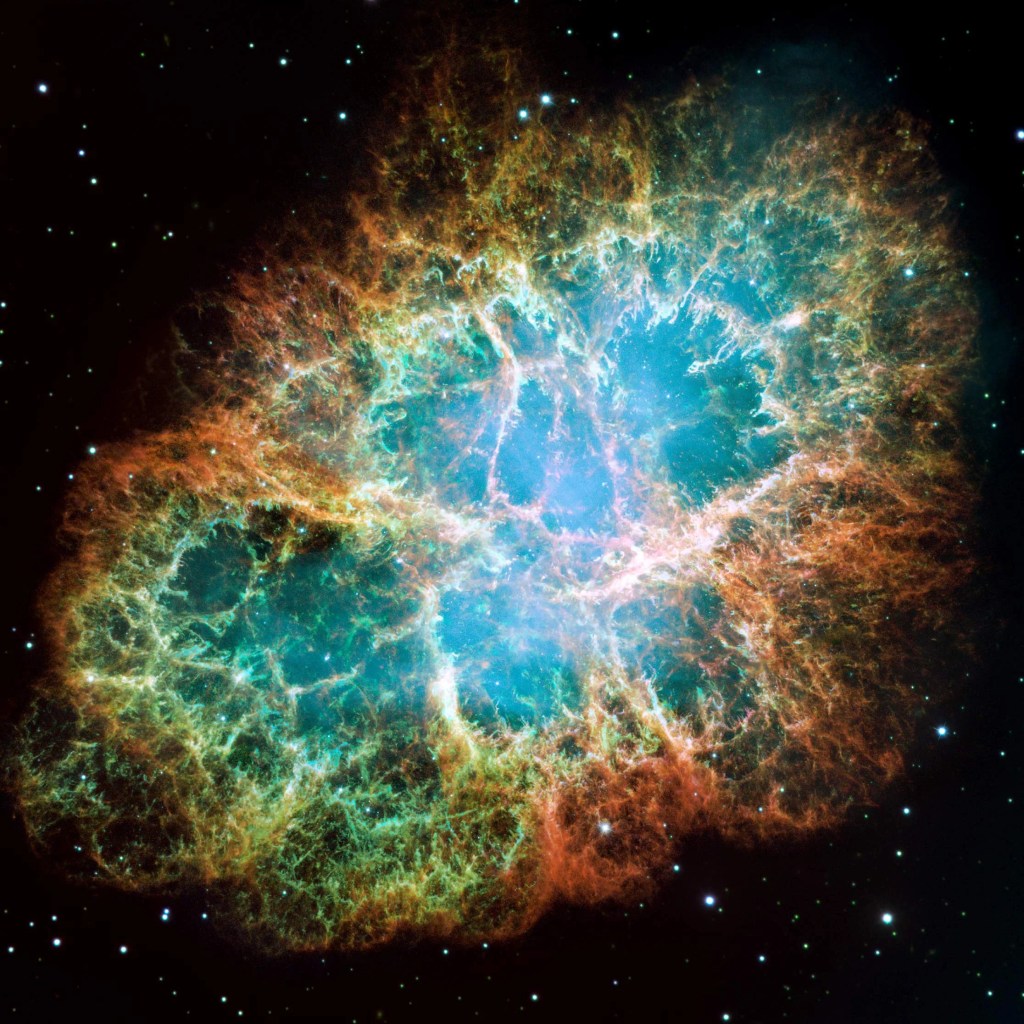

Better known as the Crab Nebula, Charles Messier originally mistook Messier 1 for Halley’s Comet, which inspired him to create…

Hubble's image of Messier 2 is comprised of visible and infrared wavelengths of light.