1 min read
STIS Reveals Invisible High-Speed Collision Around Supernova 1987a
The highest velocity material expelled in a cataclysmic stellar explosion ten years ago has been detected for the first time by the Hubble Space Telescope's Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS).
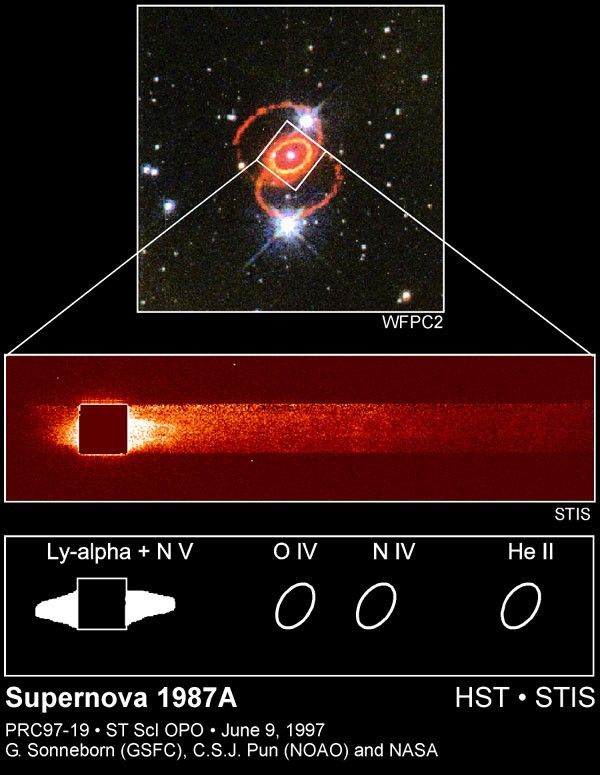
The top image, taken with Hubble's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 in 1995, shows the orange-red rings surrounding Supernova 1987A in the Large Magellanic Cloud. The glowing debris of the supernova explosion, which occurred in February 1987, is at the center of the inner ring. The small white square indicates the location of the STIS aperture used for the new far-ultraviolet observation.
The STIS spectrograph viewed the entire inner ring in far-ultraviolet light, spreading it into a spectrum. The Earth's atmosphere completely blocks ultraviolet radiation from reaching the Earth's surface, hence astronomers can study the ultraviolet universe only from orbiting telescopes. The dark square in this image is where the spectrum was processed to remove the emission from hydrogen in the Earth's outer atmosphere.
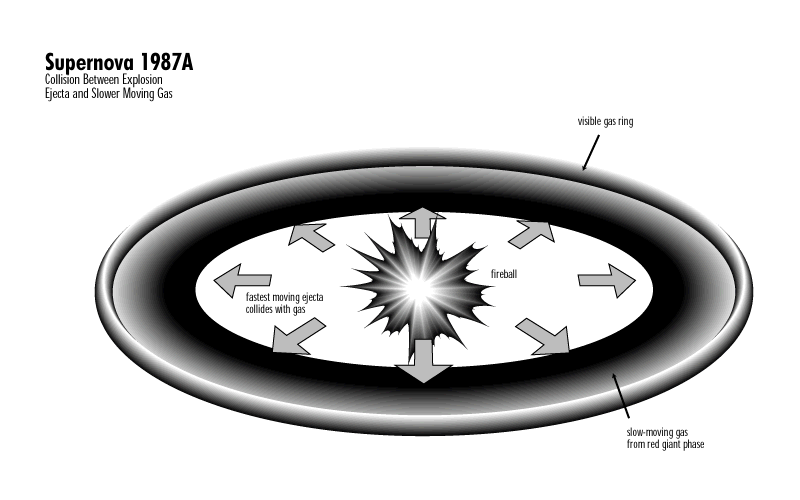
The STIS data in the middle panel (and a schematic representation in the bottom panel) shows the presence of glowing hydrogen expanding at a speed of 33 million miles per hour (15,000 kilometers per second) coming from an extended area inside the inner ring. In addition to hydrogen emission STIS also detected emission from high-velocity ionized nitrogen.
This is the first time that astronomers have measured the very fast moving gas ejected by the supernova explosion, which was invisible until observed by Hubble with the STIS ultraviolet detectors. This gas is glowing in the ultraviolet because it is slamming into the remains of the gas lost by the supernova star about 20,000 years before it exploded.
The STIS spectrum also reveals the presence of emissions from hot gasses (oxygen, nitrogen, and helium) coming from the inner ring itself. The ring is about 1.2 light-years in diameter.
Supernova 1987A is located 167,000 light-years from Earth in the Large Magellanic Cloud.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.05h 35m 28.25s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-69° 16' 13.0"
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.SN 1987A
- Release DateJune 9, 1997
- Science ReleaseHubble Reveals Invisible High-Speed Collision around Supernova 1987A
- CreditNASA, STIS IDT Team, SINS Collaboration, George Sonneborn (NASA-GSFC), Jason Pun (NOAO), Peter Challis (CfA)
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov