1 min read
The Evolution of the Stars in the Leo IV Galaxy
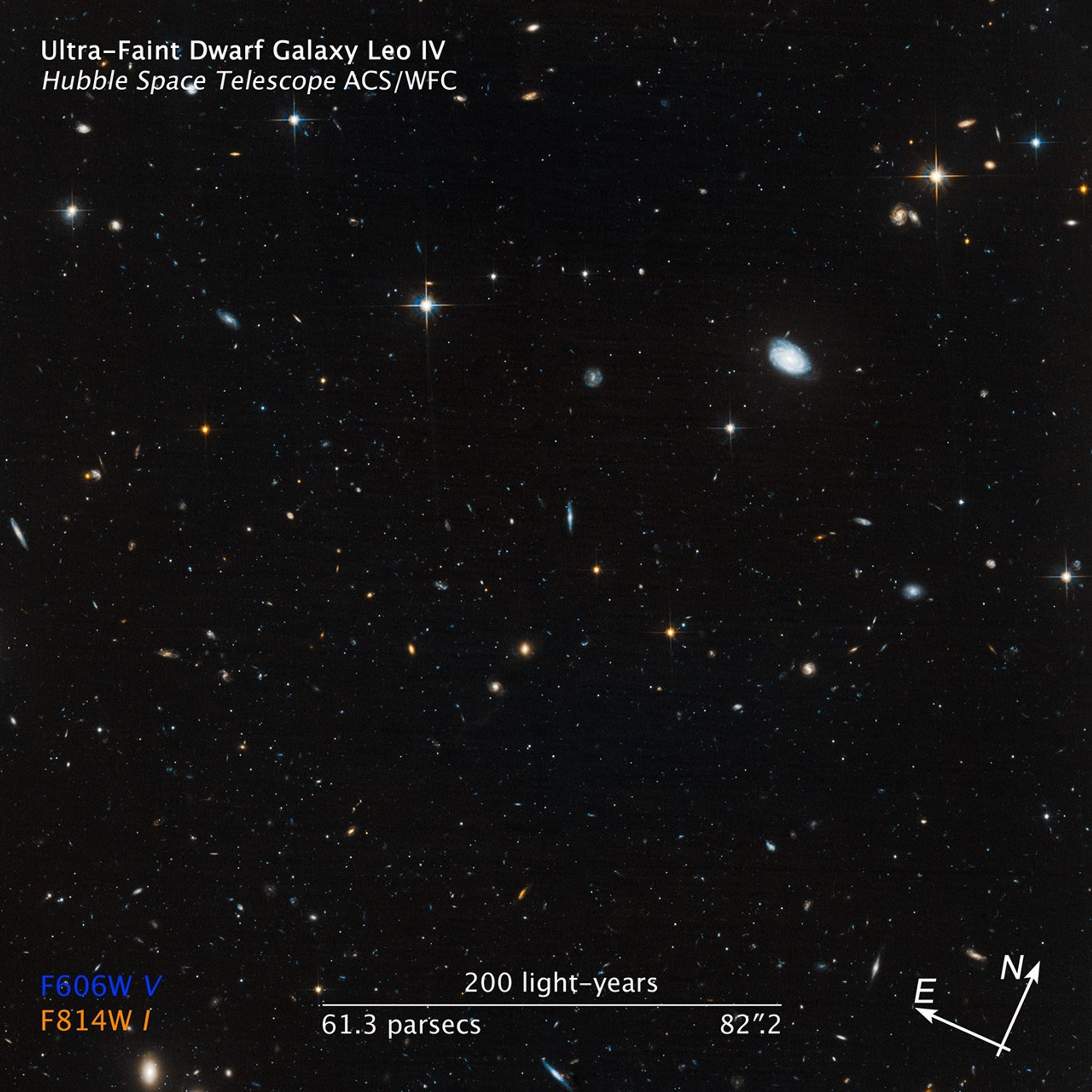
This movie shows the evolution of the stars in Leo IV, a dim dwarf galaxy in the halo of our Milky Way galaxy.
The Hubble Space Telescope measured the ages of these faint stars in Leo IV and two other similar galaxies, dubbed ultra-faint dwarf galaxies. The Hubble observations revealed that the stars in all three galaxies are more than 13 billion years old, almost as old as the 13.7-billion-year-old universe.
The movie begins with Hubble's image of the region in which the galaxy resides. The video then morphs into a view of the colors of the galaxy's stars. The stars are next shown on the Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram, which traces the types and evolution of "main-sequence" stars by showing the relationship between a star's color, based on its temperature, (horizontal scale) and its intrinsic brightness (vertical scale). Main-sequence stars are in the stable, middle phase of their development. In this diagram, the galaxy's main-sequence stars are the same mass as our Sun or smaller.
The graph then reveals how the stellar distribution would look 1 billion years after the galaxy formed. Massive and hot, blue stars fill in the upper part of the main sequence. The animation compresses billions of years into just a few seconds, showing that over time the more massive stars evolve faster. They leave the main sequence to become red giant stars (upper right). Their departure leaves behind the cooler, lower-mass stars that evolve more slowly over many billions of years.
Based on the analysis of Leo IV and the two other ultra-faint dwarf galaxies in the survey, astronomers suggest that a global event, called reionization, shut down star formation in them simultaneously more than 13 billion years ago. Reionization is a transitional phase in the early universe when the first stars burned off a fog of cold hydrogen.
Leo IV is one of at least a dozen ultra-faint dwarf galaxies near our Milky Way.
- Release DateJuly 10, 2012
- Science ReleaseHubble Unmasks Ghost Galaxies
- Credit
Related Images & Videos
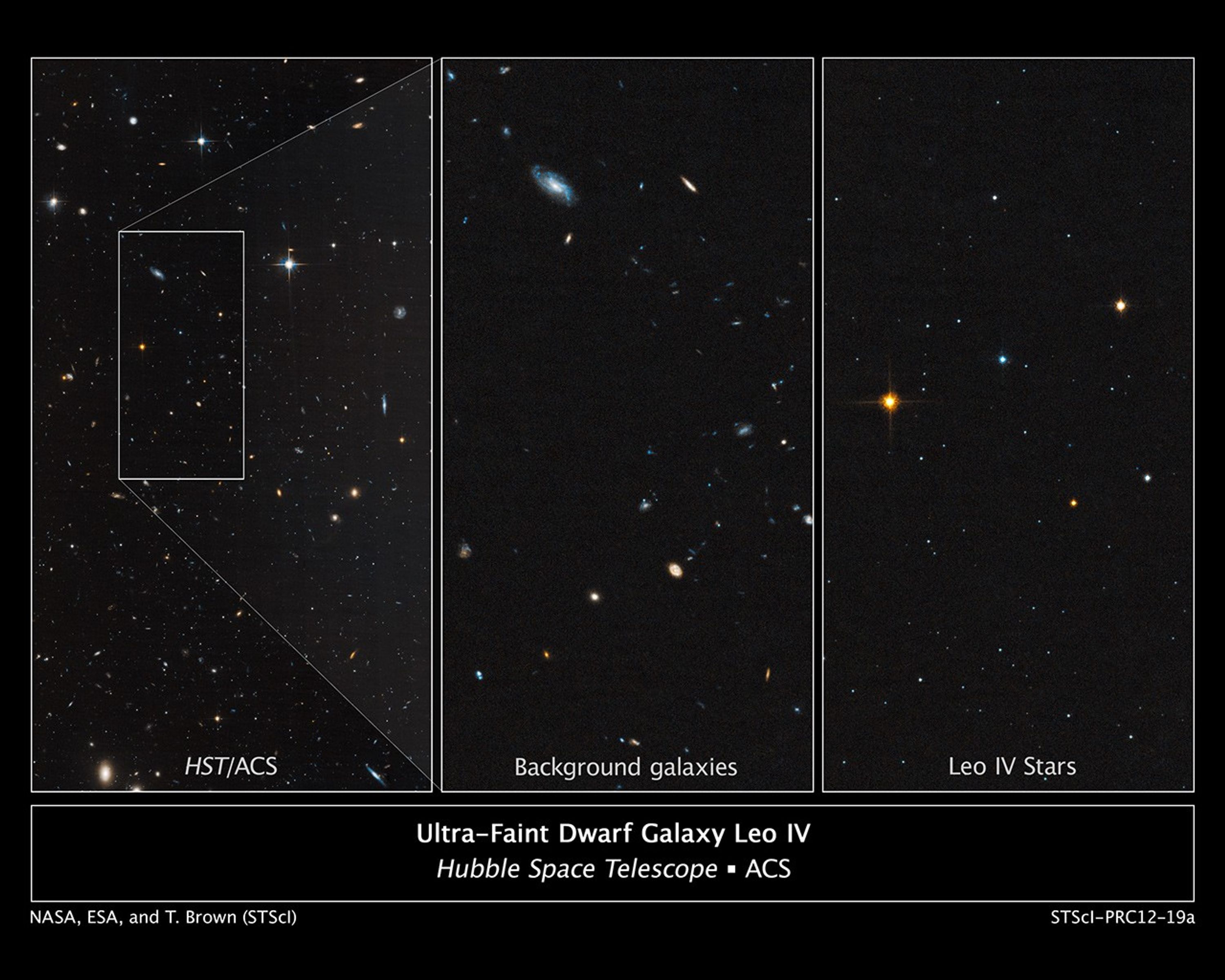

Ultra-Faint Dwarf Galaxy Leo IV
Astronomers used the Hubble Space Telescope to unmask the dim, star-starved dwarf galaxy Leo IV. These Hubble images demonstrate why astronomers had a tough time spotting this small-fry galaxy. The image at left shows part of the galaxy, outlined by the white rectangular box....
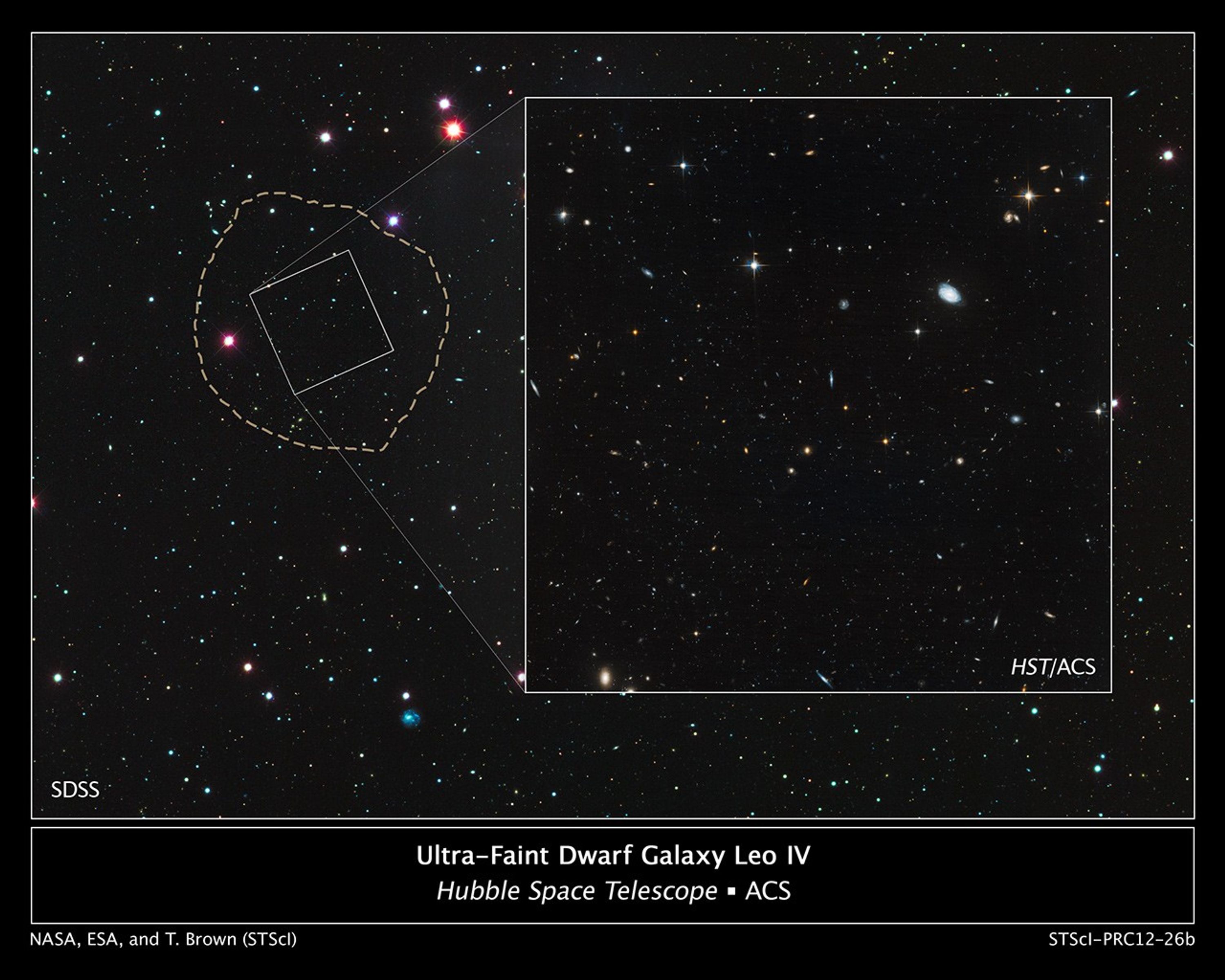
Location of Ultra-Faint Dwarf Galaxy Leo IV
These images reveal the small and faint star-starved dwarf galaxy Leo IV, a close neighbor of our Milky Way galaxy. Leo IV is one of more than a dozen ultra-faint dwarf galaxies found lurking around the Milky Way. These galaxies are dominated by dark matter, an invisible...
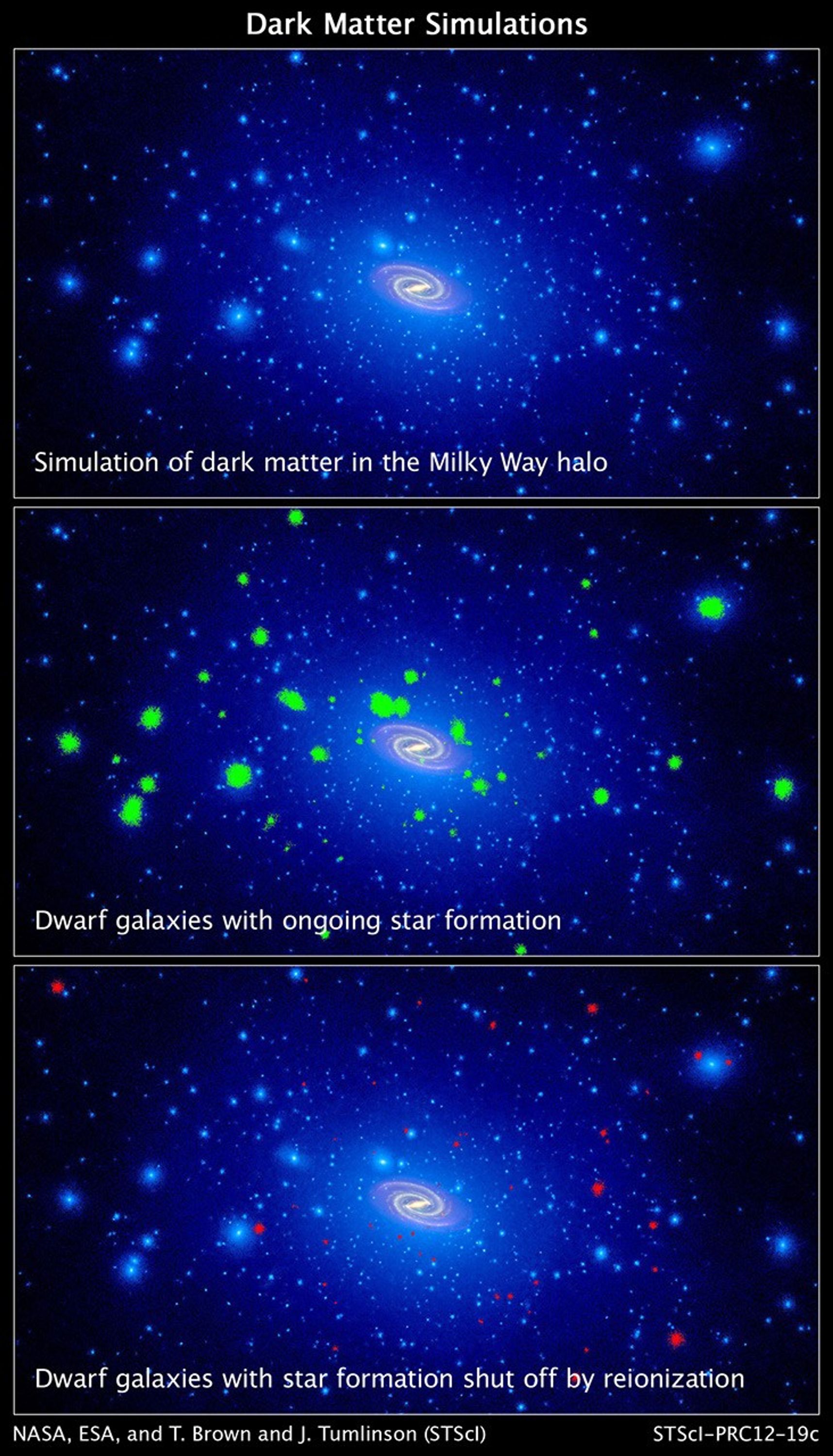
Dark Matter Simulation in Milky Way Halo
These illustrations, taken from computer simulations, show a swarm of dark matter clumps around our Milky Way galaxy. Some of the dark-matter concentrations are massive enough to spark star formation. Dark matter is an invisible substance that accounts for most of the universe's...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov