1 min read
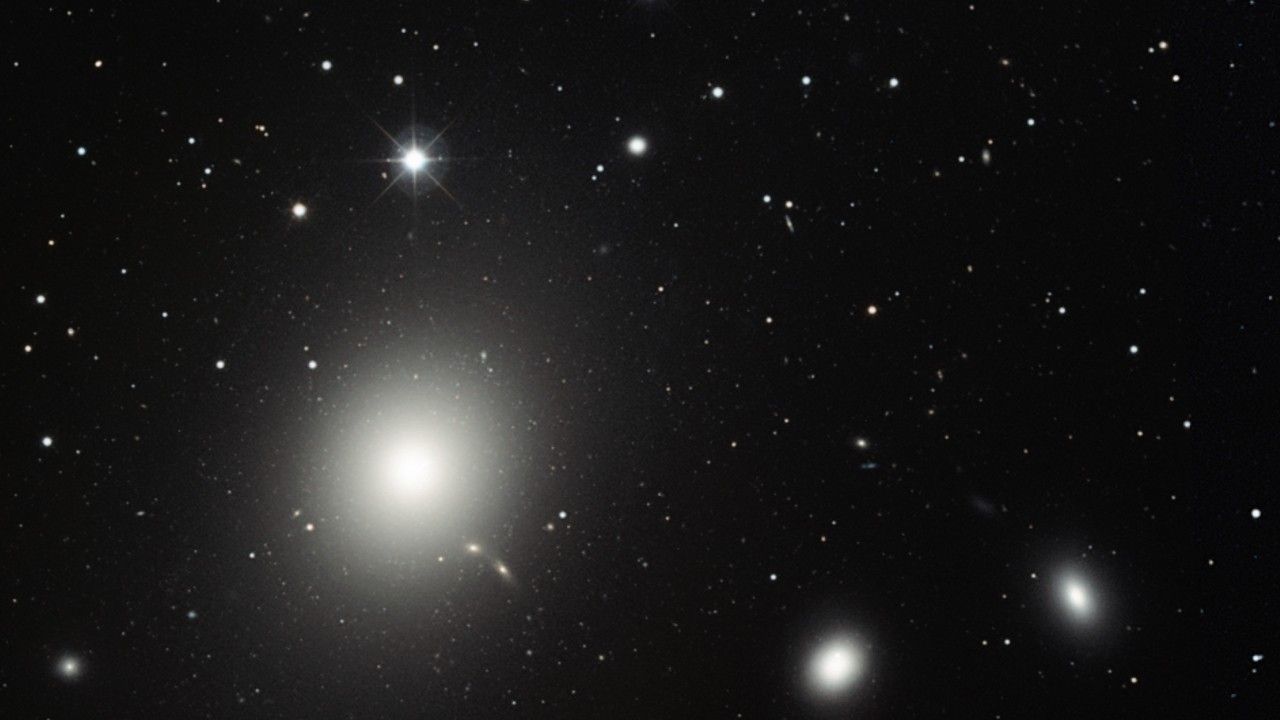
Galaxy M87 Jet (Annotated)
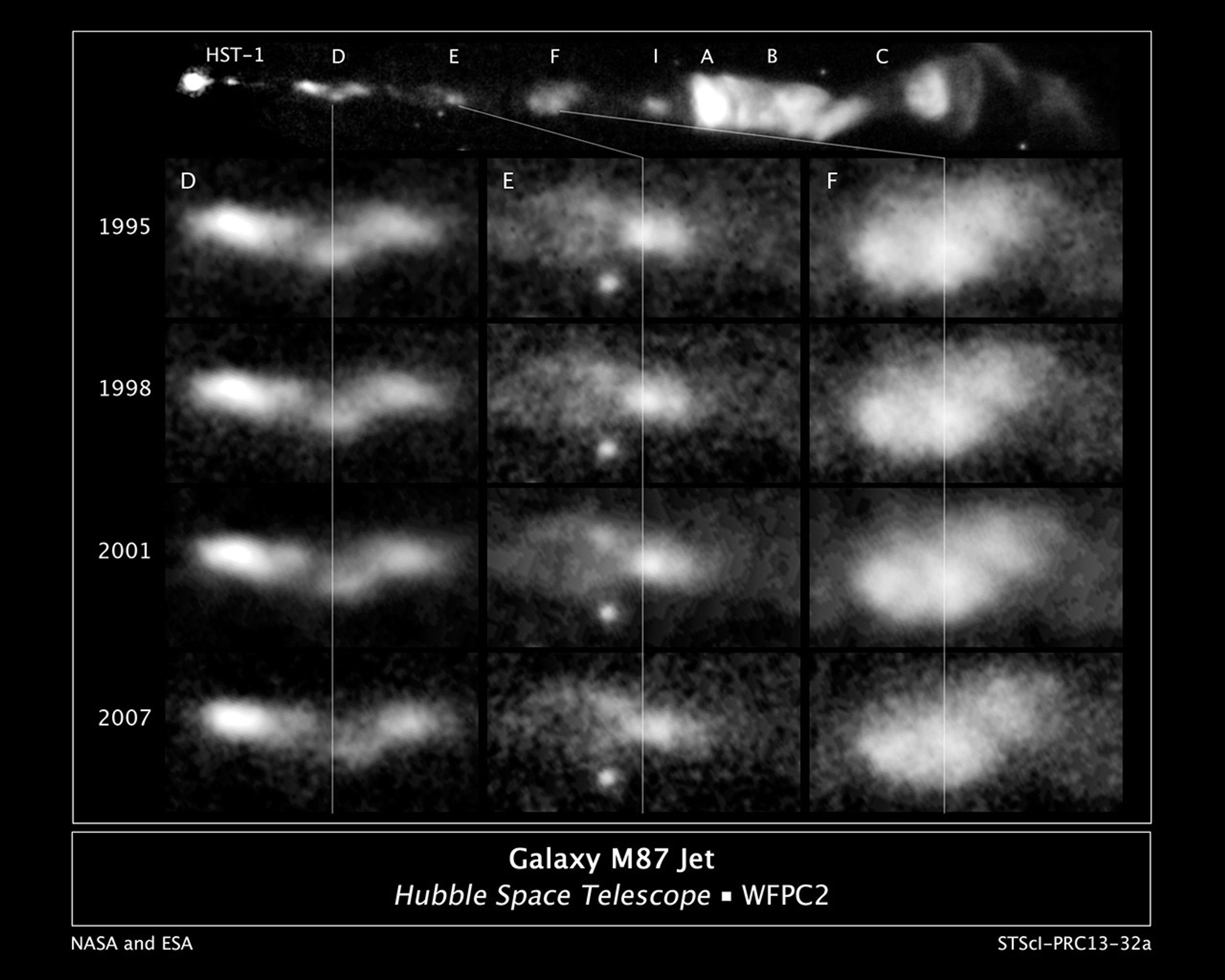
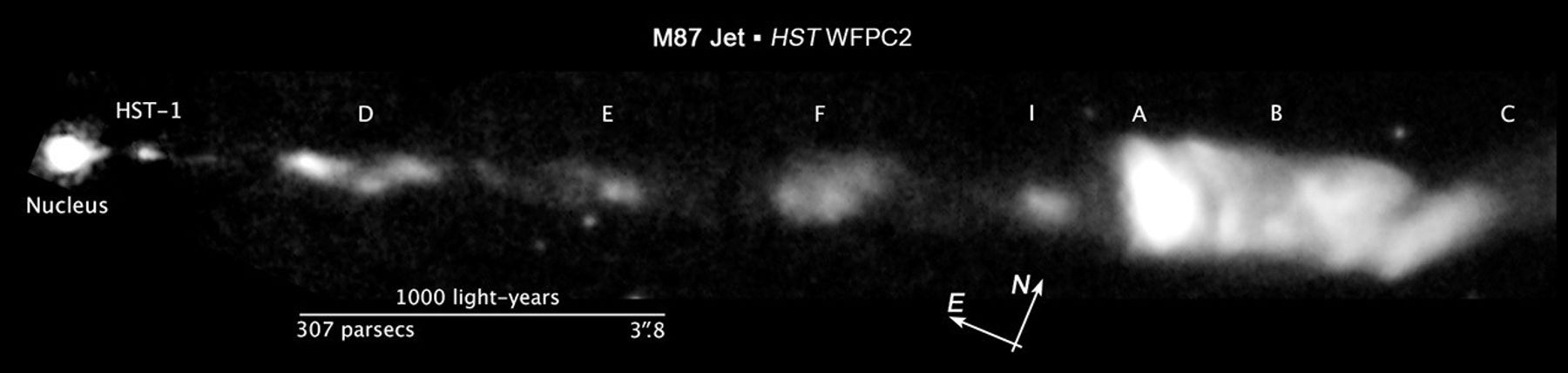
This sequence of images, taken over a 13-year span by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, reveals changes in a black-hole-powered jet of hot gas in the giant elliptical galaxy M87.
The observations show that the river of plasma, traveling at nearly the speed of light, may follow the spiral structure of the black hole's magnetic field, which astronomers think is coiled like a helix. The magnetic field is believed to arise from a spinning accretion disk of material around a black hole. Although the magnetic field cannot be seen, its presence is inferred by the confinement of the jet along a narrow cone emanating from the black hole. The visible portion of the jet extends 5,000 light-years.
M87 resides at the center of the neighboring Virgo cluster of roughly 2,000 galaxies, located 50 million light-years away.
The images are part of a time-lapse movie that reveals changes in the jet over more than a 13-year period. They were taken by Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys in 2006 and Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 in 1995, 1998, 2001, and 2007.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.12h 30m 49s.42
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.+12° 23' 28".03
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Virgo
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.54 million light-years (17 megaparsecs)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.Note: Data used in the analysis of the M87 jet are from several different instruments and numerous Hubble proposals. The science team includes: E. Meyer, W. Sparks, J. Biretta, J. Anderson, S.T. Sohn, and R. van der Marel (STScI), C. Norman (Johns Hopkins University), and M. Nakamura (Academia Sinica) - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS/WFC, HST>ACS/HRC, and HST>WFPC2
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.2002 - 2006 (ACS/WFC), 2006 (ACS/HRC), and 1995 - 2008 (HST>WFPC2)
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F814W (I)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.M87 Jet
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Giant Elliptical Galaxy with Jet
- Release DateAugust 22, 2013
- Science ReleaseHubble Takes Movies of Space Slinky
- Credit

Related Images & Videos

Magnetic Funnel Around a Supermassive Black Hole
The accretion disk of hot plasma swirling around a supermassive black hole generates powerful magnetic fields. The disk's rotation twists the field into a funnel shape. These field lines constrict and direct the outflow of high-speed plasma from the black hole's vicinity. The...

Zoom Into Black Hole Jet
This video begins with a view of the stars and galaxies in the spring constellation Virgo. We zoom into the giant elliptical galaxy M87, which lies near the center of the Virgo cluster of galaxies. A high-speed jet of hot plasma is buried deep inside the galaxy. A supermassive...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov