1 min read
Herbig-Haro Jet HH 24

Just in time for the release of the movie "Star Wars Episode VII: The Force Awakens," NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has photographed what looks like a cosmic, double-bladed lightsaber.
In the center of the image, partially obscured by a dark, Jedi-like cloak of dust, a newborn star shoots twin jets out into space as a sort of birth announcement to the universe.
"Science fiction has been an inspiration to generations of scientists and engineers, and the film series Star Wars is no exception," said John Grunsfeld, astronaut and associate administrator for NASA's Science Mission Directorate. "There is no stronger case for the motivational power of real science than the discoveries that come from the Hubble Space Telescope as it unravels the mysteries of the universe."
This celestial lightsaber does not lie in a galaxy far, far away, but rather inside our home galaxy, the Milky Way. It's inside a turbulent birthing ground for new stars known as the Orion B molecular cloud complex, located 1,350 light-years away.
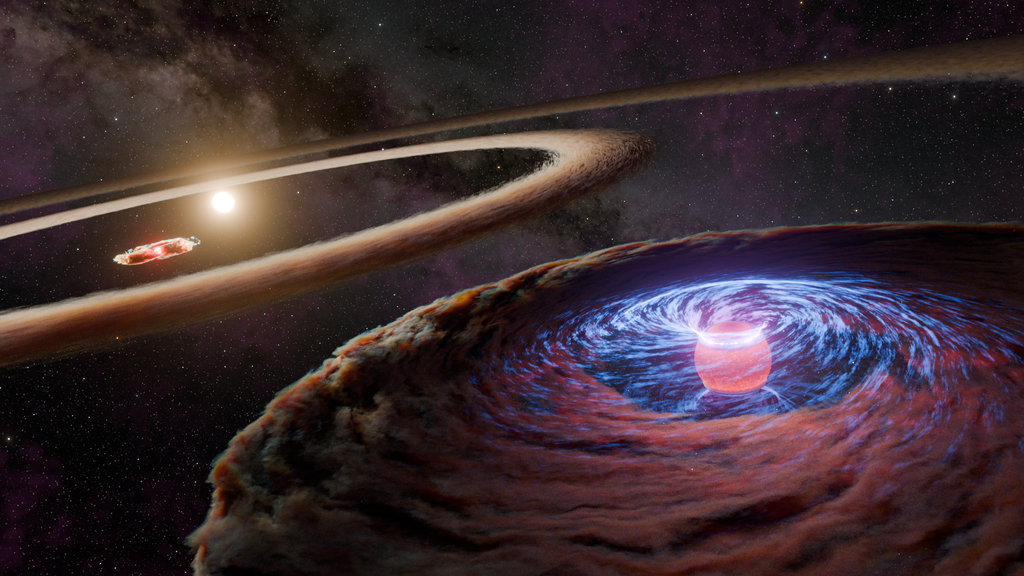
When stars form within giant clouds of cool molecular hydrogen, some of the surrounding material collapses under gravity to form a rotating, flattened disk encircling the newborn star.
Though planets will later congeal in the disk, at this early stage the protostar is feeding on the disk with a Jabba-like appetite. Gas from the disk rains down onto the protostar and engorges it. Superheated material spills away and is shot outward from the star in opposite directions along an uncluttered escape route – the star's rotation axis.
Shock fronts develop along the jets and heat the surrounding gas to thousands of degrees Fahrenheit. The jets collide with the surrounding gas and dust and clear vast spaces, like a stream of water plowing into a hill of sand. The shock fronts form tangled, knotted clumps of nebulosity and are collectively known as Herbig-Haro (HH) objects. The prominent HH object shown in this image is HH 24.
Just to the right of the cloaked star, a couple of bright points are young stars peeking through and showing off their own faint lightsabers – including one that has bored a tunnel through the cloud towards the upper-right side of the picture.
Overall, just a handful of HH jets have been spotted in this region in visible light, and about the same number in the infrared. Hubble's observations for this image were performed in infrared light, which enabled the telescope to peer through the gas and dust cocooning the newly forming stars and capture a clear view of the HH objects.
These young stellar jets are ideal targets for NASA's upcoming James Webb Space Telescope, which will have even greater infrared wavelength vision to see deeper into the dust surrounding newly forming stars.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.05h 46m 8.87s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.00° 10' 11.99"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Orion
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.1,350 light-years (414 parsecs)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator. - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>WFPC2, and HST>WFC3/IR
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.August 4, 2001, October 13, 2009, and February 18, 2014
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F814W (I), F814W (I), F164N ([Fe II])
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Herbig-Haro 24, HH 24
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Herbig-Haro Jet
- Release DateDecember 17, 2015
- Science ReleaseHubble Sees the Force Awakening in a Newborn Star
- CreditNASA and ESA; Acknowledgment: NASA, ESA, the Hubble Heritage (STScI/AURA)/Hubble-Europe (ESA) Collaboration, D. Padgett (GSFC), T. Megeath (University of Toledo), and B. Reipurth (University of Hawaii)

This image is a composite of separate exposures acquired by the WFPC2 and WFC3/IR instruments. Several filters were used to sample various wavelengths. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: F814W (I) Green: F814W (I) + F160W (H) Orange: F160W (H) Red: F164N ([Fe II])

Related Images & Videos
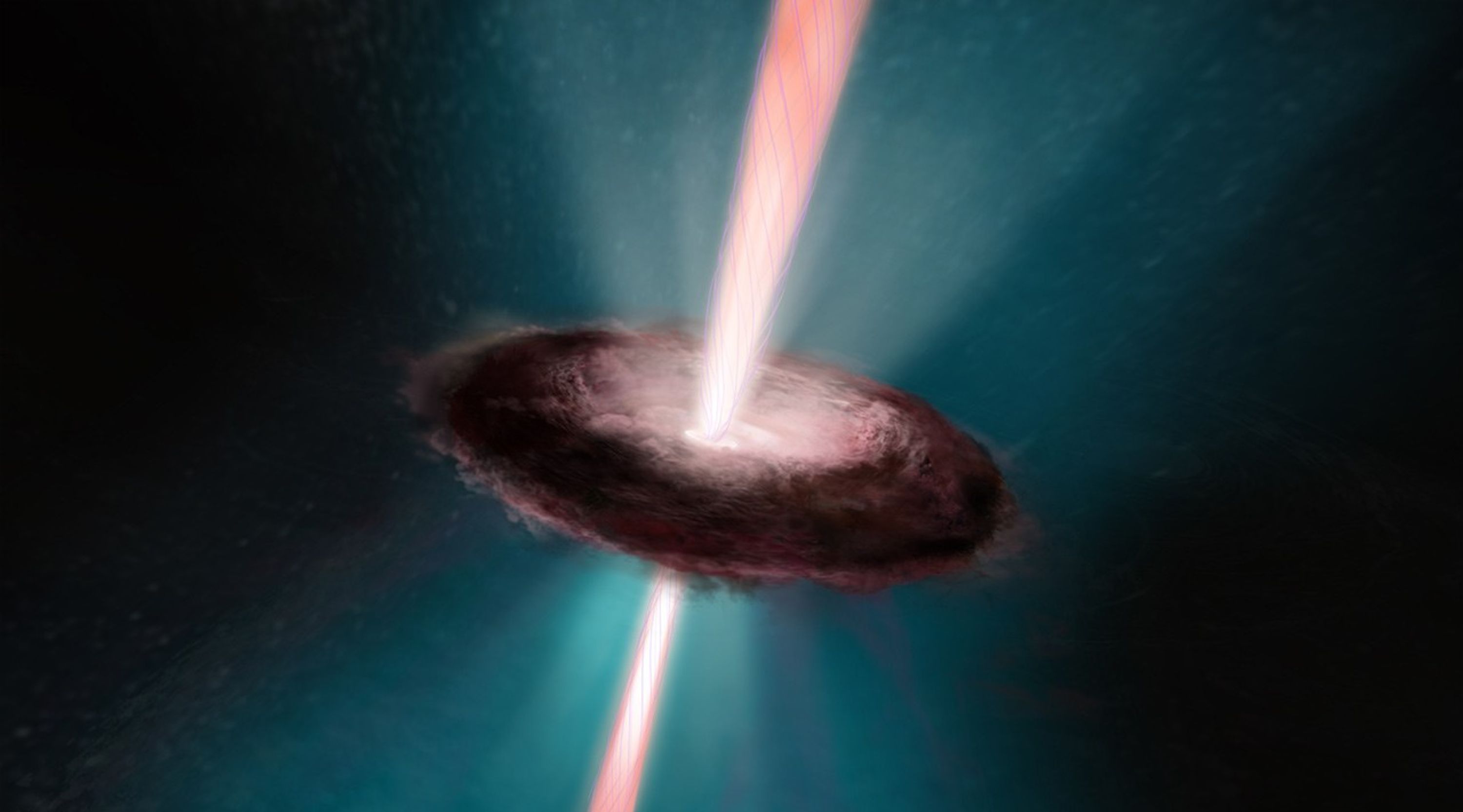

Jets From a Newborn Star
This is an artist's concept of the fireworks that accompany the birth of a star. The young stellar object is encircled by a pancake-shaped disk of dust and gas left over from the collapse of the nebula that formed the star. Gas falls onto the newly forming star and is heated to...
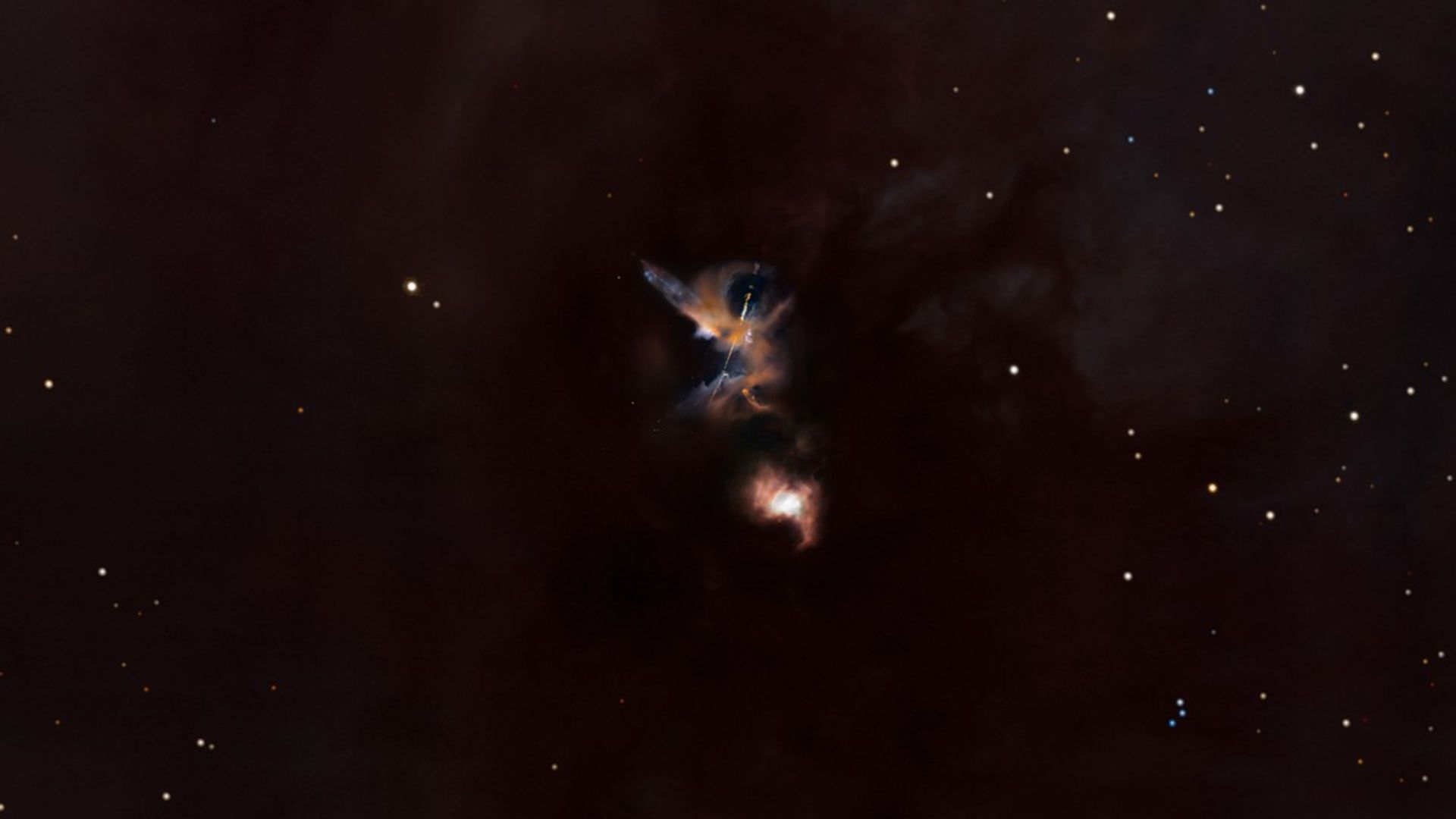

Celestial Lightsabers: The Stellar Jets of HH 24 (3-D Fly, Short Version)
This movie envisions a three-dimensional perspective on the Hubble Space Telescope's striking image of the Herbig-Haro object known as HH 24. The sequence starts with a wide-field view covering the vast dark cloud of the Orion B molecular cloud complex and a scattering of stars....
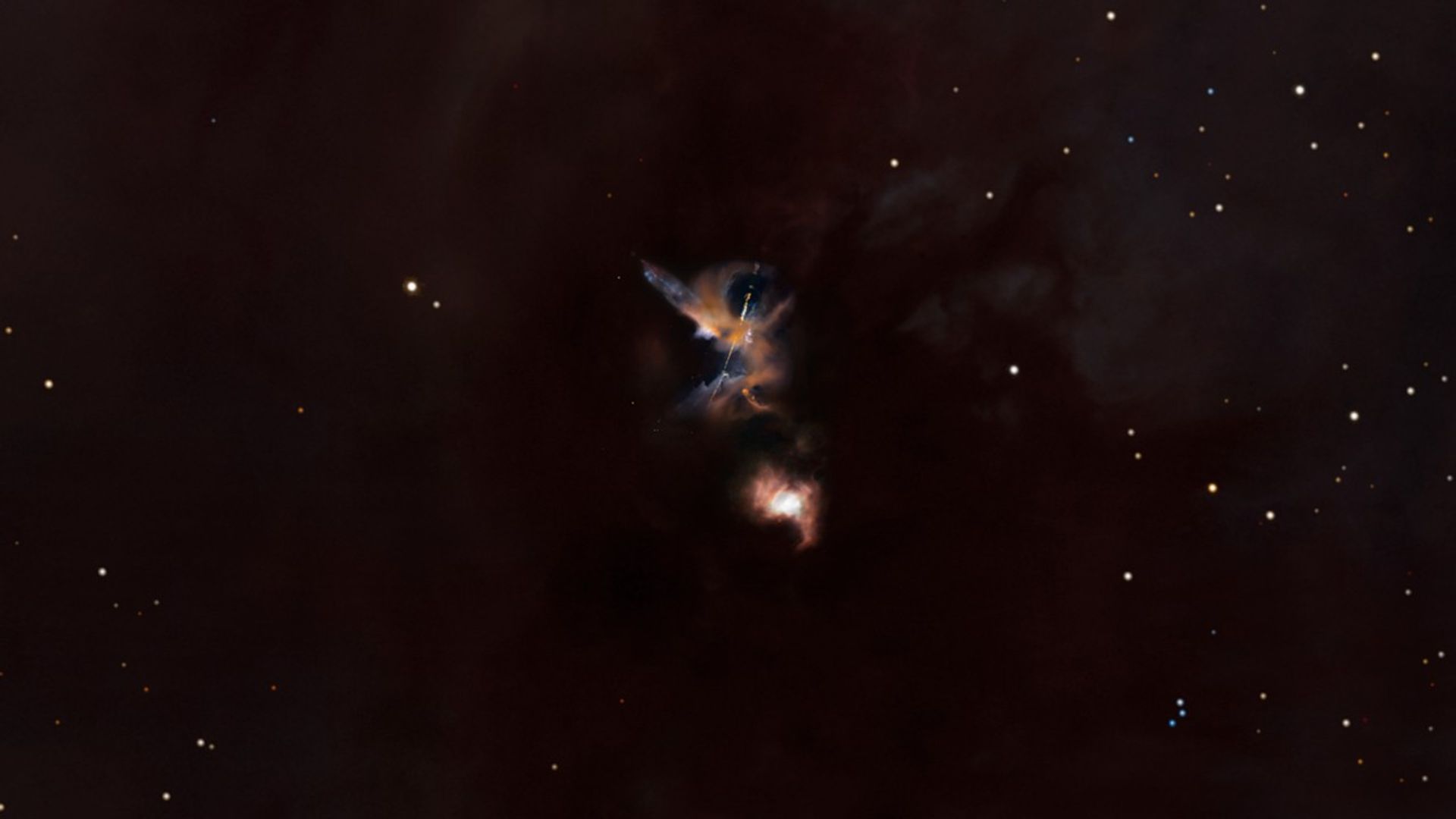

Celestial Lightsabers: The Stellar Jets of HH 24 (3-D Fly)
This movie envisions a three-dimensional perspective on the Hubble Space Telescope's striking image of the Herbig-Haro object known as HH 24. The sequence starts with a wide-field view covering the vast dark cloud of the Orion B molecular cloud complex and a scattering of stars....
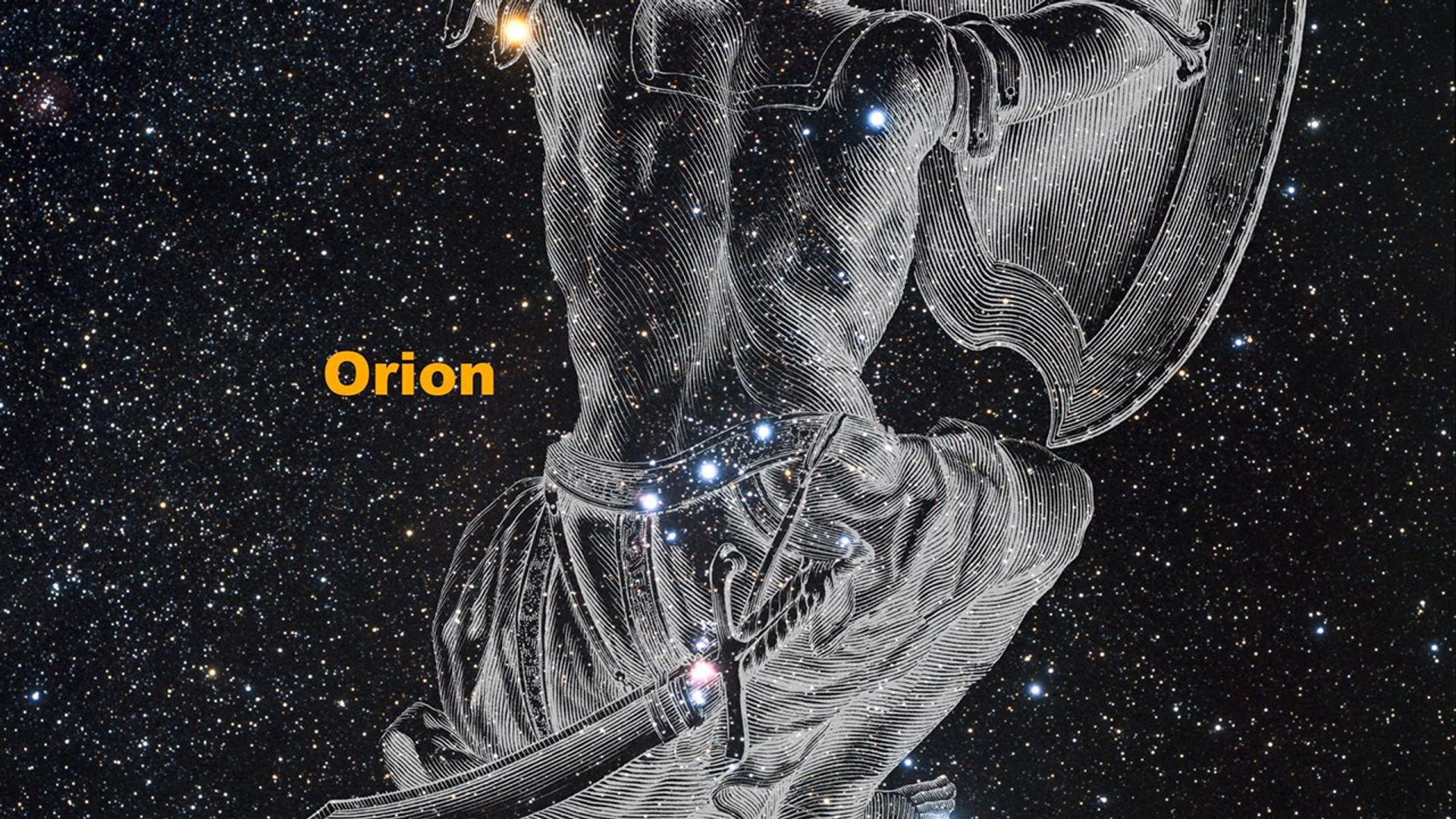
Celestial Lightsabers: The Stellar Jets of HH 24 (2-D Zoom and 3-D Fly)
This sequence combines a two-dimensional zoom and a three-dimensional flight to explore the Hubble Space Telescope's striking image of the Herbig-Haro object known as HH 24. The movie starts with a night sky view of the Orion constellation and zooms in. Located above the left...
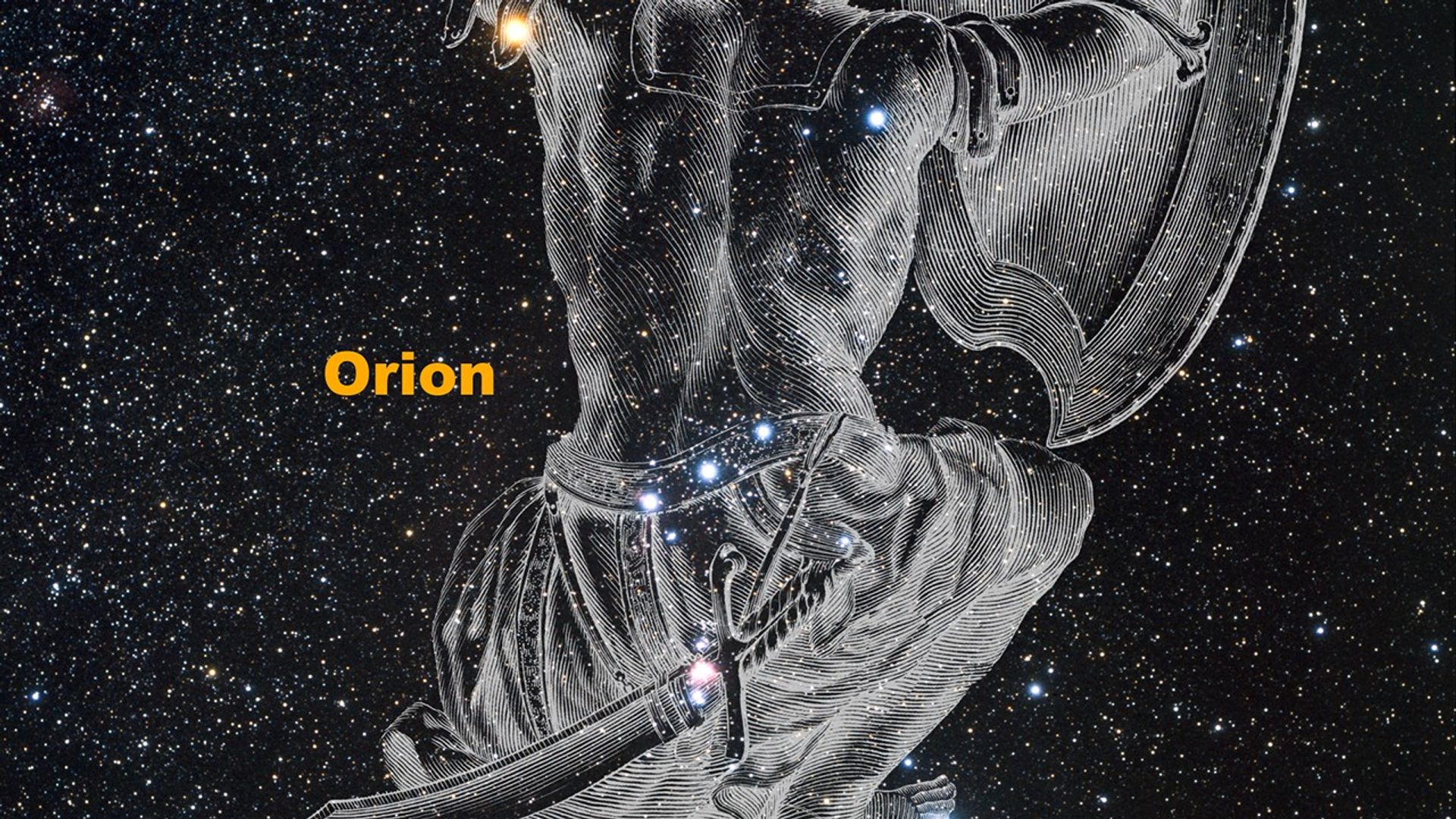
Celestial Lightsabers: The Stellar Jets of HH 24 (2-D Zoom)
This sequence zooms from a night sky view of the Orion constellation into a striking Hubble Space Telescope image of the Herbig-Haro object known as HH 24. Located above the left side of Orion's Belt is the vast dark nebula called the Orion B molecular cloud complex. Within this...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov































