1 min read
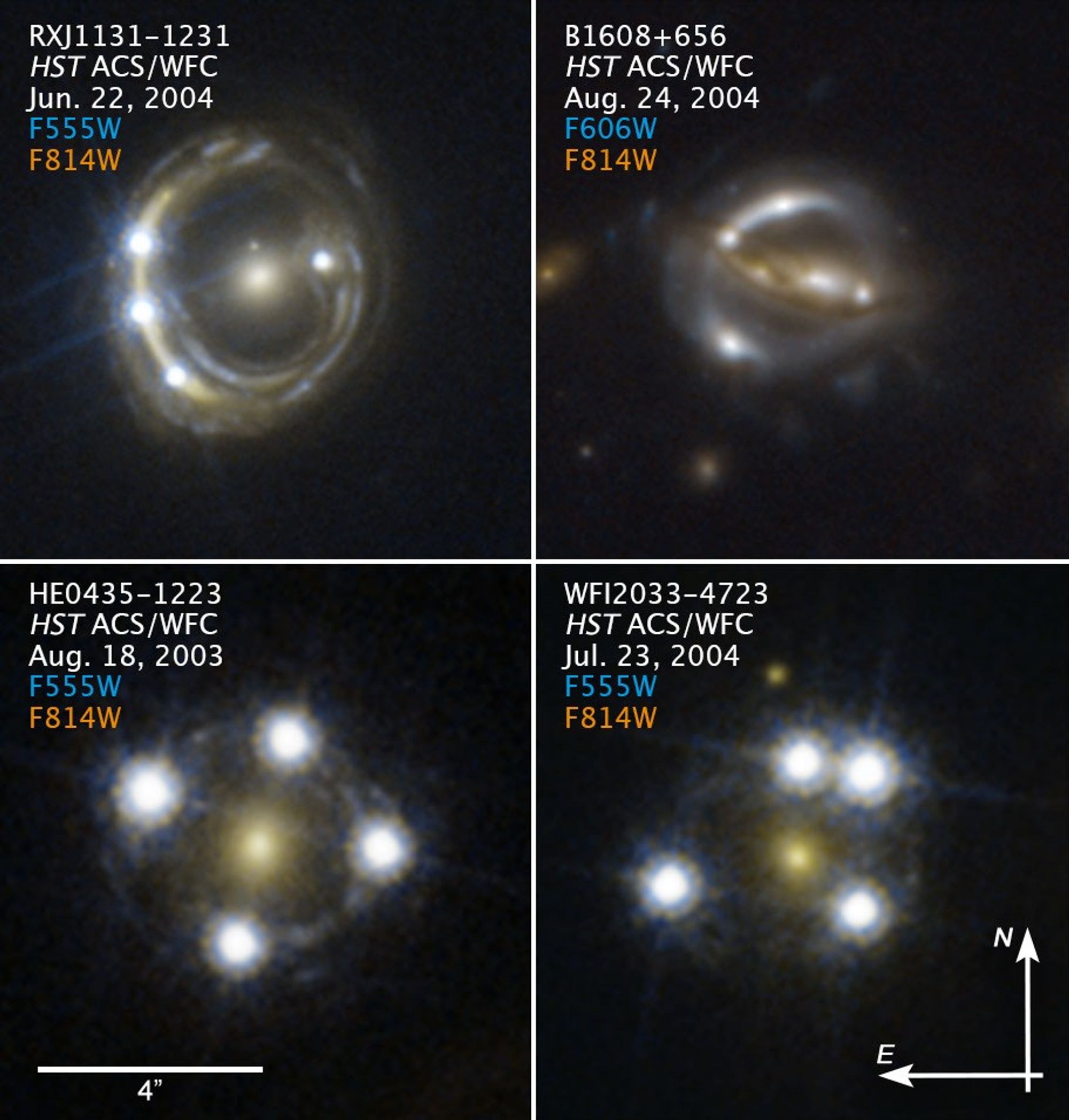
Compass Image of Gravitationally Lensed Quasars

About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator. - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.ACS/ WFC
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.22 June 2004, 24 Aug 2004, 18 Aug 2003, 23 July 2004
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F555W, F606W, F814W
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.RXJ1131-1231, B1608+656, HE0435-1223, WFI2033-4723
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Background quasars lensed by foreground galaxies
- Release DateJanuary 8, 2020
- Science ReleaseCosmic Magnifying Glasses Yield Independent Measure of Universe’s Expansion
- Credit

These images are a composite of separate exposures acquired by the ACS/WFC instrument on the Hubble Space Telescope. Several filters were used to sample narrow wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are Cyan: F555W/F606W Orange: F814W.
Related Images & Videos

Mosaic of Gravitationally Lensed Quasars
Each of these Hubble Space Telescope snapshots reveals four distorted images of a background quasar surrounding the central core of a foreground massive galaxy. The multiple quasar images were produced by the gravity of the foreground galaxy, which is acting like a magnifying...
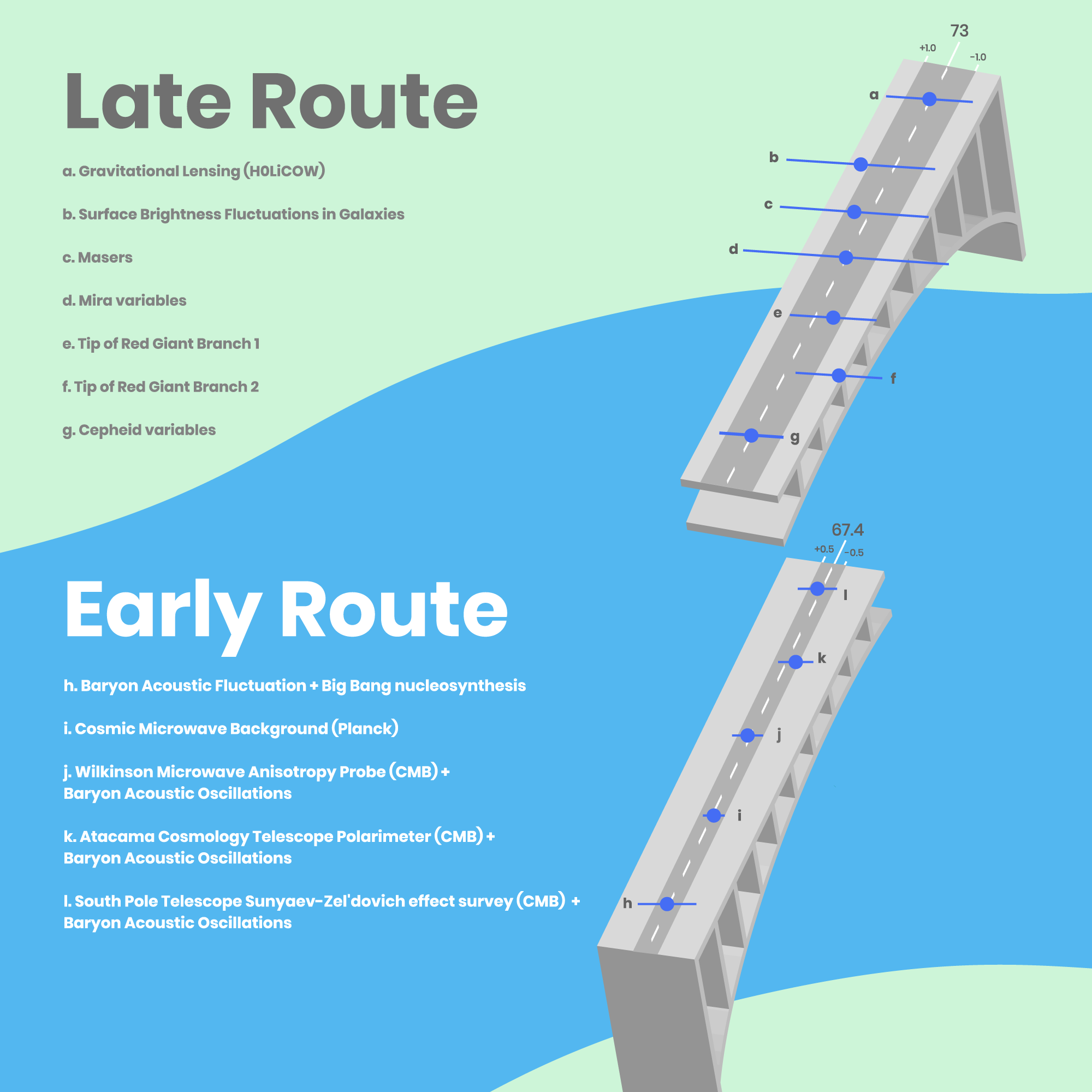
Infographic on Hubble Constant
The Wide Divide in the Expansion Rate Measurements This graphic lists the variety of techniques astronomers have used to measure the expansion rate of the universe, known as the Hubble constant. Knowing the precise value for how fast the universe expands is important for...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov



























