1 min read
A Multi-Wavelength View of Radio Galaxy Hercules A

Spectacular jets powered by the gravitational energy of a supermassive black hole in the core of the elliptical galaxy Hercules A illustrate the combined imaging power of two of astronomy's cutting-edge tools, the Hubble Space Telescope's Wide Field Camera 3, and the recently upgraded Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) radio telescope in New Mexico.
Some two billion light-years away, the yellowish elliptical galaxy in the center of the image appears quite ordinary as seen by Hubble in visible wavelengths of light. The elliptical galaxy is roughly 1,000 times more massive than the bulge of our Milky Way and harbors a 2.5-billion-solar-mass central black hole that is 1,000 times more massive than the black hole in the Milky Way. But the innocuous-looking galaxy, also known as 3C 348, has long been known as the brightest radio-emitting object in the constellation Hercules. Emitting nearly a billion times more power in radio wavelengths than our Sun, the galaxy is one of the brightest extragalactic radio sources in the entire sky.
The VLA radio data reveal enormous, optically invisible jets that, at one-and-a-half million light-years wide, dwarf the visible galaxy from which they emerge. The jets are very-high-energy plasma beams, subatomic particles and magnetic fields shot at nearly the speed of light from the vicinity of the black hole. The outer portions of both jets show unusual ring-like structures suggesting a history of multiple outbursts from the supermassive black hole at the center of the galaxy.
The innermost parts of the jets are not visible because of the extreme velocity of the material; relativistic effects confine all of the light to a narrow cone aligned with the jets, and so that light is not seen by us. Far from the galaxy, the jets become unstable and break up into the rings and wisps.
The entire radio source is surrounded by a very hot, X-ray-emitting cloud of gas, not seen in this optical-radio composite.
Hubble's view of the field also shows a companion elliptical galaxy very close to the center of the optical-radio source, which may be merging with the central galaxy. Several other elliptical and spiral galaxies that are visible in the Hubble data may be members of a cluster of galaxies. Hercules A is by far the brightest and most massive galaxy in the cluster.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.16h 51m 8.14s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.04° 59' 33.32"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Hercules
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.2.1 billion light-years (637 million parsecs or redshift z = 0.156)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The image was created from Hubble data from proposal 13065: S. Baum and C. O'Dea (Rochester Institute of Technology) and J. Stoke and F. Lo (Associated Universities, Inc.). Notes:The VLA data are from the National Radio Astronomy Observatory observation project TDEM0011: R. Perley, W. Cotton, and U. Rao (NRAO/AUI/NSF). These data were taken August 2010 through September 2011. Frequencies 4-9 GHz were measured. - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>WFC3/UVIS and National Radio Astronomy Observatory VLA
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.October 8, 2012, Exposure Time: 1 hour
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.WFC3/UVIS: F606W (V) and F814W (I) VLA: C Band Low (4-6 GHz), C Band High (6-8 GHz), and X Band Low (8-9 GHz)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Hercules A, Herc A, 3C 348
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Active Galaxy; Radio Galaxy
- Release DateNovember 29, 2012
- Science ReleaseA Multi-Wavelength View of Radio Galaxy Hercules A
- CreditNASA, ESA, S. Baum and C. O'Dea (RIT), R. Perley and W. Cotton (NRAO/AUI/NSF), and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)

This image is a composite of separate exposures acquired by Hubble's WFC3 instrument and the VLA. Several filters were used to sample various wavelengths/frequencies. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Orange: F814W (I) Blue: WFC3/UVIS F606W (V) + VLA X Band Low (8-9 GHz) Green: VLA C Band High (6-8 GHz) Red: VLA C Band Low (4-6 GHz)

Related Images & Videos
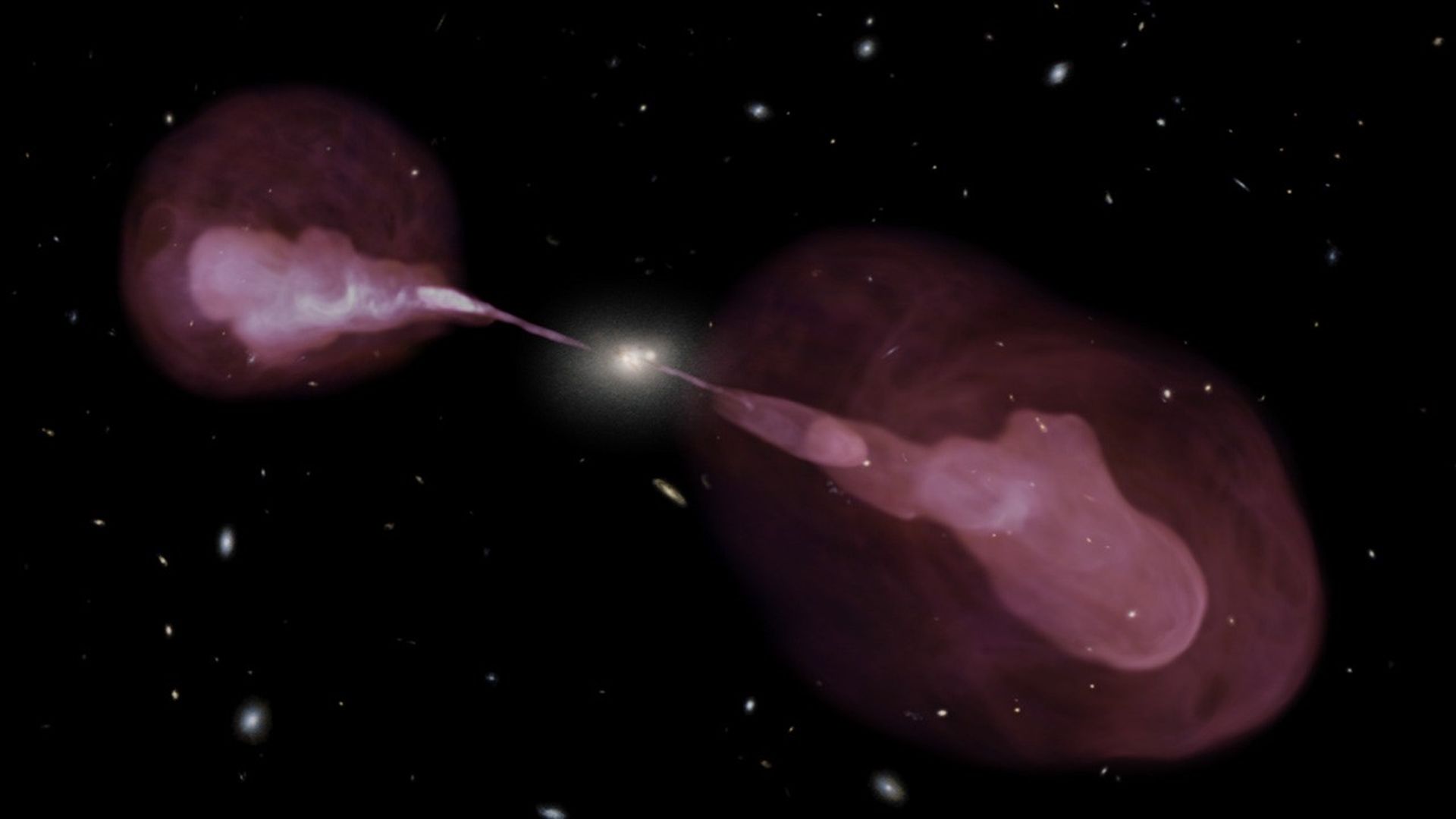

A 3-D Perspective on Hercules A
This video envisions a three-dimensional look at the combined visible light and radio emission from the active galaxy Hercules A. Unusually, this giant elliptical galaxy is not found in a large cluster of galaxies, but rather within a comparatively small group of galaxies. The...
Hercules A Zoom Sequence (Annotated)
This video zooms in on the active radio galaxy Hercules A. Spectacular jets powered by the gravitational energy of a supermassive black hole in the core of the elliptical galaxy Hercules A illustrate the combined imaging power of two of astronomy's cutting-edge tools, the Hubble...

Hercules A Zoom Sequence
This video zooms in on the active radio galaxy Hercules A. Spectacular jets powered by the gravitational energy of a supermassive black hole in the core of the elliptical galaxy Hercules A illustrate the combined imaging power of two of astronomy's cutting-edge tools, the Hubble...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov



































