1 min read
Age-Dating the Universe
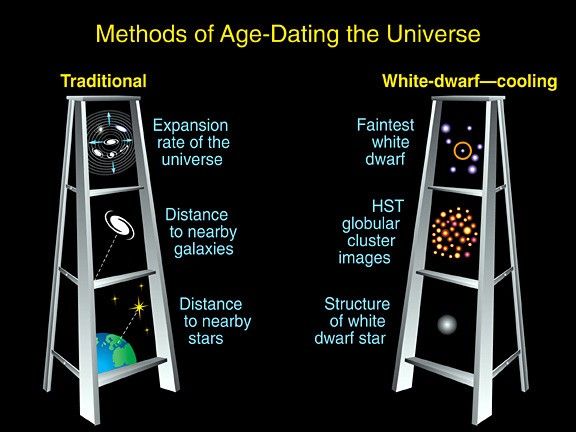
This illustration outlines the two techniques astronomers have used to determine the universe's age.
In the "traditional method," astronomers used measurements of the universe's expansion rate to calculate the age of the cosmos. They determined the expansion rate by measuring the distances to nearby galaxies. They then compared those measurements with the speed at which those galaxies are receding from Earth. Astronomers used that data to calculate the universe's age.
In the "white-dwarf-cooling method," astronomers studied the faintest white dwarfs in a globular cluster. Globular clusters are among the oldest clusters of stars in the universe. And the faintest and coolest white dwarfs within globular clusters represent the oldest stars in the clusters. Earlier Hubble observations showed that the first stars formed less than 1 billion years after the universe's birth in the big bang. So, finding the oldest stars puts astronomers within arm's reach of the universe's age.
- Release DateApril 24, 2002
- Science ReleaseHubble Uncovers Oldest “Clocks” in Space to Read Age of Universe
- Credit
Related Images & Videos
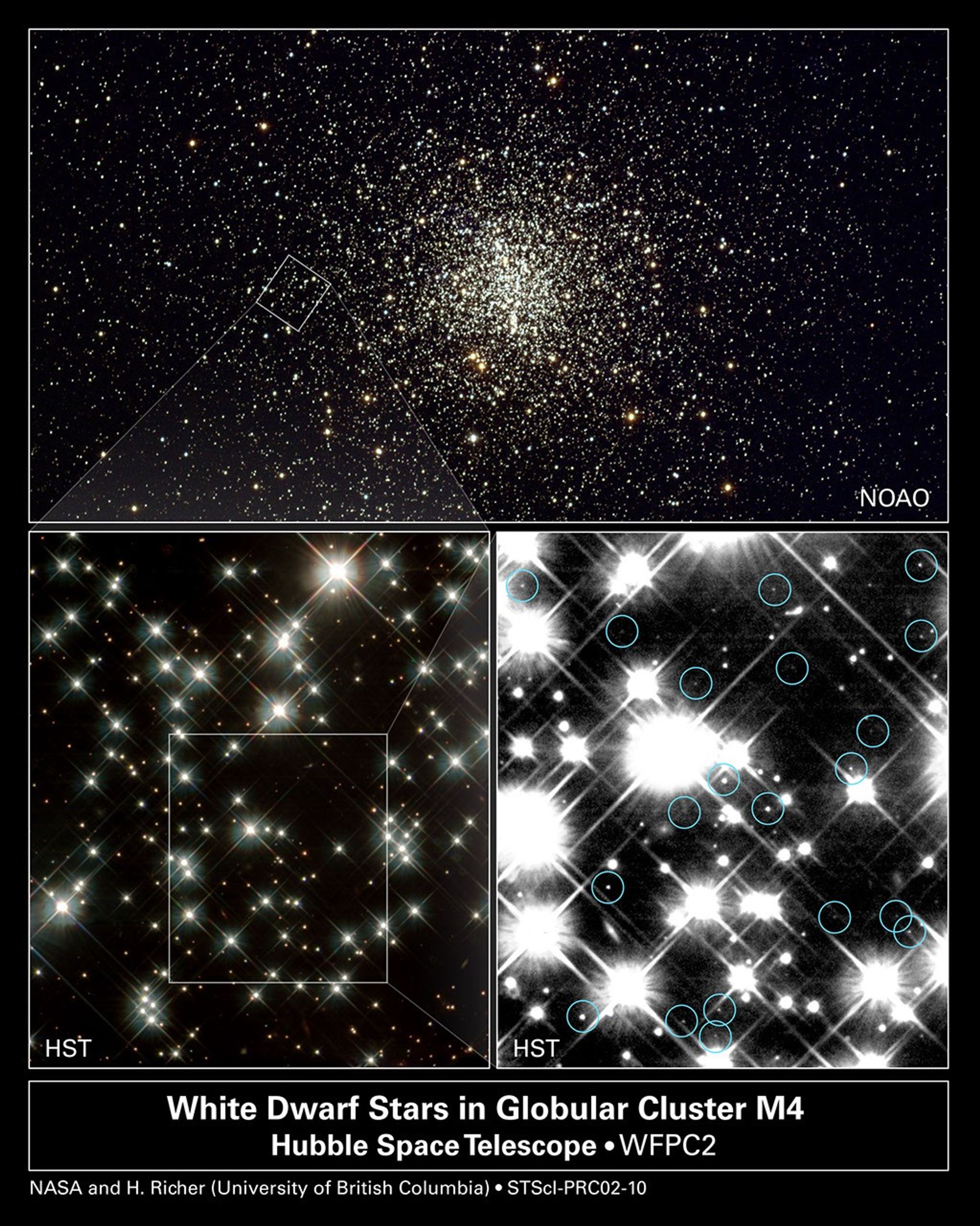
Hubble Pinpoints White Dwarfs in Globular Cluster
Peering deep inside a cluster of several hundred thousand stars, NASA's Hubble Space Telescope uncovered the oldest burned-out stars in our Milky Way Galaxy. Located in the globular cluster M4, these small, dying stars - called white dwarfs - are giving astronomers a fresh...

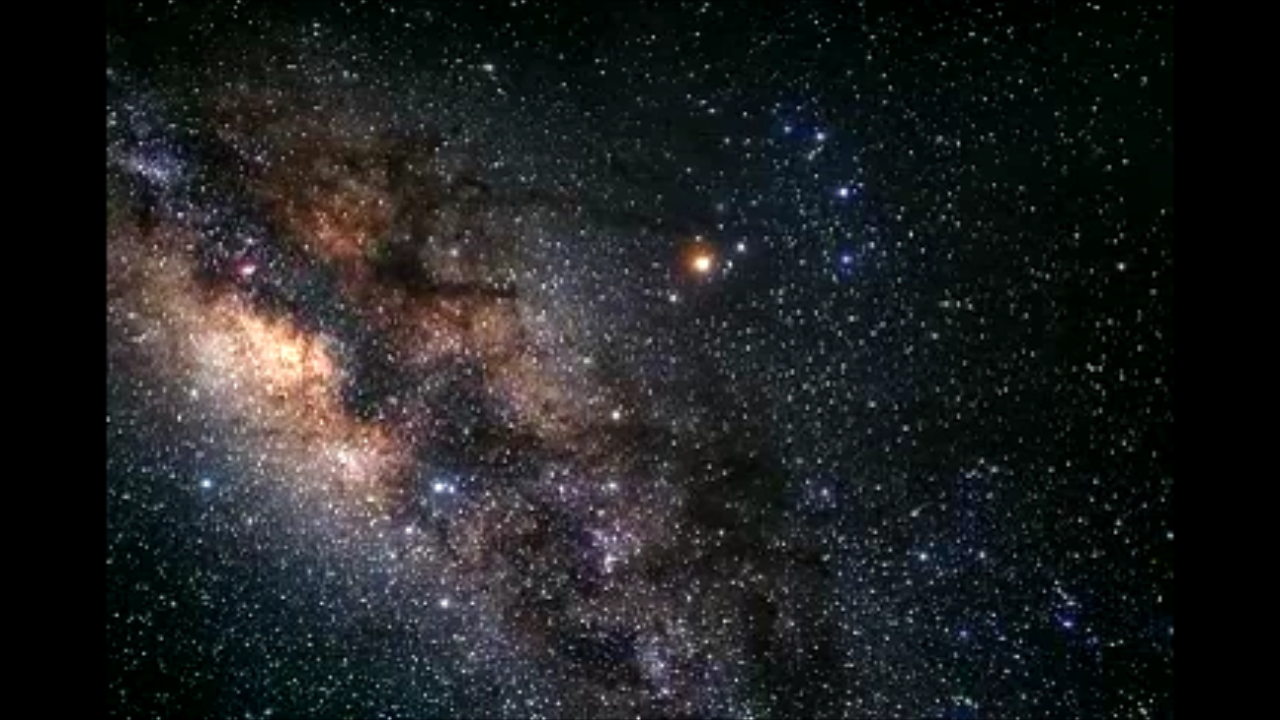
Globular Cluster M4's Location in Milky Way
This illustration shows the location of the globular cluster M4 in our Milky Way Galaxy, which is depicted "edge-on" or from the side. Globular clusters like M4 are the first pioneer settlers of the Milky Way. Many coalesced to build the hub of our galaxy and formed billions of...
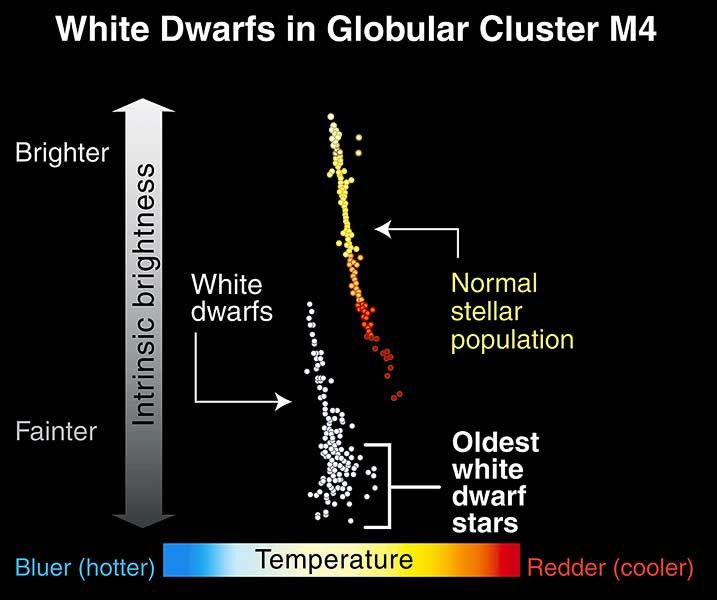
White Dwarfs in Globular Cluster M4
This graph shows the relationship between the temperature and brightness of a sampling of stars in the globular cluster M4. The line of dots at upper right represents main-sequence stars, those whose cores are fusing hydrogen. Normal stars like our Sun fall in the middle of this...

Birth of Our Galaxy
This is an artist's concept of the early formative years of our Milky Way galaxy, circa 12.7 billion years ago. That long ago, the majestic spiral arms of our galaxy had not yet formed; the sky was a sea of globular star clusters. The bright blue star cluster at center left is...

Animation Zoom into M4 Globular Cluster
Sequence begins with a backyard view of the Scorpius region, then zooms to the Hubble Space Telescope's Wide Field Planetary Camera view of the M4 globular star cluster, located in the Milky Way Galaxy's stellar halo. Circles fade in, indicating the location of the cooling white...

Globular Cluster Age: White Dwarf Ages in M4
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has found the oldest burned-out stars in our Milky Way Galaxy. These extremely dim and old "clockwork stars" provide a completely independent reading of the age of the universe. By measuring the temperature of white dwarf stars in a globular star...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov































