1 min read
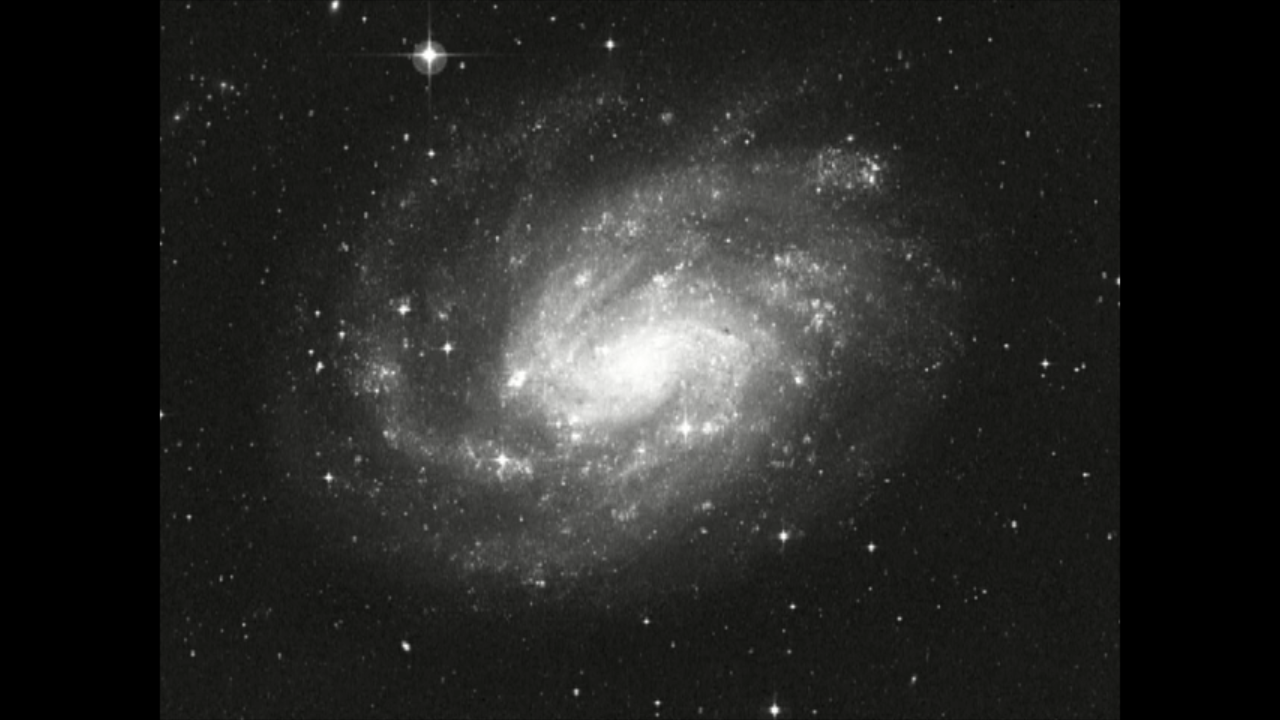
Digitized Sky Survey Image of NGC 300

About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.00h 54m 53.49s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-37° 40' 58.99"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Sculptor
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.6.5 million light-years (2 Megaparsecs)
About the Data
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.DSS
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.NGC 300
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Spiral Galaxy
- Release DateApril 8, 2004
- Science ReleaseHubble Sees Stars as Numerous as Grains of Sand in Nearby Galaxy
- CreditNASA, ESA, and The Hubble Heritage Team (AURA/STScI); Acknowledgment: F. Bresolin (Institute for Astronomy, U. Hawaii) and the Digitized Sky Survey
Related Images & Videos
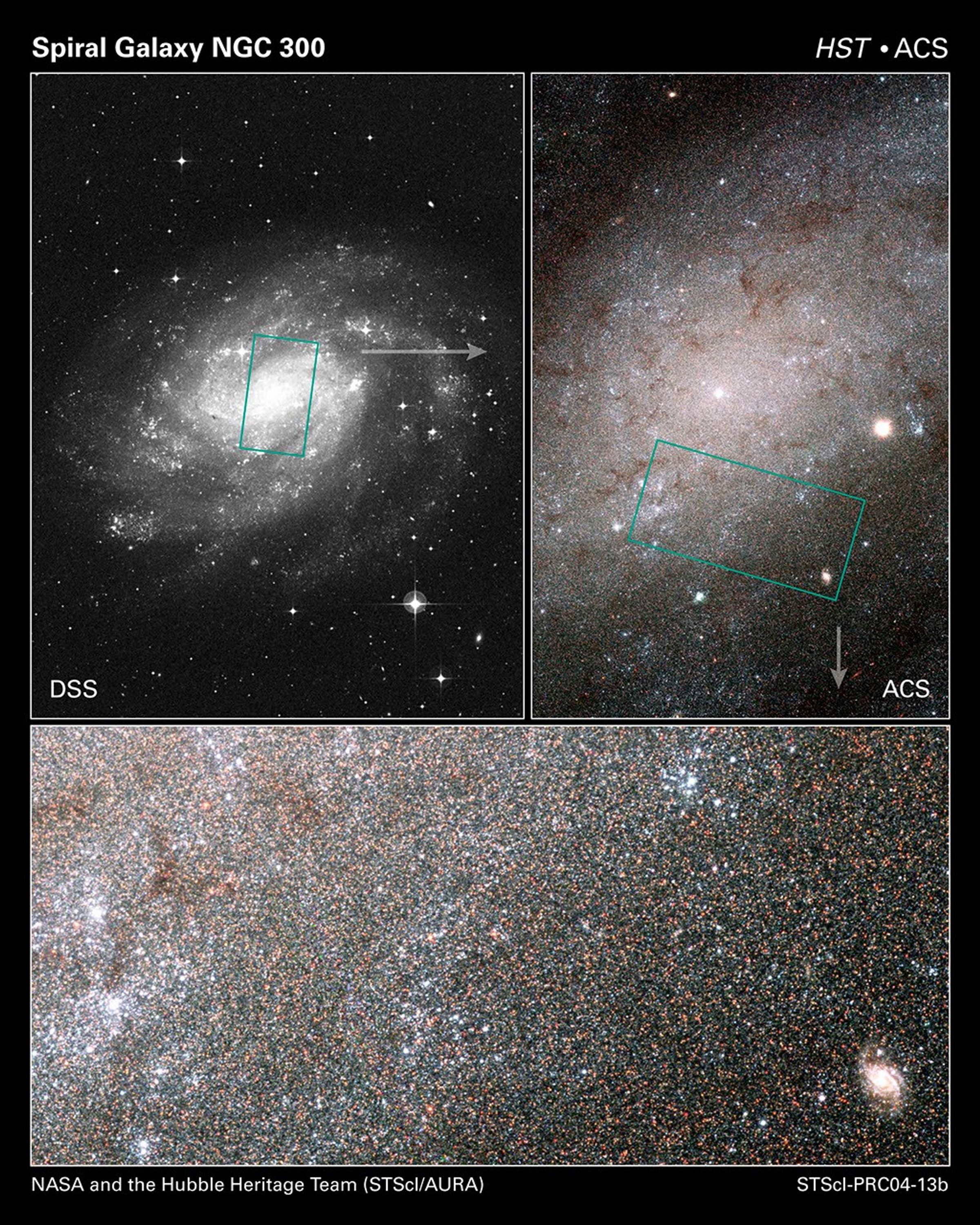

Hubble Sees Stars as Numerous as Grains of Sand in Nearby Galaxy
What appear as individual grains of sand on a beach in this image obtained with NASA's Hubble Space Telescope are actually myriads of stars embedded deep in the heart of the nearby galaxy NGC 300. The Hubble telescope's exquisite resolution enables it to see the stars as...

Myriad of Stars in Spiral Galaxy NGC 300 – Central Detail
Myriads of stars embedded in the heart of the nearby galaxy NGC 300 can be singled out like grains of sand on a beach in this Hubble Space Telescope image. The Hubble telescope's exquisite resolution enables it to see the stars as individual points of light, despite the fact...
Share
Details
Last Updated
Aug 17, 2025
Contact
Media
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov