1 min read
Eta Carinae Light Echo
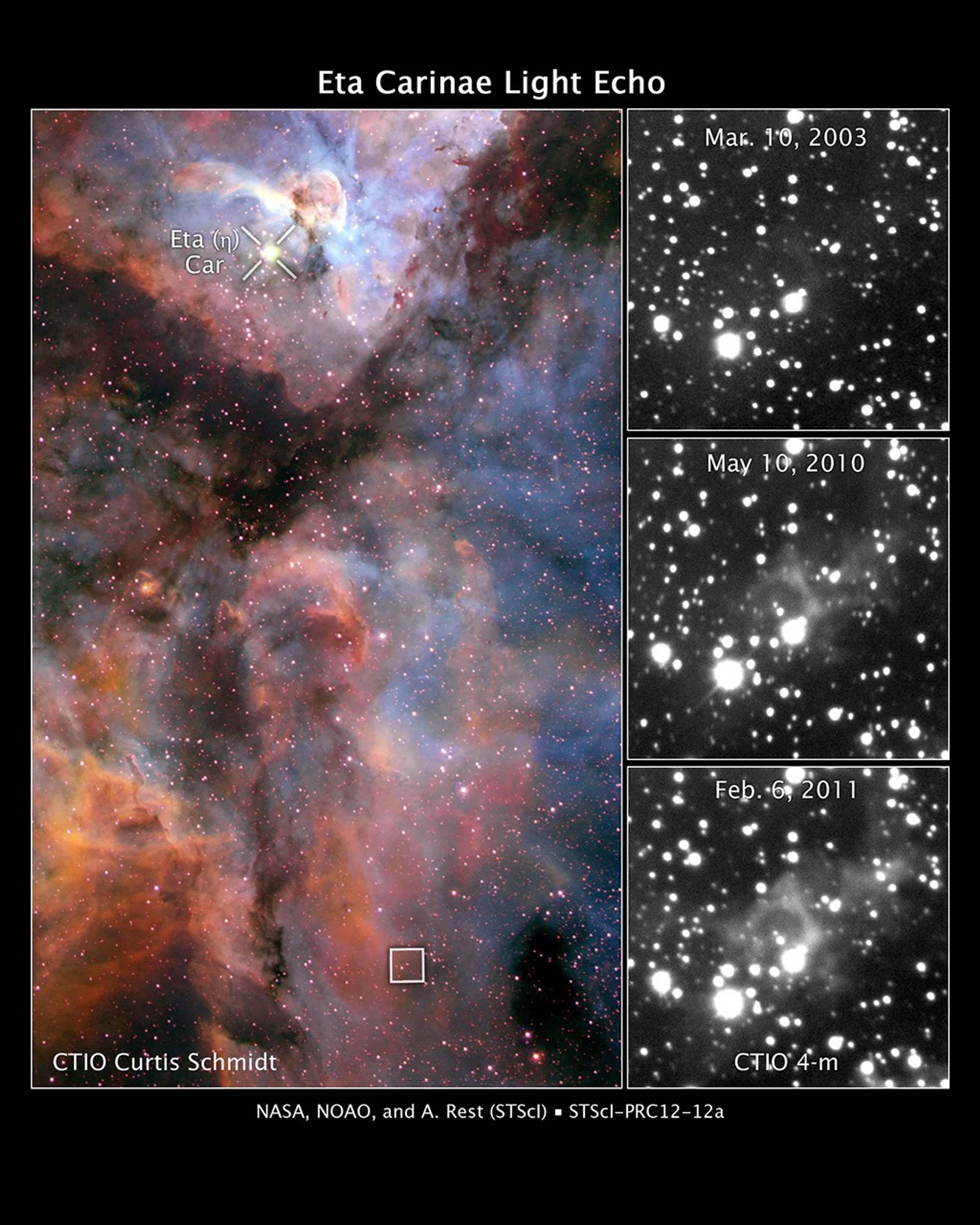
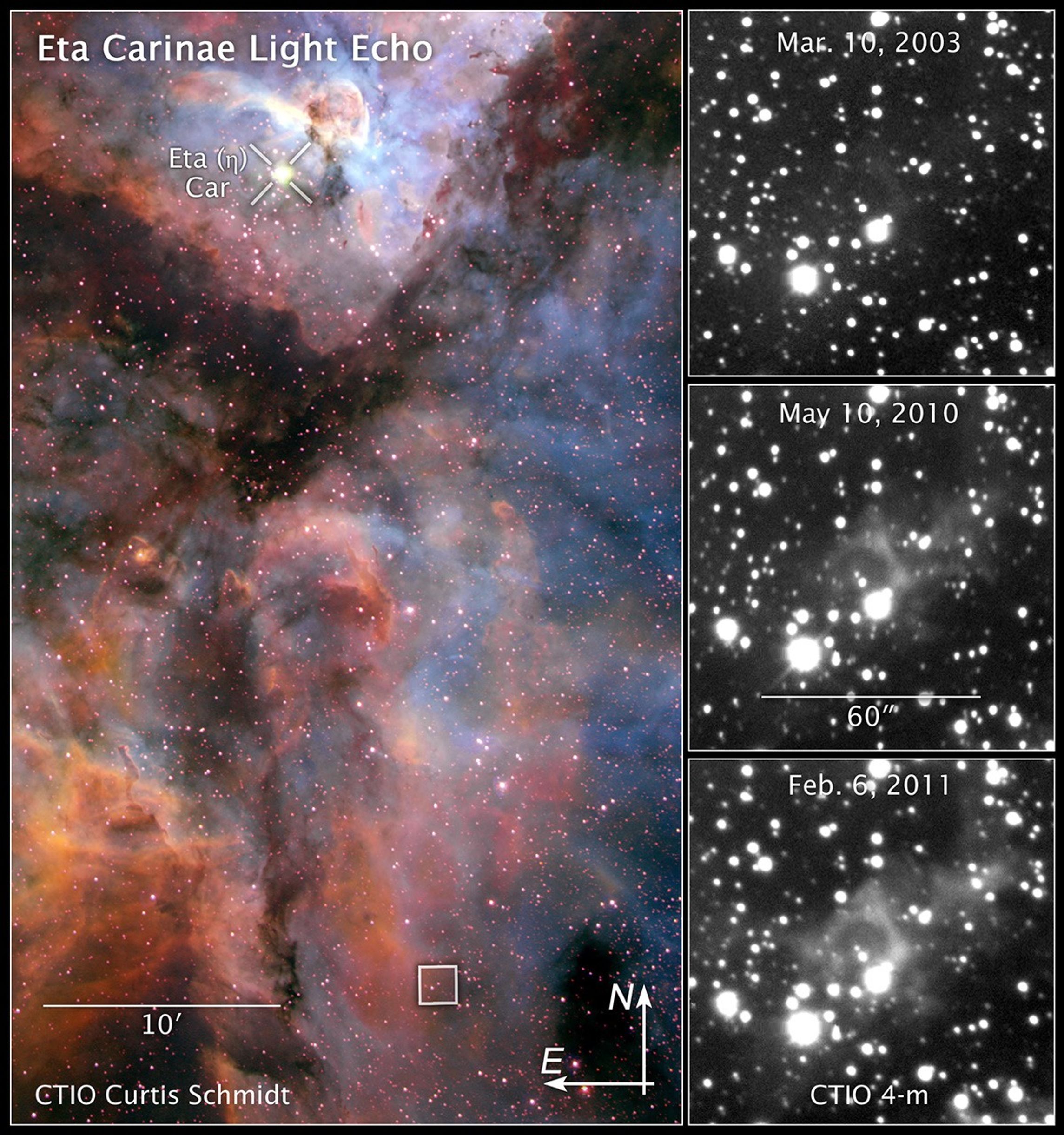
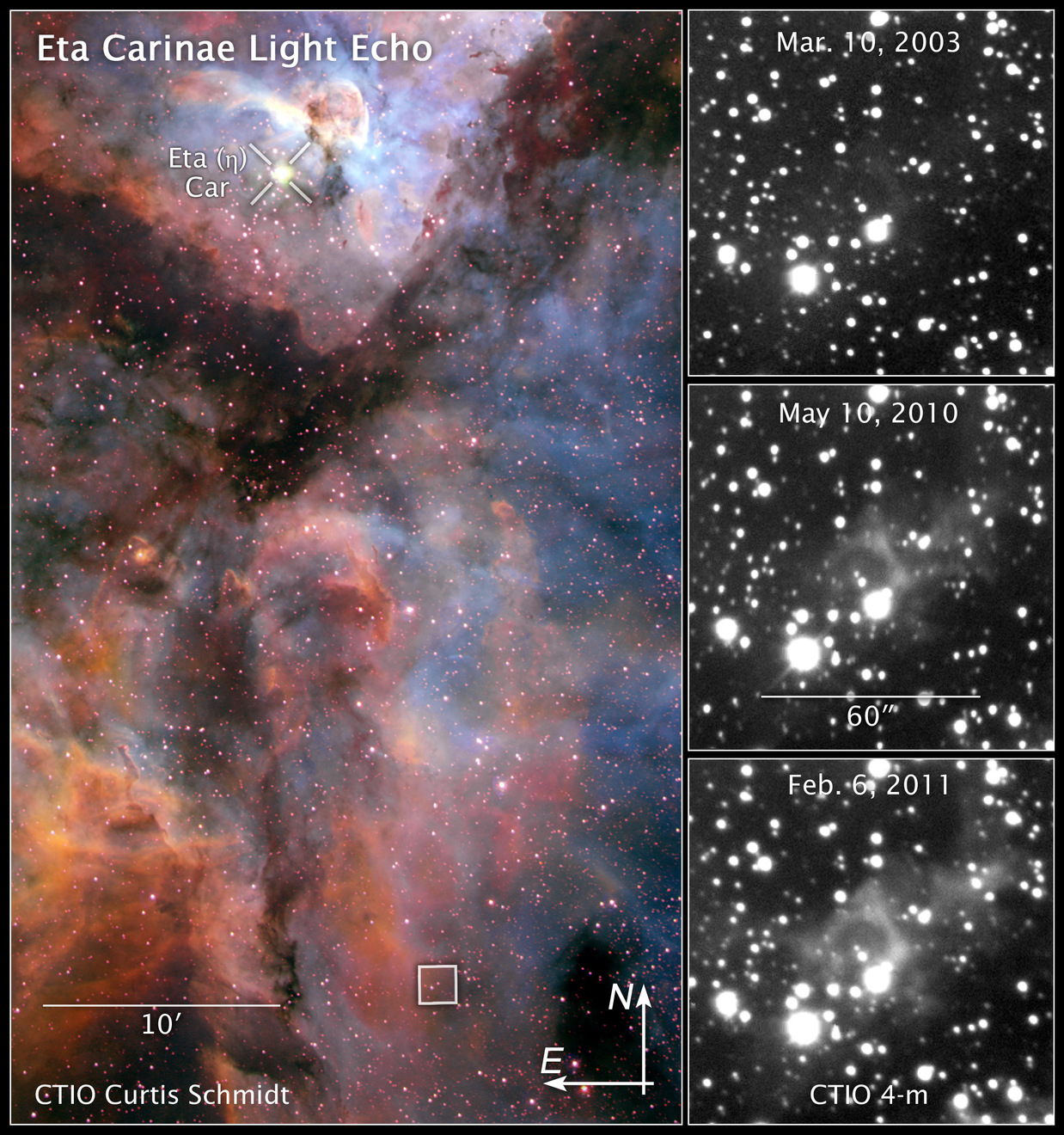
These images reveal light from a massive stellar outburst in the Carina Nebula reflecting off dust clouds surrounding a behemoth double-star system.
The color image at left shows the Carina Nebula, a star-forming region located 7,500 light-years from Earth. The massive double-star system Eta Carinae resides near the top of the image. The star system, about 120 times more massive than the Sun, produced a spectacular outburst that was seen on Earth from 1837 to 1858.
But some of the light from the eruption took an indirect path and is just now reaching our planet. The light bounced off dust clouds (the boxed region about 100 light-years away at the bottom of the image) and was rerouted to Earth, a phenomenon called a light echo. The image was taken in February 2000 by the U.S. National Optical Astronomy Observatory's Curtis Schmidt Telescope at the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO) in Chile.
The three black-and-white images at right show light from the eruption illuminating dust clouds near the doomed star system as it moves through them. The effect is like shining a flashlight on different regions of a vast cavern. The images were taken over an eight-year span by the U.S. National Optical Astronomy Observatory's Blanco 4-meter telescope at the CTIO.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.10h 44m 12s.127
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-60° 16' 01".69
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Carina
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.7,500 light-years (2,300 parsecs)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The science team studying the Eta Car light echo was led by A. Rest (STScI). The color image (left) of a portion of the Carina Nebula was taken with the CTIO Curtis Schmidt telescope on February 25, 2000. The filter and color assignments are as follows: oxygen (blue), hydrogen (green), and sulfur (red). The single-filter images of the light echo (below right) were taken in 2003, 2010, and 2011 with the CTIO 4-m Blanco telescope. - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.CTIO Curtis Schmidt telescope (color image), and CTIO 4-m Blanco telescope (grayscale images)
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.February 25, 2000 (color image), and March 10, 2003, May 10, 2010 and February 6, 2011 (grayscale images)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Carina Nebula
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Carina Nebula and Light Echo Caused by the Massive/Variable Star Eta Car
- Release DateFebruary 15, 2012
- Science ReleaseAstronomers Watch Delayed Broadcast of a Powerful Stellar Eruption
- CreditNASA, NOAO, and A. Rest (Space Telescope Science Institute, Baltimore, Md.); Acknowledgment: NOAO, AURA, NSF, and N. Smith (University of Arizona)

Blue: oxygen Green: hydrogen Red: sulfur

Related Images & Videos

Eta Carinae Light Echo Region - March 10, 2003
The double-star system Eta Carinae, about 120 times more massive than the Sun, produced a spectacular outburst that was seen on Earth from 1837 to 1858. This image shows an area near Eta Carinae that is not illuminated by the double-star system's outburst. The image was taken in...

Eta Carinae Light Echo Brightening - May 10, 2010
The double-star system Eta Carinae, about 120 times more massive than the Sun, produced a spectacular outburst that was seen on Earth from 1837 to 1858. This image shows the light from Eta Carinae's outburst illuminating the dust clouds near the doomed star system as it moves...

Eta Carinae Light Echo Brightening - February 6, 2011
The double-star system Eta Carinae, about 120 times more massive than the Sun, produced a spectacular outburst that was seen on Earth from 1837 to 1858. This image shows the light from Eta Carinae's outburst illuminating the dust clouds near the doomed star system as it moves...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov






























