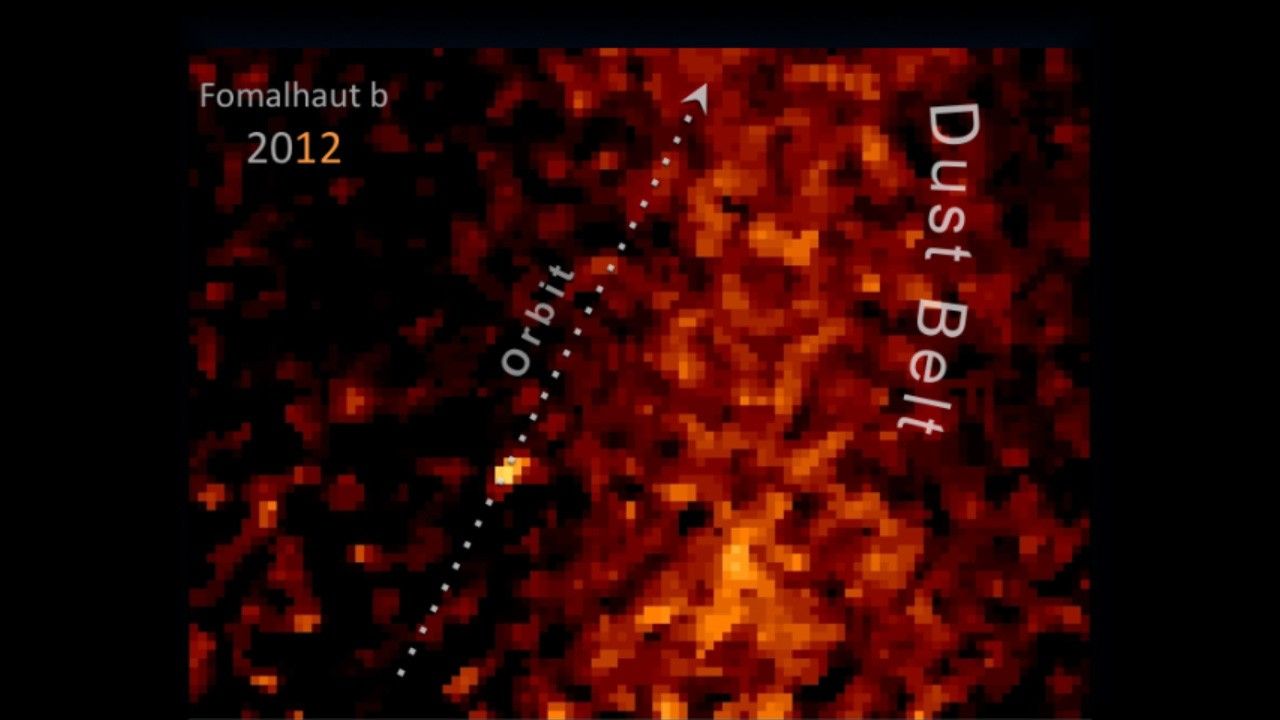
1 min read
Fomalhaut System

About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.22h 57m 39.04s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-29° 37' 20.04"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Piscis Austrinus
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.25 light-years (8 parsecs)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created from HST data from proposals 10390, 10598, 11818, and 12576; PI: P. Kalas (University of California, Berkeley). The science team includes: P. Kalas (University of California, Berkeley and SETI Institute, Mountain View, Calif.), J. Graham (University of California, Berkeley and University of Toronto), M. Fitzgerald (UCLA), and M. Clampin (NASA/GSFC). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>STIS/CCD
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.May 2012
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Fomalhaut
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Exoplanet Orbiting Fomalhaut: This image is roughly 462 astronomical units (60 arcseconds) wide.
- Release DateJanuary 8, 2013
- Science ReleaseHubble Reveals Rogue Planetary Orbit for Fomalhaut b
- Credit

This image is a composite of many separate exposures made by the STIS instrument on the Hubble Space Telescope. This image was originally black and white and recorded only overall brightness. These brightness values were translated into a range of reddish hues. Such color "maps" can be useful in helping to distinguish subtly varying brightness in an image. Red: STIS/CCD
Related Images & Videos
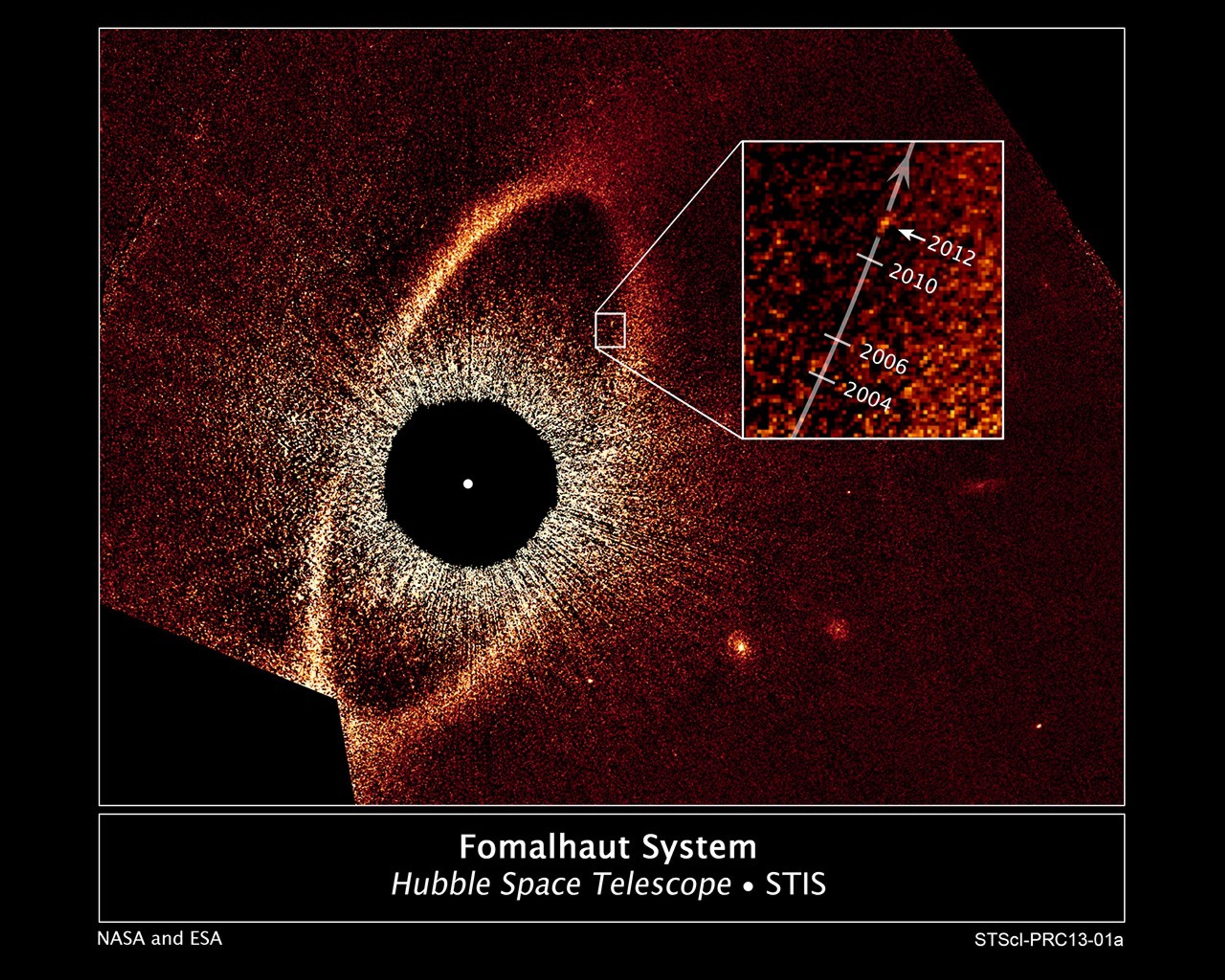
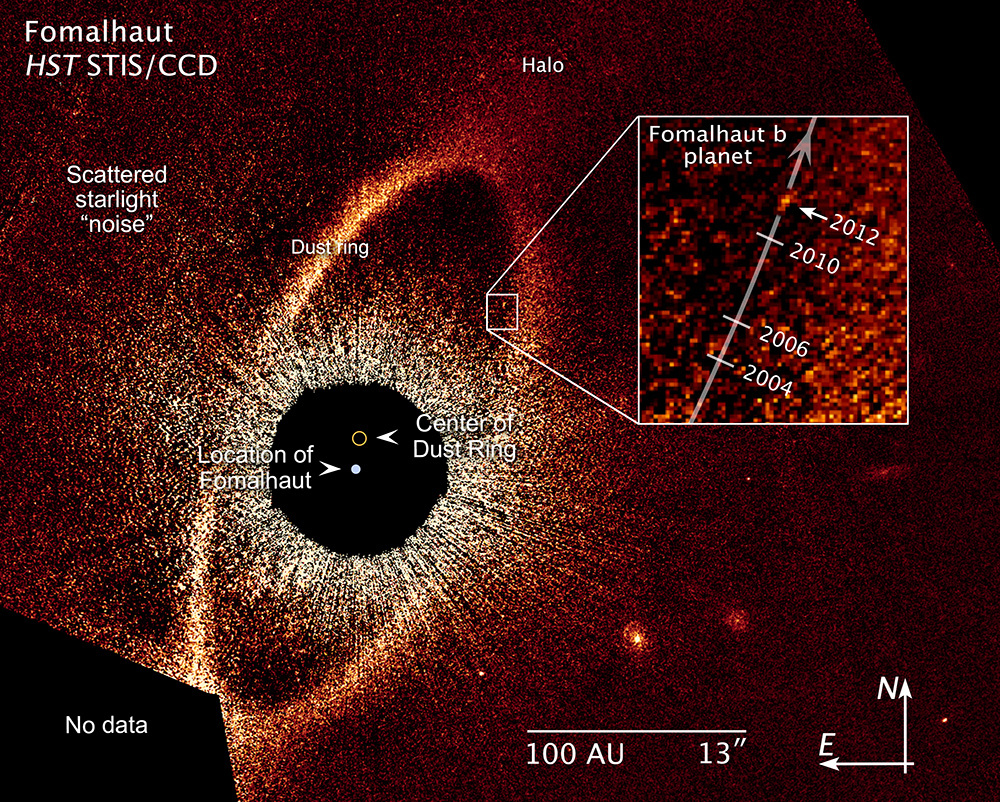
Rogue Planetary Orbit for Fomalhaut b
This false-color composite image, taken with the Hubble Space Telescope, reveals the orbital motion of the planet Fomalhaut b. Based on these observations, astronomers calculated that the planet is in a 2,000-year-long, highly elliptical orbit. The planet will appear to cross a...
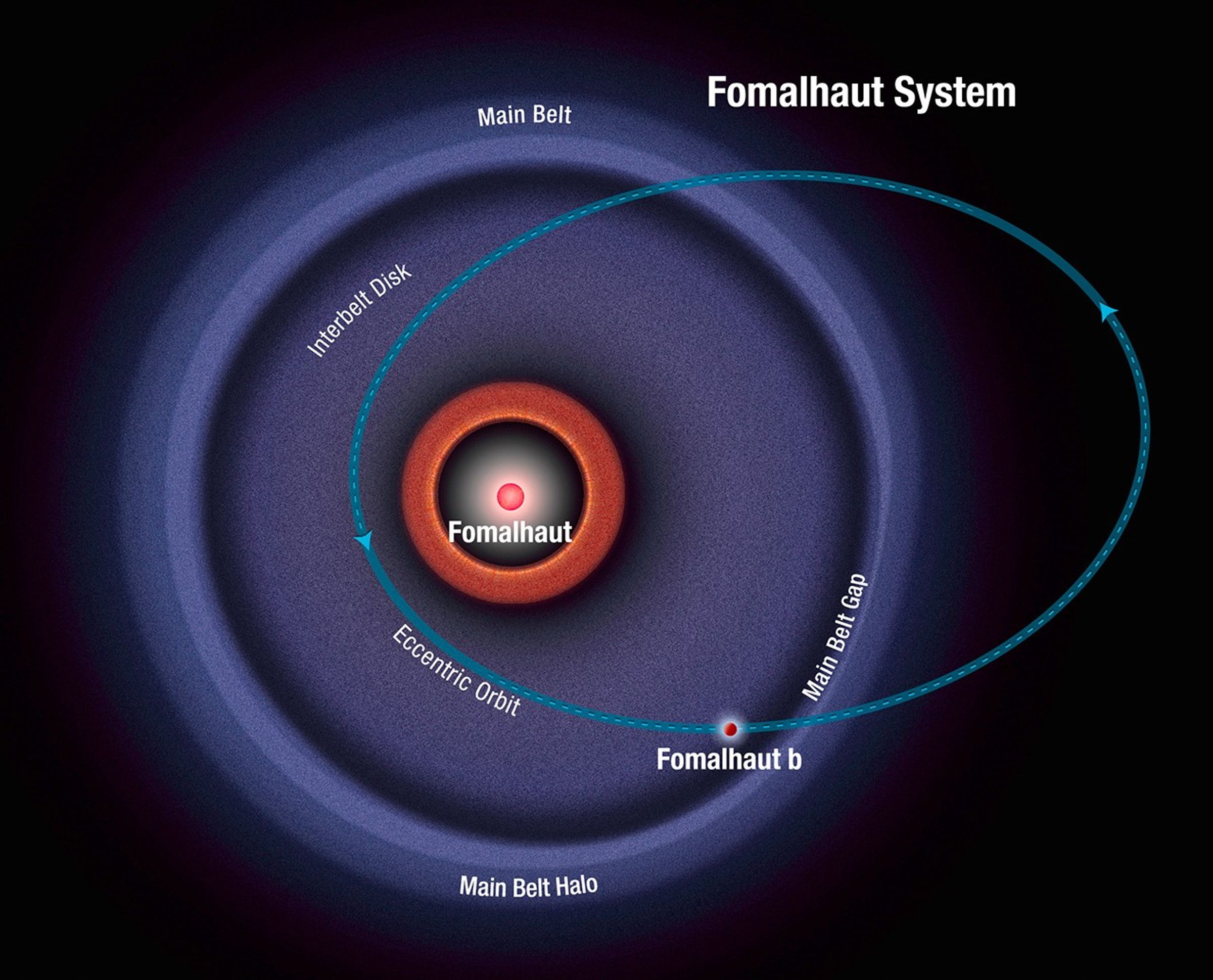
Schematic of Fomalhaut System
This diagram shows the orbit of the exoplanet Fomalhaut b as calculated from recent Hubble Space Telescope observations. The planet follows a highly elliptical orbit that carries it across a wide belt of debris encircling the bright star Fomalhaut. The planet swings as close to...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov