1 min read
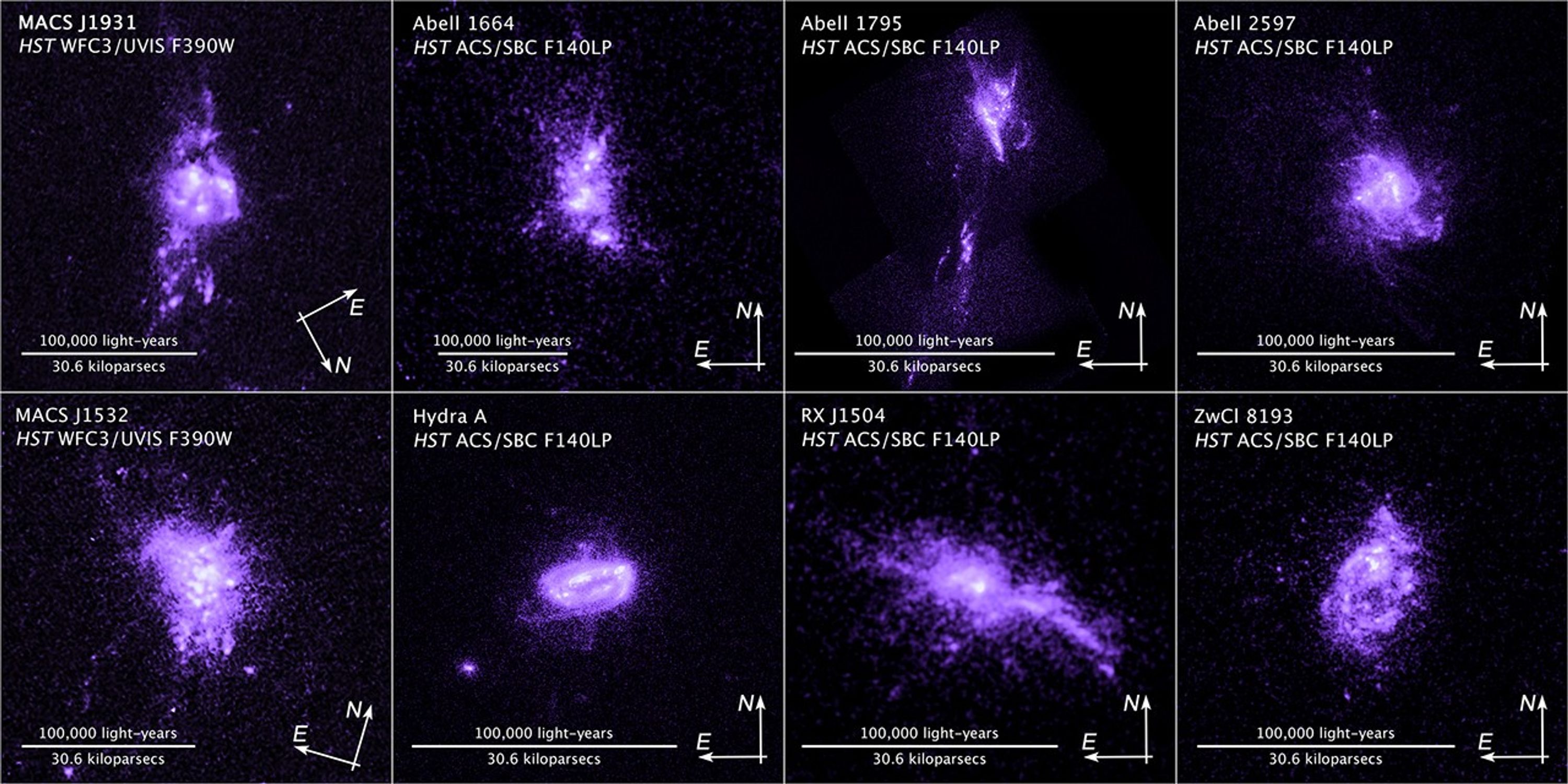
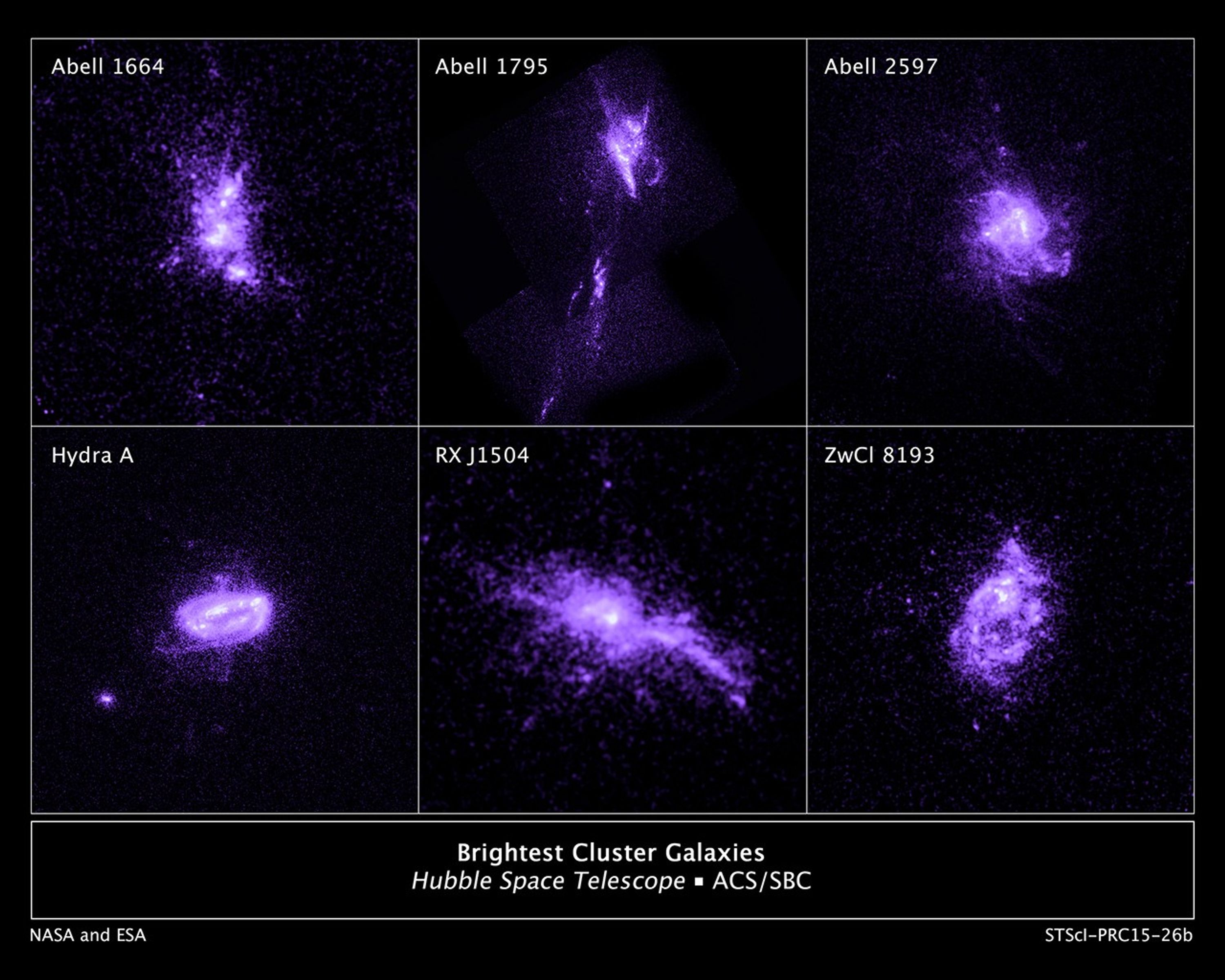
Galaxy Abell 1664

About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.13h 3m 41.79s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-24° 13' 6.0"
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.Redshift: 0.1283
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.Data for galaxies taken with the ACS/SBC instrument were obtained from proposal: 12220, PI: R. Mittal (Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics) et al. The ACS/SBC BCG science team comprises: G. Tremblay (Yale University/ESO), C. O’Dea and S. Baum (University of Manitoba/RIT), R. Mittal (RIT/Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics), M. McDonald (Kavli Institute/MIT), F. Combes (Observatoire de Paris/CNRS), Y. Li (University of Michigan, Ann Arbor), B. McNamara (Waterloo University, Ontario/Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics), M. Bremer (University of Bristol, UK), T. Clarke (Naval Research Laboratory), M. Donahue (Michigan State University), A. Edge (Durham University), A. Fabian (Institute of Astronomy), S. Hamer (Observatoire de Paris/CNRS), M. Hogan (Waterloo University, Ontario), J. Oonk (Netherlands Institute for Radio Astronomy), A. Quillen (University of Rochester), J. Sanders (Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics), P. Salomé (Observatoire de Paris/CNRS), and M. Voit (Michigan State University). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS/SBC
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Abell 1664
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Brightest Cluster Galaxies (BCG)
- Release DateAugust 6, 2015
- Science ReleaseNASA’s Hubble Finds Evidence of Galaxy Star Birth Regulated by Black-Hole Fountain
- Credit

Compass and Scale
Compass and ScaleAn astronomical image with a scale that shows how large an object is on the sky, a compass that shows how the object is oriented on the sky, and the filters with which the image was made.
Related Images & Videos

CLASH Survey Brightest Cluster Galaxies and Simulations
In this comparison of actual observations with simulations, the top images show Hubble observations of the density of gas in the central portion of two galaxies. The bottom images are computer simulations that are remarkably similar to the Hubble observations. Knots of star...

Star Formation Triggered by Black-Hole Jets (Artist's Concept)
This artist's rendering shows a central black hole interacting with gas in the galaxy's halo to create a self-regulating cycle. In this cycle, jets shooting out of the galaxy's center heat a halo of surrounding gas, controlling the rate at which the gas cools and falls into the...
Share
Details
Last Updated
Aug 17, 2025
Contact
Media
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov