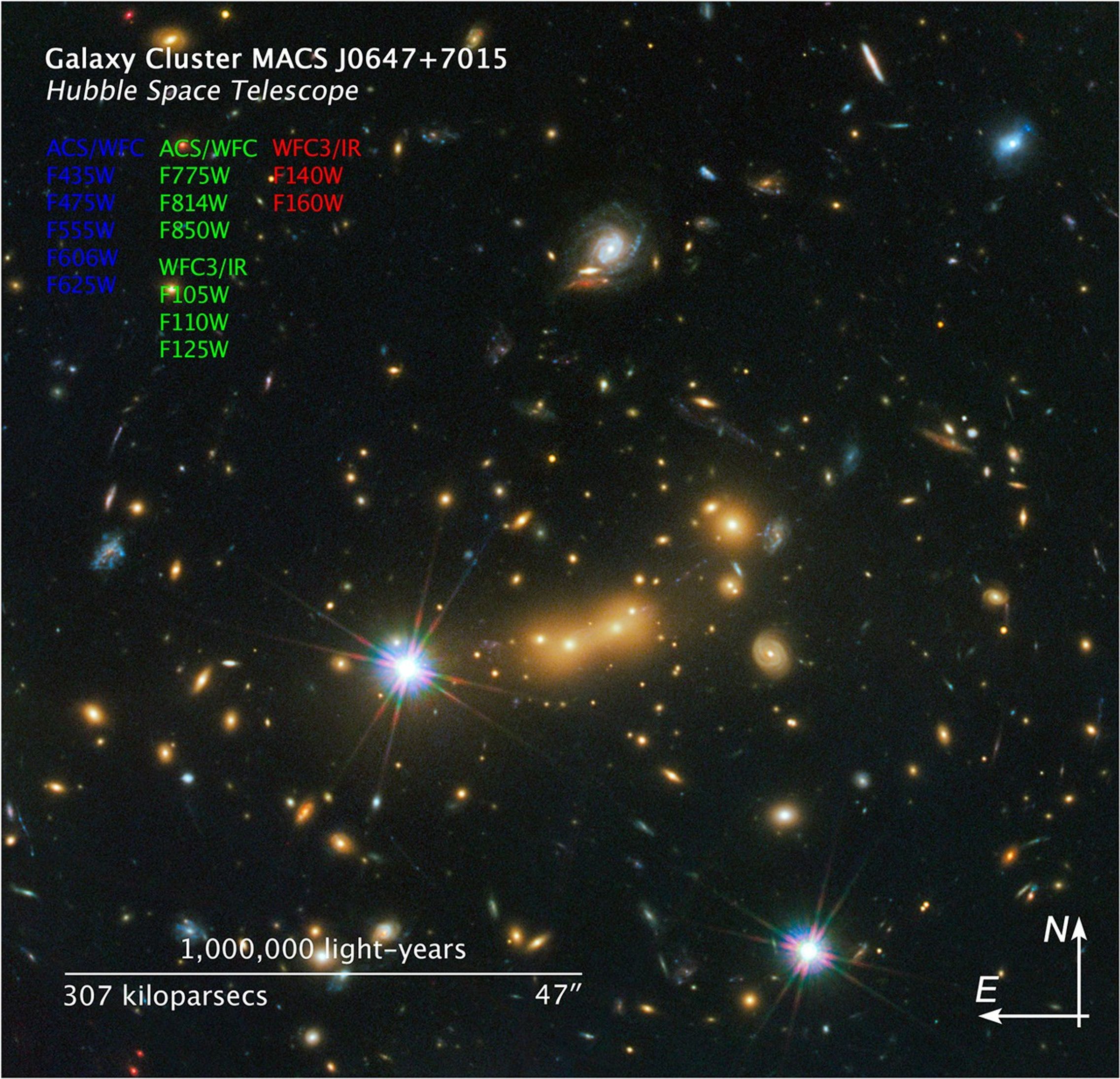
1 min read
Galaxy Cluster MACS J0647

About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.06h 47m 49.78s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.70° 14' 56.4"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Camelopardalis
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.5.6 billion light-years (1.7 billion parsecs or redshift z = 0.591)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator. - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS/WFC and HST>WFC3/IR
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.2004, 2005, 2007, and 2011, Exposure Time: 27.5 hours
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.ACS/WFC: F435W (B), F475W (g), F555W (V), F606W (V), F625W (r), F775W (I), F814W (I), and F850LP (z) WFC3/IR: F105W (Y), F110W (YJ), F125W (J), F140W (JH), and F160W (H)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.MACS J0647+7015
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Galaxy Cluster/Gravitational Lens
- Release DateNovember 15, 2012
- Science ReleaseNASA Great Observatories Find Candidate for Most Distant Galaxy Yet Known
- Credit

This image is a composite of separate exposures acquired by the ACS and WFC3 instruments. Several filters were used to sample various wavelengths. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: ACS/WFC F435W (B) + F475W (g) + F555W (V) + F606W (V) + F625W (r) Green: ACS/WFC F775W (I) + F814W (I) + F850LP (z), and WFC3/IR F105W (Y) + F110W (YJ) + F125W (J) Red: WFC3/IR F140W (JH) + F160W (H)

Related Images & Videos

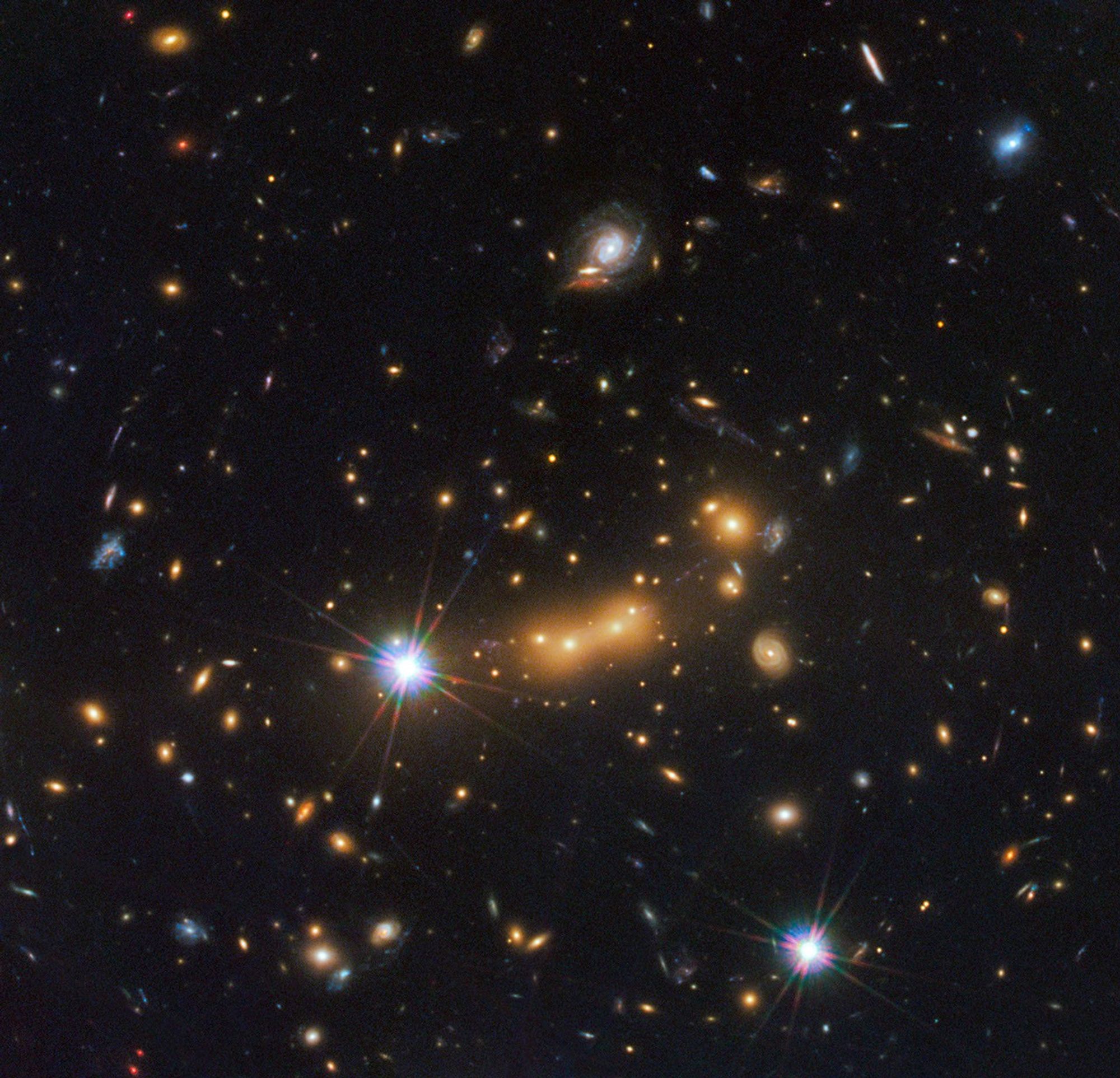
Distant Galaxy Lensed by Cluster MACS J0647
In this image, astronomers use NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and a cosmic zoom lens to uncover the farthest known galaxy in the universe. The newly discovered galaxy, named MACS0647-JD, is very young and only a tiny fraction of the size of our Milky Way. The object is observed...
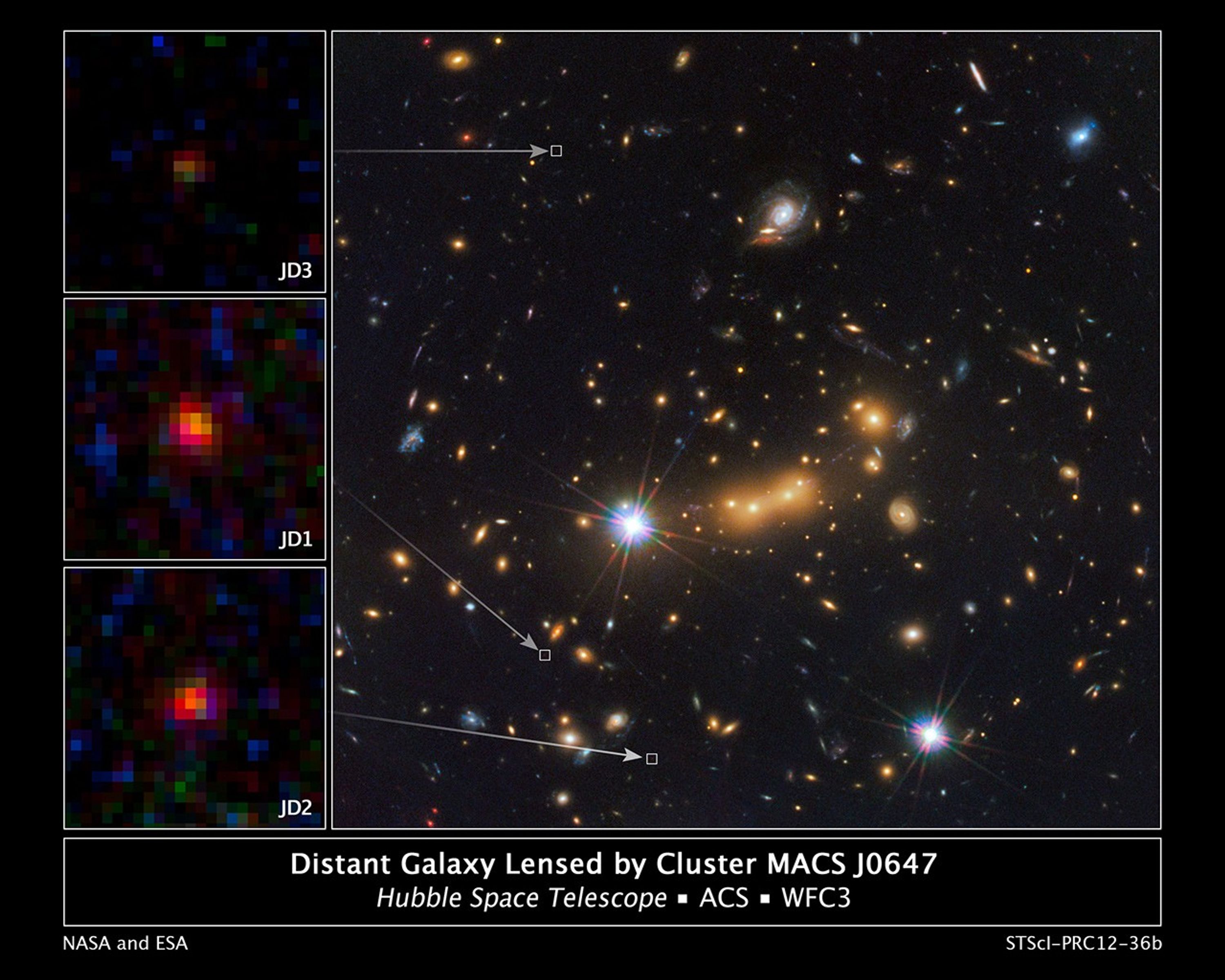
Cluster MACS J0647 Provides Three Magnified Views of Distant Galaxy
In this image, astronomers use NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and a cosmic zoom lens to uncover the farthest known galaxy in the universe. The newly discovered galaxy, named MACS0647-JD, is very young and only a tiny fraction of the size of our Milky Way. The object is observed...
MACS J0647 Zoom Sequence (Annotated)
This video zooms in on distant galaxy cluster MACS J0647+7015 (or MACS J0647 for short). Astronomers used this massive galaxy cluster as a giant cosmic telescope to uncover the farthest known galaxy in the universe to date, called MACS0647-JD. This is the latest discovery from a...

MACS0647-JD Zoom Sequence (Annotated)
This video zooms in on distant galaxy cluster MACS J0647+7015, or MACS J0647 for short. Astronomers used this massive galaxy cluster as a giant cosmic telescope to uncover the farthest known galaxy in the universe to date. The newly discovered galaxy, called MACS0647-JD, is very...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov