1 min read
Hubble Ultra Deep Field Image Reveals Galaxies Galore
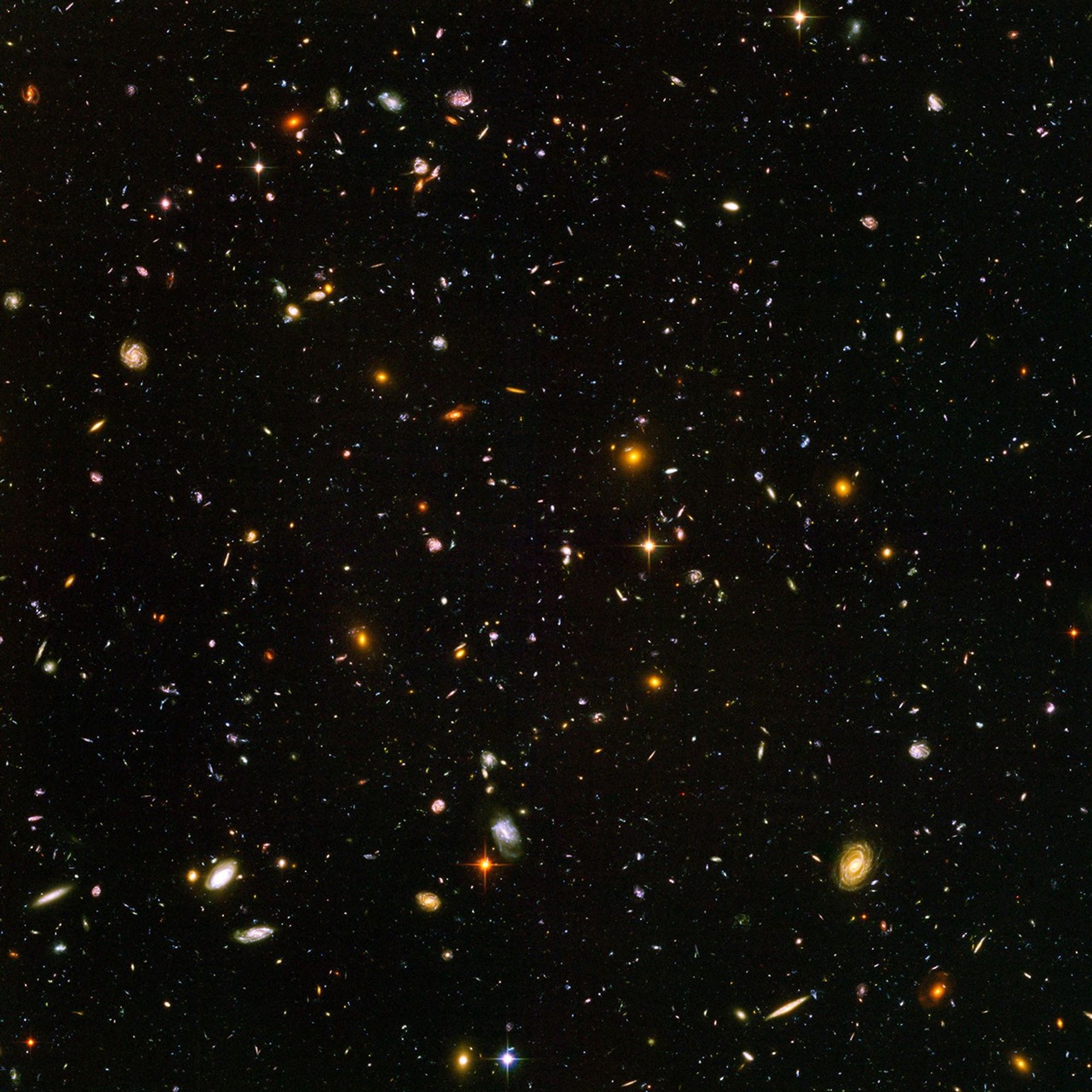

Galaxies, galaxies everywhere - as far as NASA's Hubble Space Telescope can see. This view of nearly 10,000 galaxies is the deepest visible-light image of the cosmos. Called the Hubble Ultra Deep Field, this galaxy-studded view represents a "deep" core sample of the universe, cutting across billions of light-years.
The snapshot includes galaxies of various ages, sizes, shapes, and colors. The smallest, reddest galaxies, about 100, may be among the most distant known, existing when the universe was just 800 million years old. The nearest galaxies - the larger, brighter, well-defined spirals and ellipticals - thrived about 1 billion years ago, when the cosmos was 13 billion years old.
In vibrant contrast to the rich harvest of classic spiral and elliptical galaxies, there is a zoo of oddball galaxies littering the field. Some look like toothpicks; others like links on a bracelet. A few appear to be interacting. These oddball galaxies chronicle a period when the universe was younger and more chaotic. Order and structure were just beginning to emerge.
The Ultra Deep Field observations, taken by the Advanced Camera for Surveys, represent a narrow, deep view of the cosmos. Peering into the Ultra Deep Field is like looking through an eight-foot-long soda straw.
In ground-based photographs, the patch of sky in which the galaxies reside (just one-tenth the diameter of the full Moon) is largely empty. Located in the constellation Fornax, the region is so empty that only a handful of stars within the Milky Way galaxy can be seen in the image.
In this image, blue and green correspond to colors that can be seen by the human eye, such as hot, young, blue stars and the glow of Sun-like stars in the disks of galaxies. Red represents near-infrared light, which is invisible to the human eye, such as the red glow of dust-enshrouded galaxies.
The image required 800 exposures taken over the course of 400 Hubble orbits around Earth. The total amount of exposure time was 11.3 days, taken between Sept. 24, 2003 and Jan. 16, 2004.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.03h 32m 39.99s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-27° 48' 0.0"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Fornax
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.The image is 3 arc minutes square
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created from HST data from the following proposal: 9978: S. Beckwith, S. Malhotra, M. Giavalisco, N. Panagia, J. Rhoads, M. Stiavelli, R. Somerville, S. Casertano, B. Margon, C. Blades, J. Caldwell, and M. Clampin (STScI), M. Corbin (CSC), M. Dickinson, H. Ferguson, and A. Fruchter (STScI), R. Hook (STScI/ECF), S. Jogee, A. Koekemoer, R. Lucas, M. Sosey and L. Bergeron (STScI). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS/WFC
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.September 24, 2003 - January 16, 2004, Exposure Time: 11.3 days
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F435W (B), F606W (V), F775W (i), F850LP (z)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Hubble Ultra Deep Field, HUDF
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Optical Survey
- Release DateMarch 9, 2004
- Science ReleaseHubble’s Deepest View Ever of the Universe Unveils Earliest Galaxies
- Credit

Blue: F435W (B) Green: F606W (V) + F775W (i) Red: F850LP (z)

Related Images & Videos

Hubble Ultra Deep Field Infrared View of Galaxies Billions of Light-Years Away
This infrared view reveals galaxies far, far away that existed long, long ago. Taken by the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-object Spectrometer aboard NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, the image is part of the Hubble Ultra Deep Field survey, the deepest portrait ever taken of the...
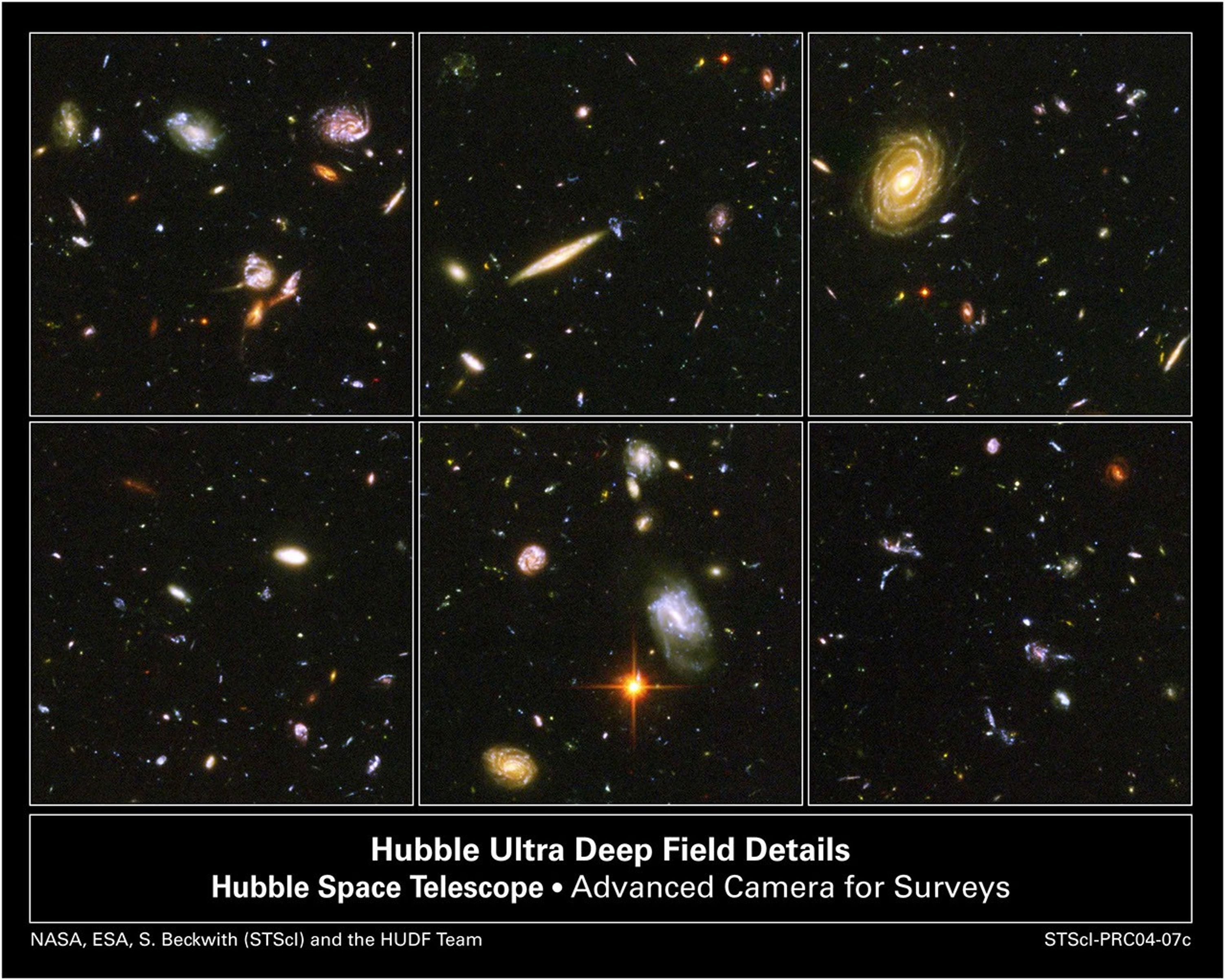

A Sampling of Galaxies From the Hubble Ultra Deep Field Image
A galactic brawl. A close encounter with a spiral galaxy. Blue wisps of galaxies. These close-up snapshots of galaxies in the Hubble Ultra Deep Field reveal the drama of galactic life. Almost every panel shows oddball-shaped galaxies engaged in boxing matches with galactic...
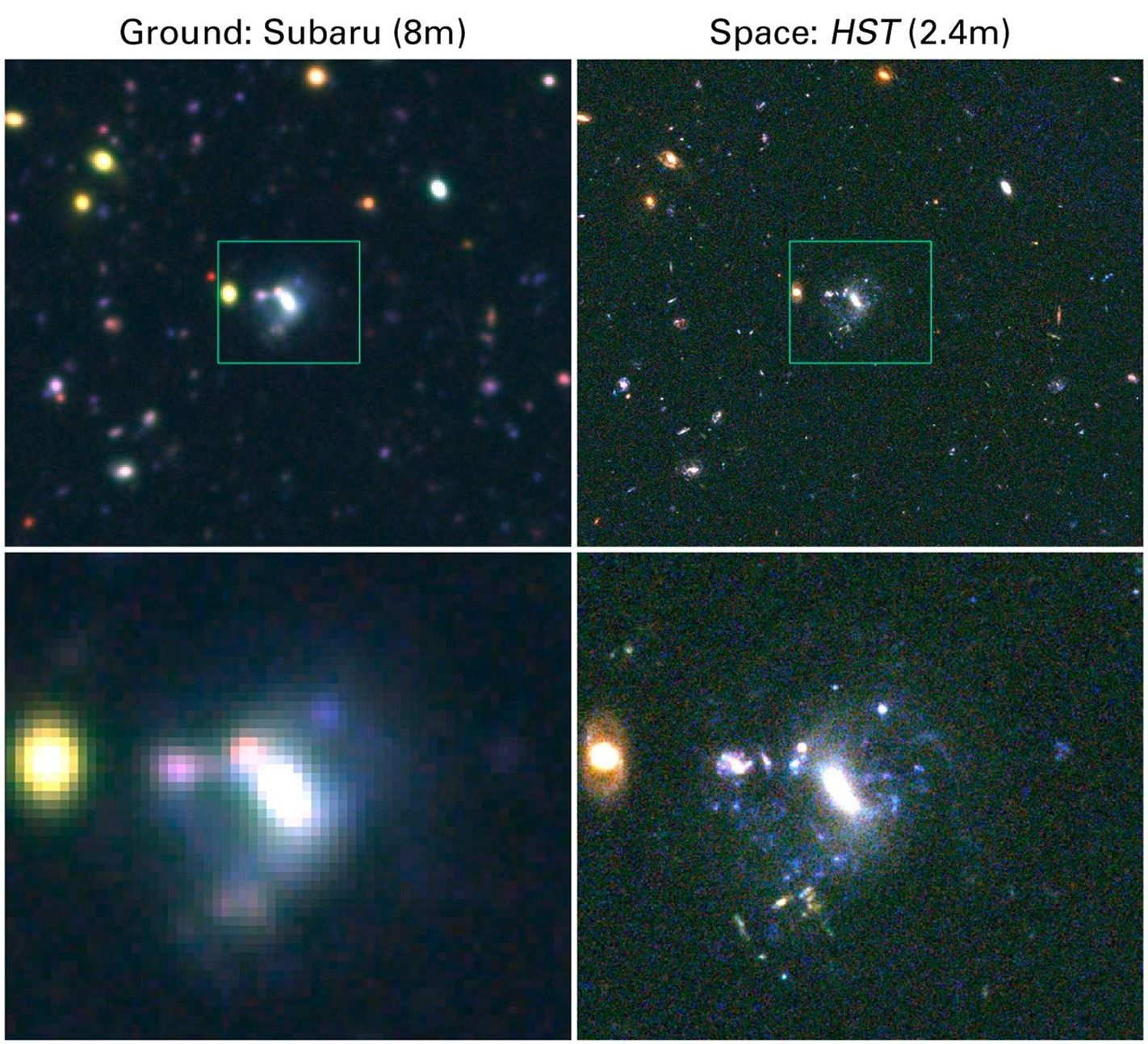
Comparison of Imaging from the Ground and Space
This picture shows a comparison of images of the same region of the sky obtained with the Hubble Space Telescope Advanced Camera for Surveys (right) and the Subaru 8 meter telescope's Supreme camera. The region is an area from the GOODS North field. Both images are color...

Zoom into Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys Ultra Deep Field – Version 1
The establishing shot starts with a very wide view of the sky centered on the Fornax constellation as seen by a photographic camera image taken by Akira Fujii. The image dissolves into the Digitized Sky Survey, through the Hubble GOODS South and ending on the HUDF.
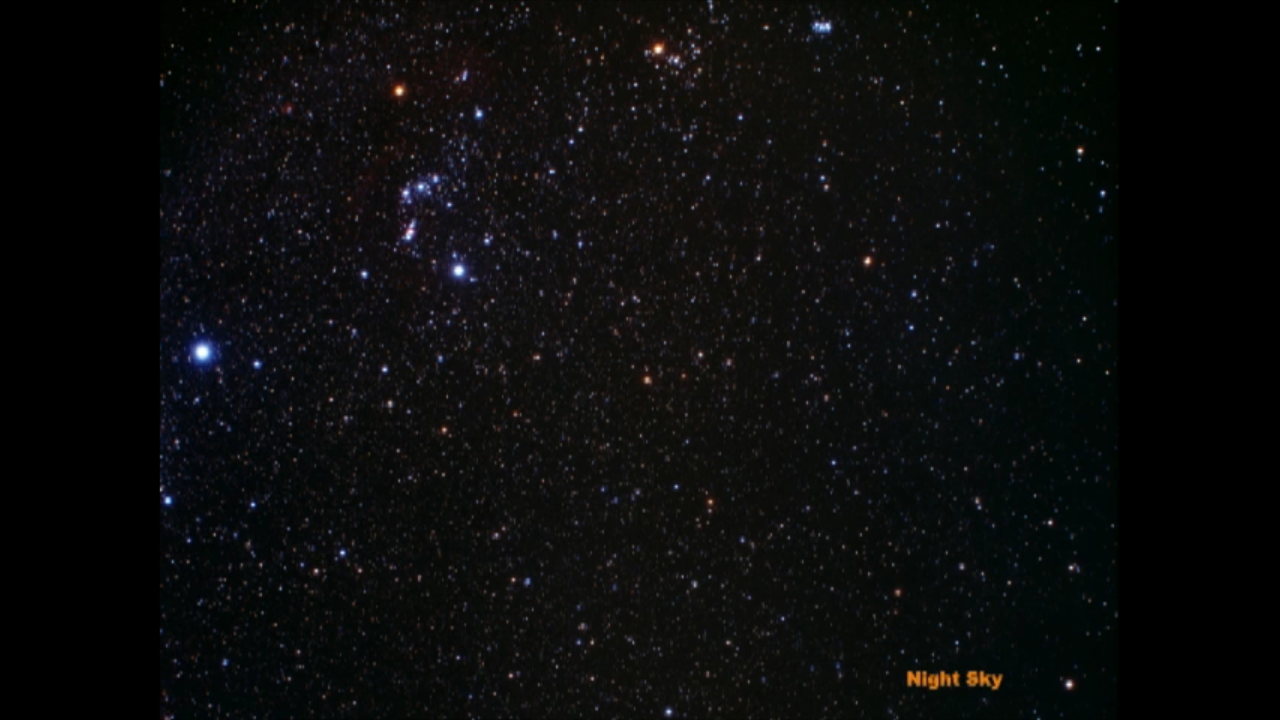

Zoom into Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys Ultra Deep Field – Version 2 (Annotated)
The establishing shot starts with a very wide view of the sky as seen by a small ground-based telescope centered on the Fornax constellation. The image dissolves into the Digitized Sky Survey, through the Hubble GOODS South and ending on the HUDF. Constellations and fields are...
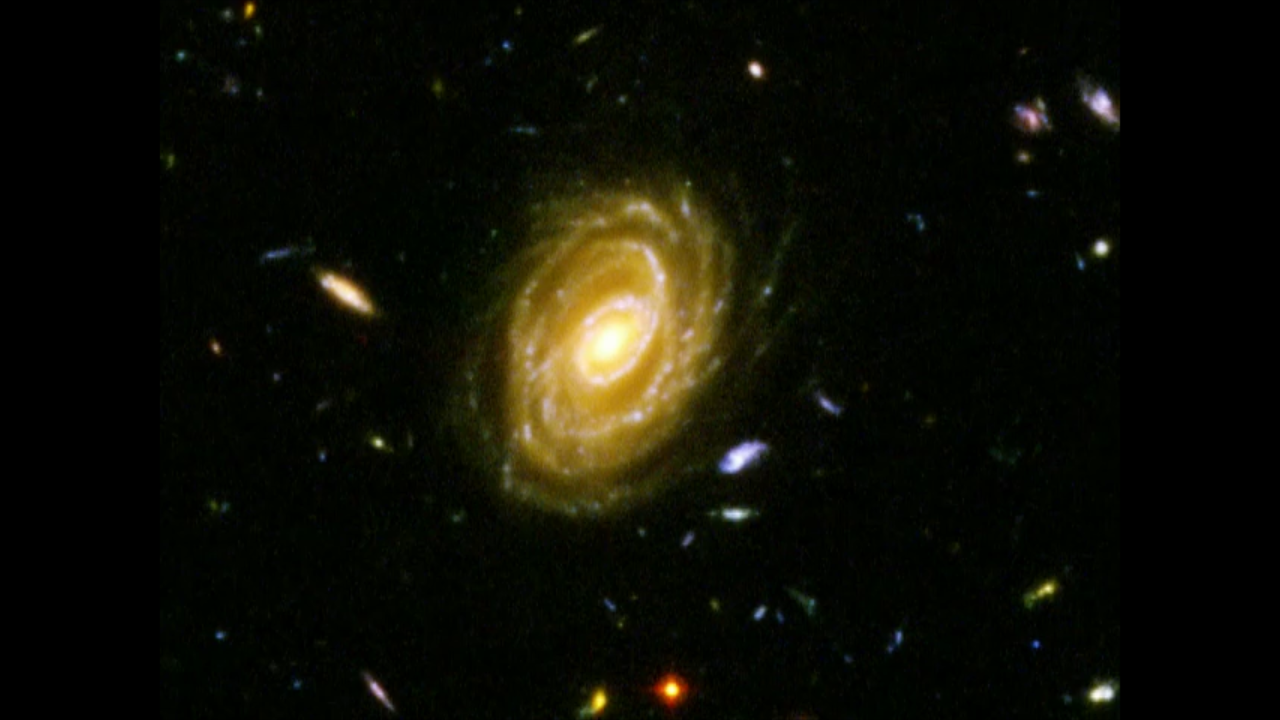

Pan across the Hubble's Advance Camera for Surveys Ultra Deep Field – Version 1
This pan across the Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys Ultra Deep Field shows the density of galaxies and morphology of very faint galaxies. This field of view is twice the size and higher in density than the original Hubble Deep Field. Beautiful galaxies are revealed as the...
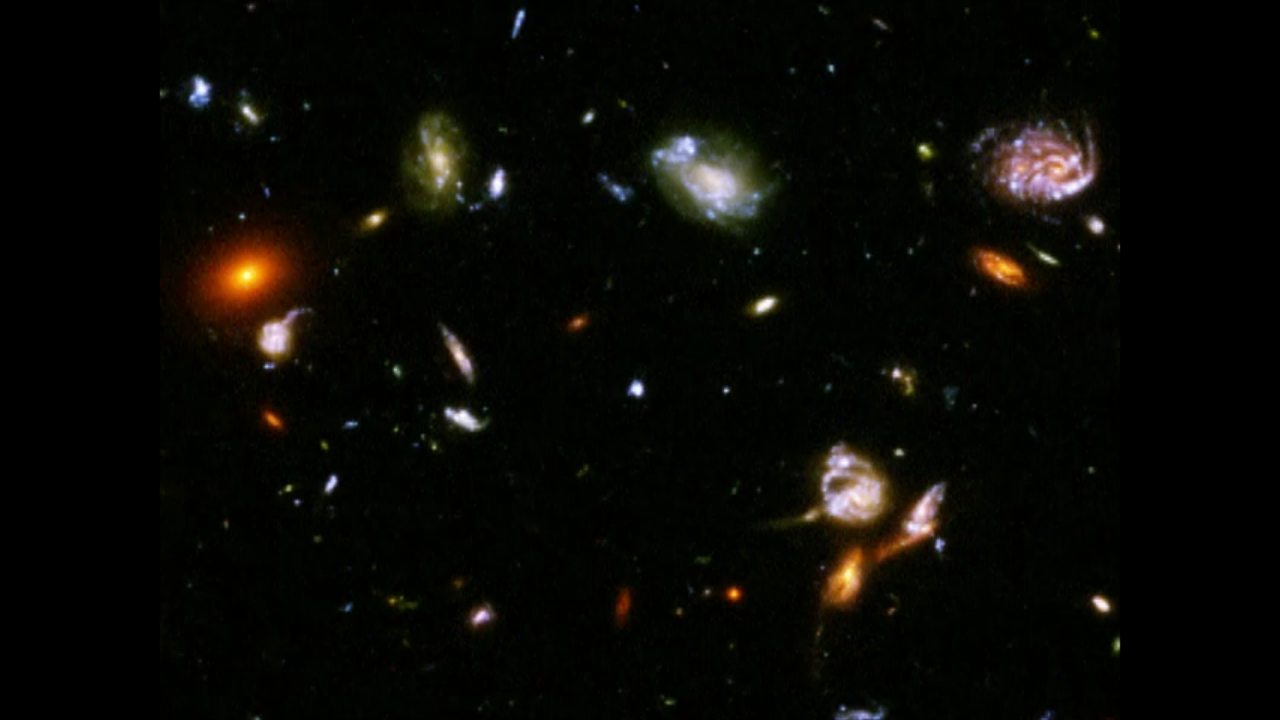

Pan across the Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys Ultra Deep Field – Version 2 (longer)
This pan across the Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys Ultra Deep Field shows the density of galaxies and morphology of very faint galaxies. This field of view is twice the size and higher in density than the original Hubble Deep Field. Beautiful galaxies are revealed as the...

Interview with Sangeeta Malhotra (STScI): Clip 1
Interview segment with Sangeeta Malhotra, Astronomer at the Space Telescope Science Institute. Clip references what the team expects to discover with the Hubble Advanced Camera for Surveys grism follow-up programs, their expectations from ground-based, follow-up programs, and...

Interview with Sangeeta Malhotra (STScI): Clip 2
Interview segment with Sangeeta Malhotra, Astronomer at the Space Telescope Science Institute. Clip references what the team expects to discover with the Hubble Advanced Camera for Surveys grism follow-up programs, their expectations from ground-based, follow-up programs, and...

Interview with Sangeeta Malhotra (STScI): Clip 3
Interview segment with Sangeeta Malhotra, Astronomer at the Space Telescope Science Institute. Clip references what the team expects to discover with the Hubble Advanced Camera for Surveys grism follow-up programs, their expectations from ground-based, follow-up programs, and...

Interview with Anton Koekemoer (STScI): Clip 1
Interview segment with Anton Koekemoer, Astronomer at the Space Telescope Science Institute. Clip references how the Hubble Ultra Deep Field survey compares to other surveys and how the team was able to estimate the redshift of the distant objects identified in these data.

Interview with Anton Koekemoer (STScI): Clip 2
Interview segment with Anton Koekemoer, Astronomer at the Space Telescope Science Institute. Clip references how the Hubble Ultra Deep Field survey compares to other surveys and how the team was able to estimate the redshift of the distant objects identified in these data.

Interview with Anton Koekemoer (STScI): Clip 3
Interview segment with Anton Koekemoer, Astronomer at the Space Telescope Science Institute. Clip references how the Hubble Ultra Deep Field survey compares to other surveys and how the team was able to estimate the redshift of the distant objects identified in these data.

Interview with Massimo Robberto (STScI): Clip 1
Interview segment with Massimo Robberto, Astronomer at the Space Telescope Science Institute. Clip references how the Hubble Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer data were combined. Comparison of this field to the other Hubble UDF fields and how all these data...

Interview with Massimo Robberto (STScI): Clip 2
Interview segment with Massimo Robberto, Astronomer at the Space Telescope Science Institute. Clip references how the Hubble Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer data were combined. Comparison of this field to the other Hubble UDF fields and how all these data...

Interview with Massimo Robberto (STScI): Clip 3
Interview segment with Massimo Robberto, Astronomer at the Space Telescope Science Institute. Clip references how the Hubble Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer data were combined. Comparison of this field to the other Hubble UDF fields and how all these data...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov














































