1 min read
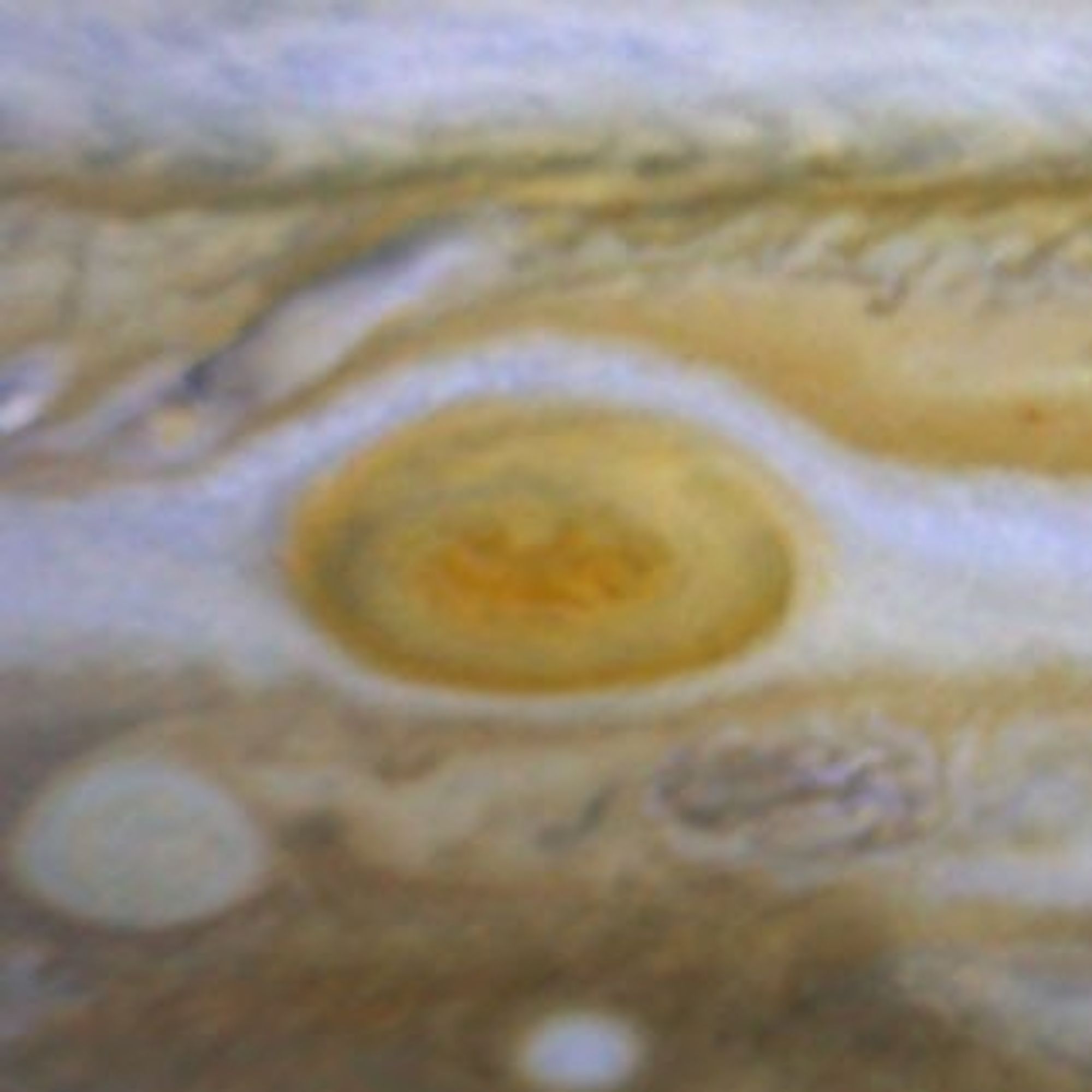
Jupiter WFPC2 February 1995

About the Object
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.5.2 Astronomical Units (778 million km or 483 million miles )
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.142,984 km or 88,789 miles (at equator). Diameter of Great Red Spot: 24,800 km or 15,400 miles (lengthwise). Visual Magnitude: -2.6 magnitude (at opposition)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.Principal Astronomers: A. Simon (Cornell U.), R. Beebe (NMSU), and collaborators, H. B. Hammel (Space Science Institute, MIT), R. Beebe (NMSU), J. T. Clarke (U. Michigan) , R. A. West (JPL), A. Storrs (STScI), and collaborators, H. Bond, C. Christian, J. English, L. Frattare, F. Hamilton, A. Kinney, Z. Levay, K. Noll (The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>WFPC2
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.February 1995
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F410M, F439 (B), F555W (V), F673N [SII], F718, F953N [SIII]
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Jupiter's Great Red Spot
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.High-pressure Cyclonic Storm on Jupiter
- Release DateAugust 5, 1999
- Science ReleaseHubble Views Ancient Storm in the Atmosphere of Jupiter
- Credit
Related Images & Videos

The Great Red Spot: An Ancient Storm in Jupiter's Atmosphere
When 17th-century astronomers first turned their telescopes to Jupiter, they noted a conspicuous reddish spot on the giant planet. This Great Red Spot is still present in Jupiter's atmosphere, more than 300 years later. It is now known that it is a vast storm, spinning like a...
Share
Details
Last Updated
Aug 17, 2025
Contact
Media
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov