1 min read
Martian Cloud Cover
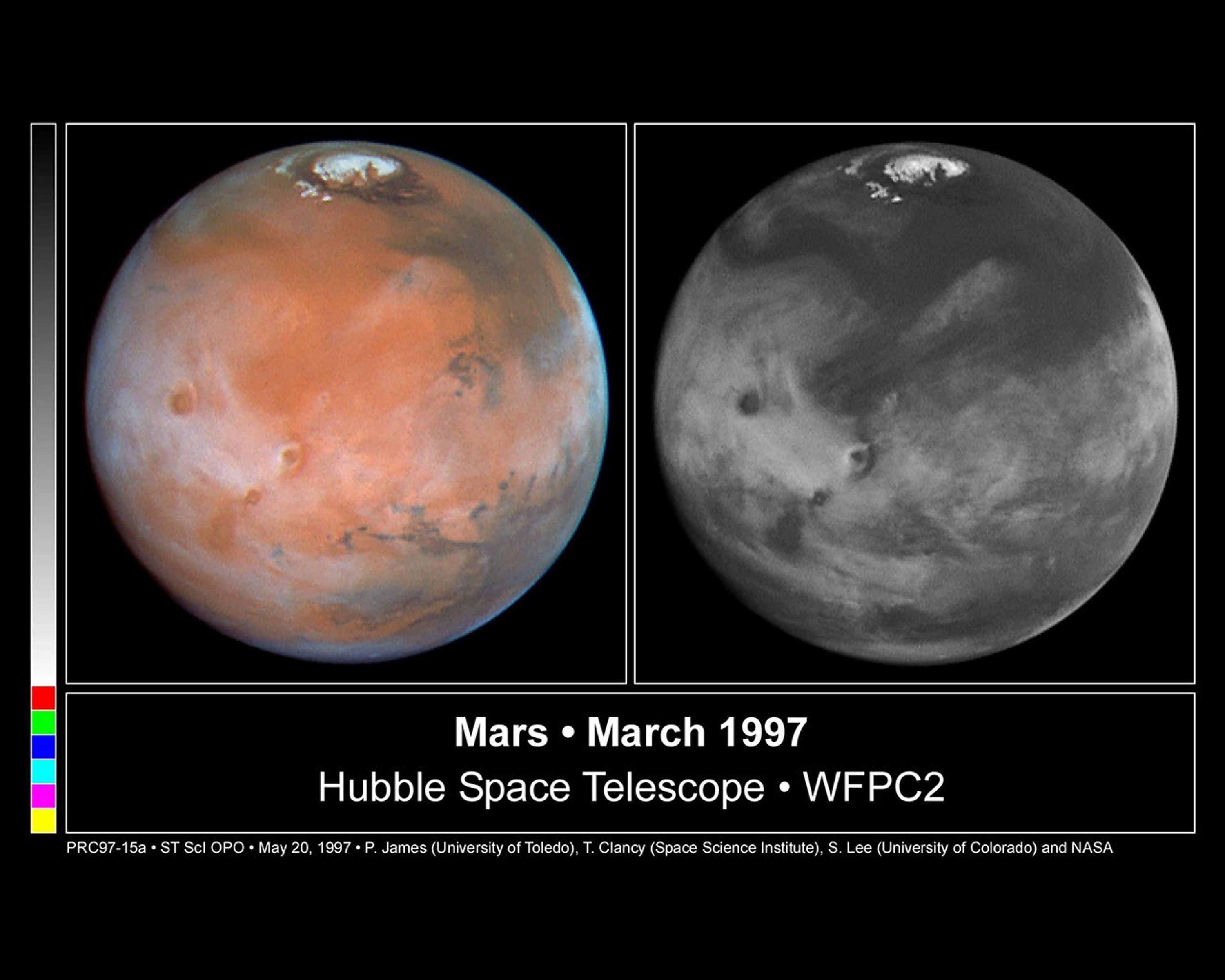
These color and black and white pictures of Mars were taken by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope just two weeks after Earth made its closest approach to the Red Planet during the 1997 opposition. When the Hubble pictures were taken Mars was at a distance of 62 million miles (100 million kilometers) and the resolution at the center of the disk is 13.5 miles/pixel (22 kilometers/pixel). Both images were made with the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2. The color composite (left image) is constructed from three images taken in red (673 nanometers), green (502 nm) and blue (410 nm) light. The right image, in blue light only, brings out details in the cloud structure and is remarkably similar to weather satellite pictures taken of Earth. A planetary-scale wave curls around the north pole, similar in behavior to high latitude cold fronts which descend over North America and Europe during springtime.
The picture was taken when Mars was near aphelion, its farthest point from the Sun. The faint sunlight results in cold atmospheric conditions which stimulate the formation of water ice clouds. The clouds themselves further reduce atmospheric temperatures. Atmospheric heating, resulting when sunlight is absorbed by the dust, is reduced when ice forms around the dust particles and causes the dust to gravitationally settle to the ground.
These images of Mars are centered at approximately 94 degrees longitude and 23 degrees N latitude (oriented with north up). The four largest Tharsis Montes (massive extinct volcanoes) are visible as dark spots extending through the clouds. The vast canyon system, Valles Marineris, stretches across the eastern (lower right) half of the image; the Pathfinder landing site is near the eastern edge of the image.
It is early summer in the northern hemisphere, and the North polar cap has retreated to about 80 degrees N latitude; the "residual" summer cap, which is composed of water ice, is about one-third the size of the "seasonal" winter cap, which consists mostly of carbon-dioxide frost (dry ice) condensed on the surface. The polar cap is surrounded by a "sand sea" made up of dark sand dunes. A distinct belt of water-ice clouds extends over much of this hemisphere.
About the Object
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.At the 1997 Mars opposition, the planet was approximately 62 million miles (100 million kilometers) from Earth.
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.The planet has a diameter of 4,222 miles (6,794 km) at the equator.
About the Data
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>WFPC2
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.March 1997
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.410 nm, 502 nm, and 673 nm
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Mars
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Planet
- Release DateMay 20, 1997
- Science ReleaseHubble Finds Cloudy, Cold Weather Conditions for Mars-Bound Spacecraft
- CreditPhil James (Univ. Toledo), Todd Clancy (Space Science Inst., Boulder, CO), Steve Lee (Univ. Colorado), and NASA

Color image Blue: 410 n nanometers Green: 502 nanometers Red: 673 nanometers Grayscale image Blue: 410 n nanometers
Related Images & Videos
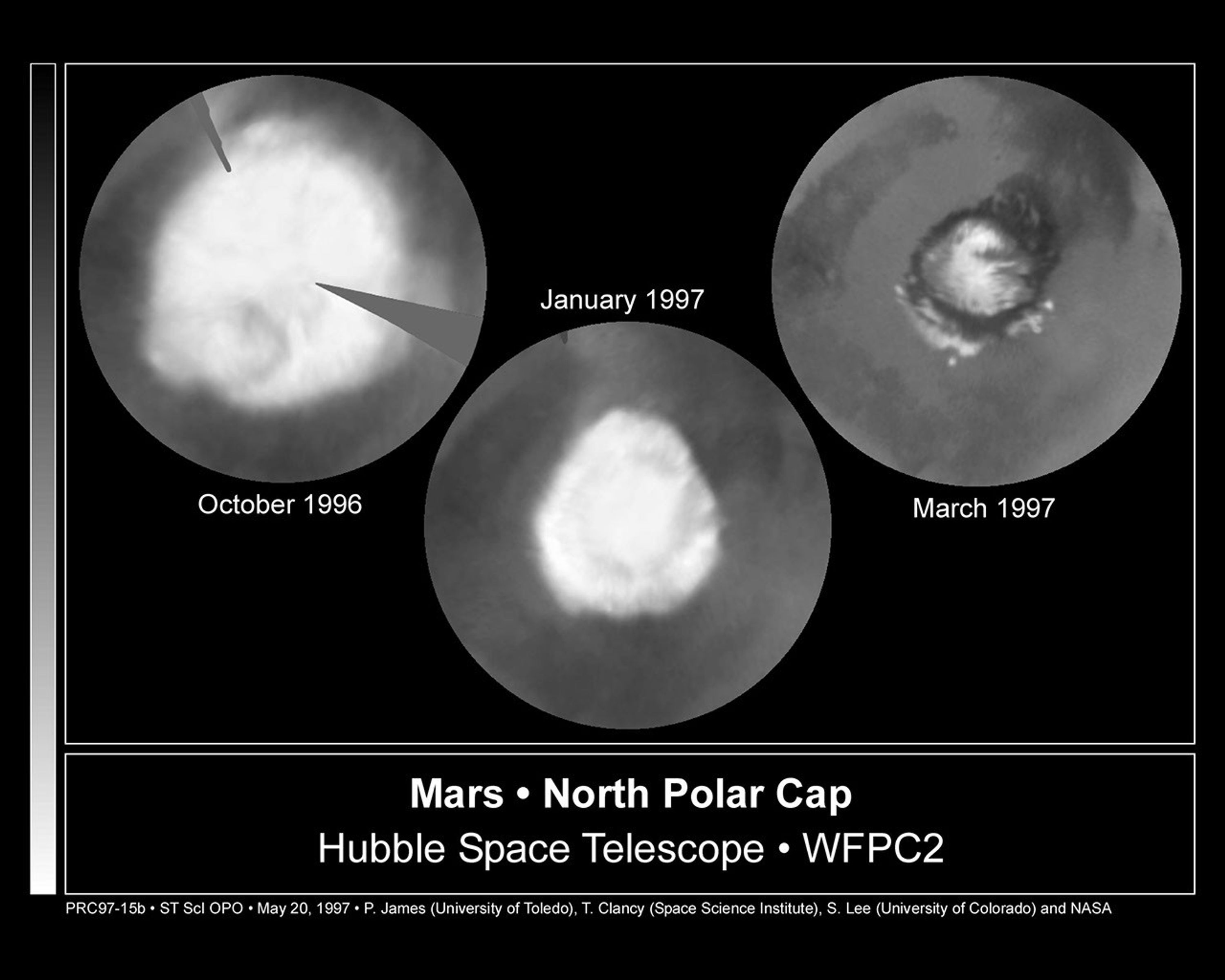
Seasonal Changes in Mars' North Polar Ice Cap
These images, which seem to have been taken while NASA's Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was looking directly down on the Martian North Pole, were actually created by assembling mosaics of three sets of images taken by HST in October, 1996 and in January and March, 1997 and...

Four View of Mars In Northern Summer
Four faces of Mars as seen on March 30, 1997 are presented in this montage of NASA Hubble Space Telescope images. Proceeding in the order upper-left, upper-right, lower-left, lower-right, Mars has rotated about ninety degrees between each successive time step. For example the...

Seasonal Changes in the Martian North Polar Ice Cap
These views from above the Martian pole were assembled from mosaics of three sets of images and projected to appear as if from above. This series captures the seasonal retreat of the polar cap from its greatest extent of the year (October, 1996) at 60 degrees N latitude through...

Hubble and Viking Views of the Pathfinder Landing Site, July 4, 1997
Pathfinder is landing on the Ares Valles, shown at the center of a Hubble Space Telescope full-color disk of Mars. The next map is a closeup of the Hubble image, and finally the Viking image shows the terrain near the Mars Pathfinder landing site, marked by an oval.
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov
































