1 min read
NGC 2174

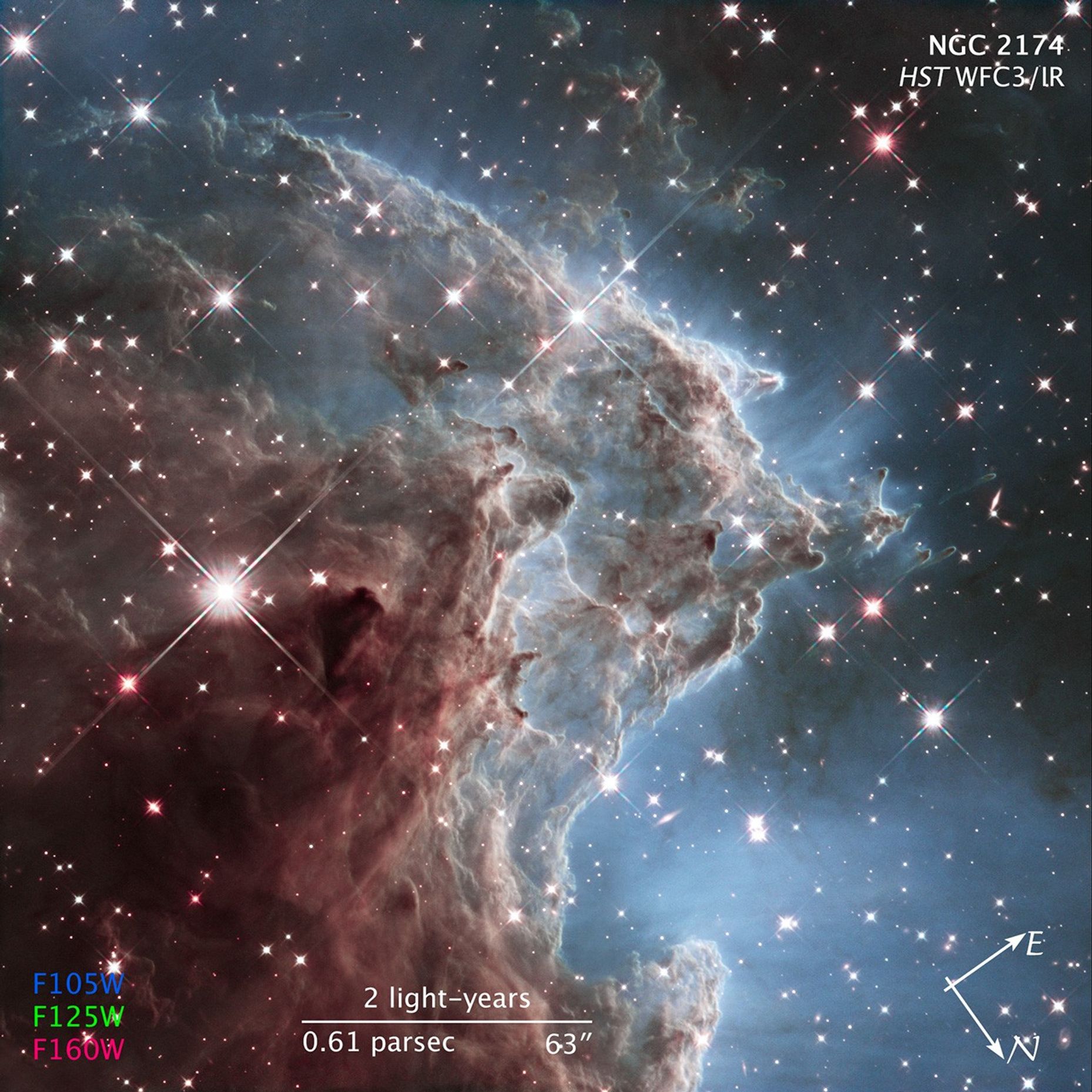
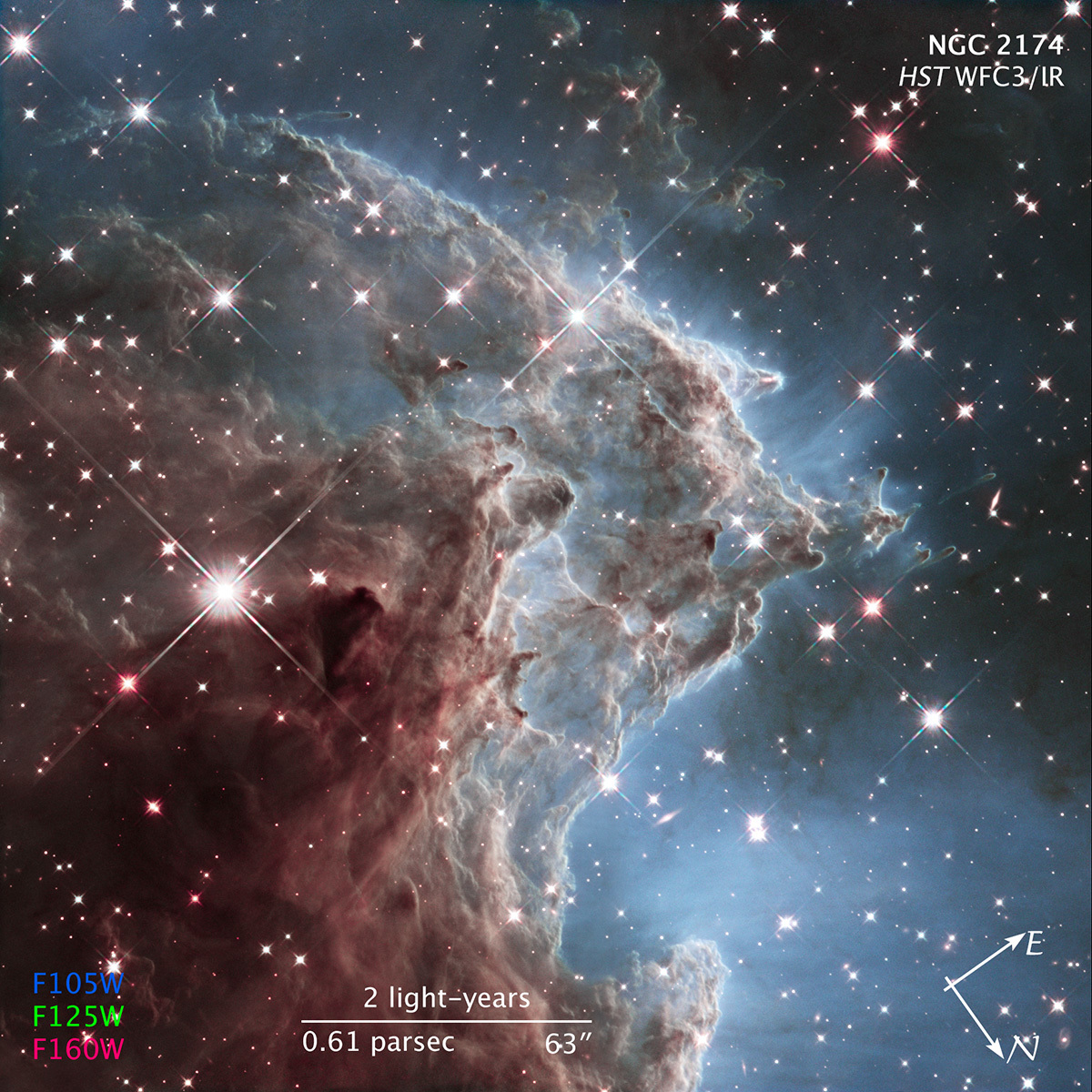
In celebration of the 24th anniversary of the launch of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope (on April 24, 1990) astronomers have taken an infrared-light portrait of a roiling region of starbirth located 6,400 light-years away.
The Hubble mosaic unveils a collection of carved knots of gas and dust in a small portion of the Monkey Head Nebula (also known as NGC 2174 and Sharpless Sh2-252). The nebula is a star-forming region that hosts dusky dust clouds silhouetted against glowing gas.
Massive, newly formed stars near the center of the nebula (and toward the right in this image) are blasting away at dust within the nebula. Ultraviolet light from these bright stars helps carve the dust into giant pillars. The nebula is mostly composed of hydrogen gas, which becomes ionized by the ultraviolet radiation.
As the interstellar dust particles are warmed from the radiation from the stars in the center of the nebula, they heat up and begin to glow at infrared wavelengths.
The image demonstrates Hubble's powerful infrared vision and offers a tantalizing hint of what scientists can expect from the upcoming James Webb Space Telescope.
Observations of NGC 2174 were taken in February 2014.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.06h 9m 10.0s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.20° 27' 20.0"
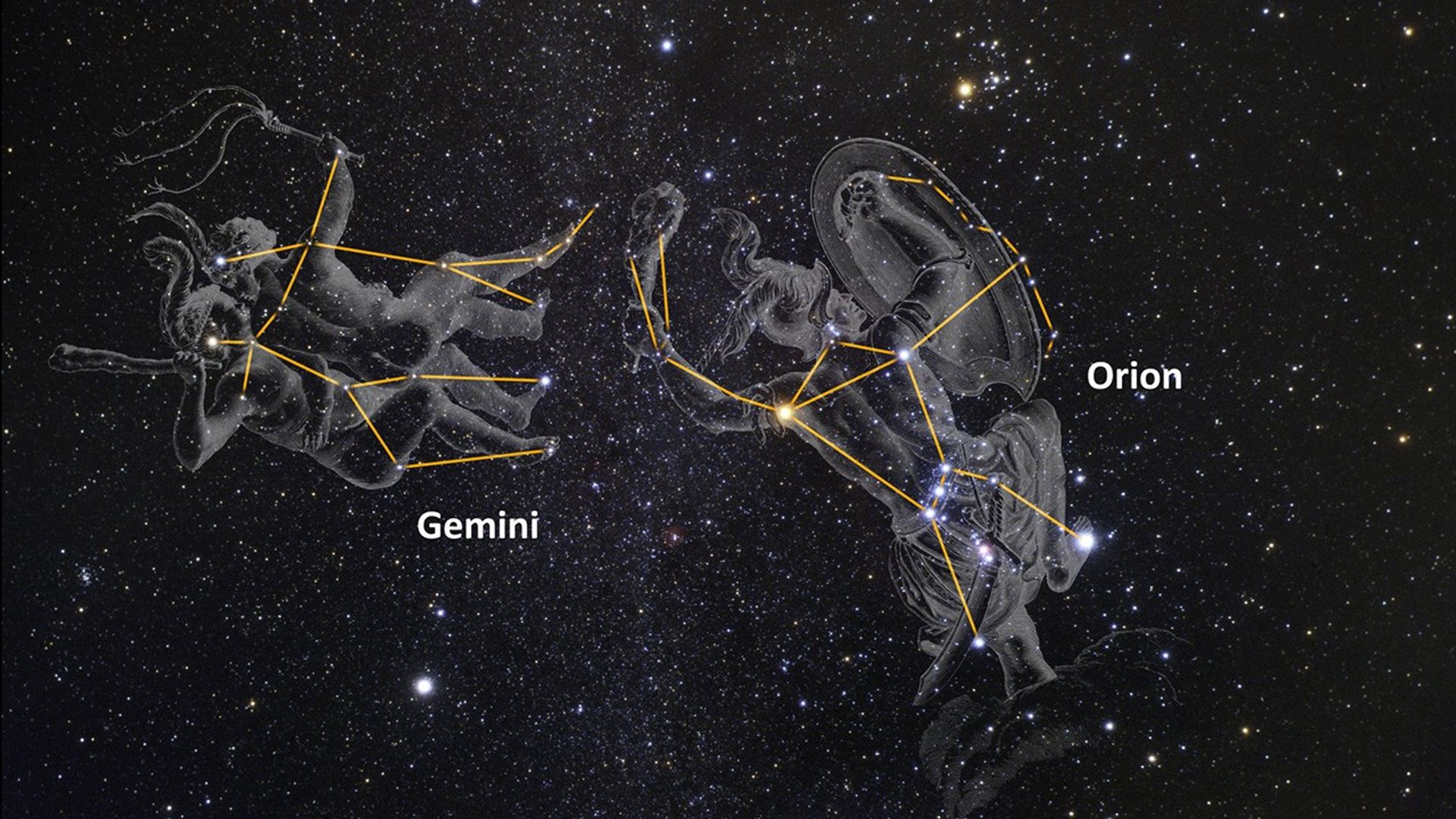
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Orion
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.6,400 light-years (2,000 parsecs)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The Hubble data are from proposal 13623: Hubble Heritage Team/STScI/AURA: Z. Levay (PI; STScI), K. Noll (GSFC), and M. Mutchler, J. Mack, C. Christian, M. Livio, L. Frattare, J. Sokol, and S. Meyett (STScI). High-level science products for these data are available from the MAST archive. - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>WFC3/IR
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.February 7 - 24, 2014
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F105W (Y), F125W (J), and F160W (H)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.NGC 2174, Monkey Head Nebula, Sharpless Sh2-252
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Star-forming Region
- Release DateMarch 17, 2014
- Science ReleaseHubble Celebrates Its 24th Anniversary with an Infrared Look at a Nearby Star Factory
- CreditNASA, ESA, Hubble Heritage Project

This composite image includes exposures acquired by the WFC3 instruments on the Hubble Space Telescope. Several filters were used to sample broad wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: F105W (Y) Green: F125W (J) Red: F160W (H)
Related Images & Videos

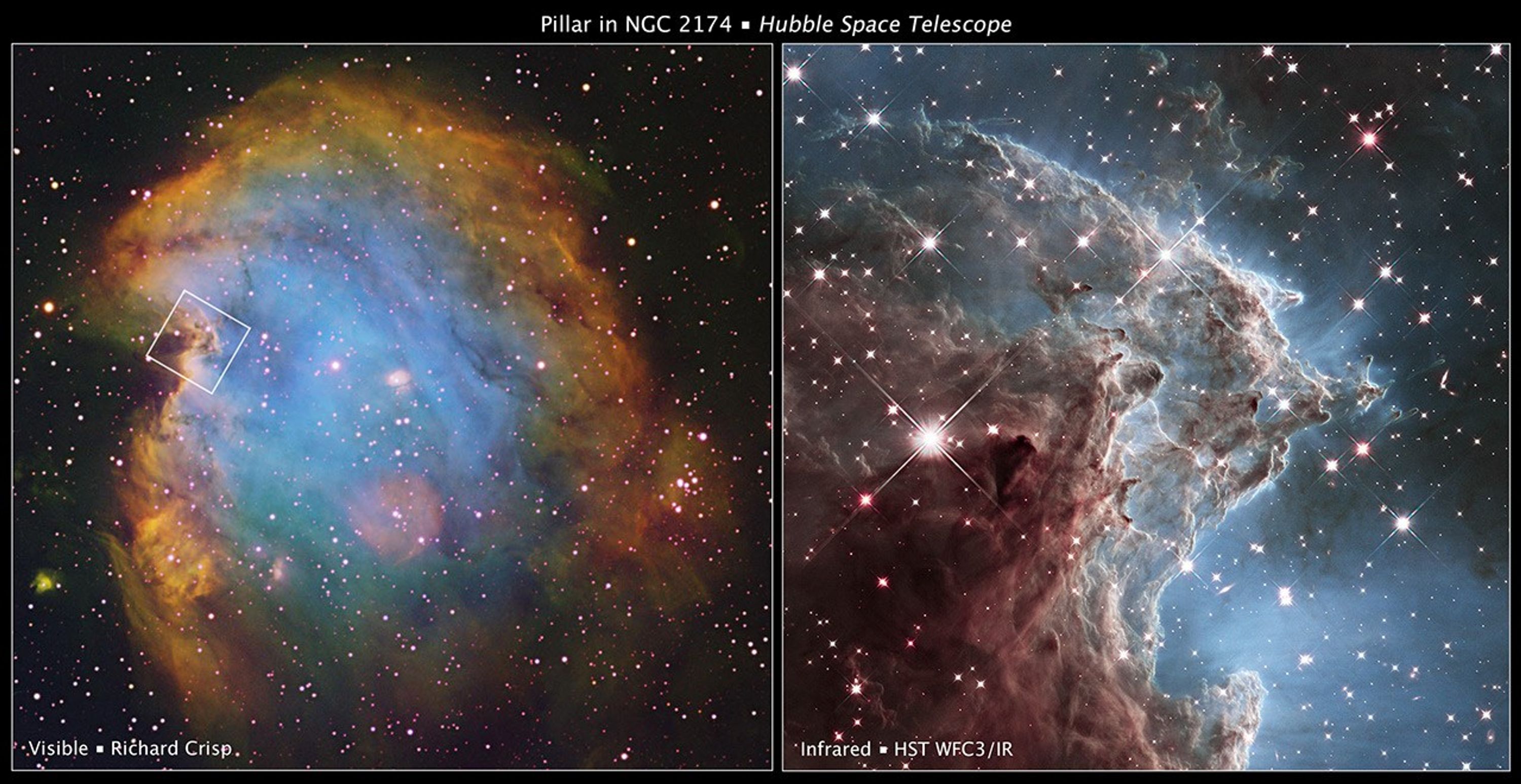
Visible and Infrared Comparison of NGC 2174
This graphic compares visible-light and infrared views of the same detailed area in the star-forming nebula NGC 2174 from the Hubble Space Telescope. On the left is a visible-light image made by WFPC2 in 2001 and on the right is an image made by the WFC3 infrared camera....
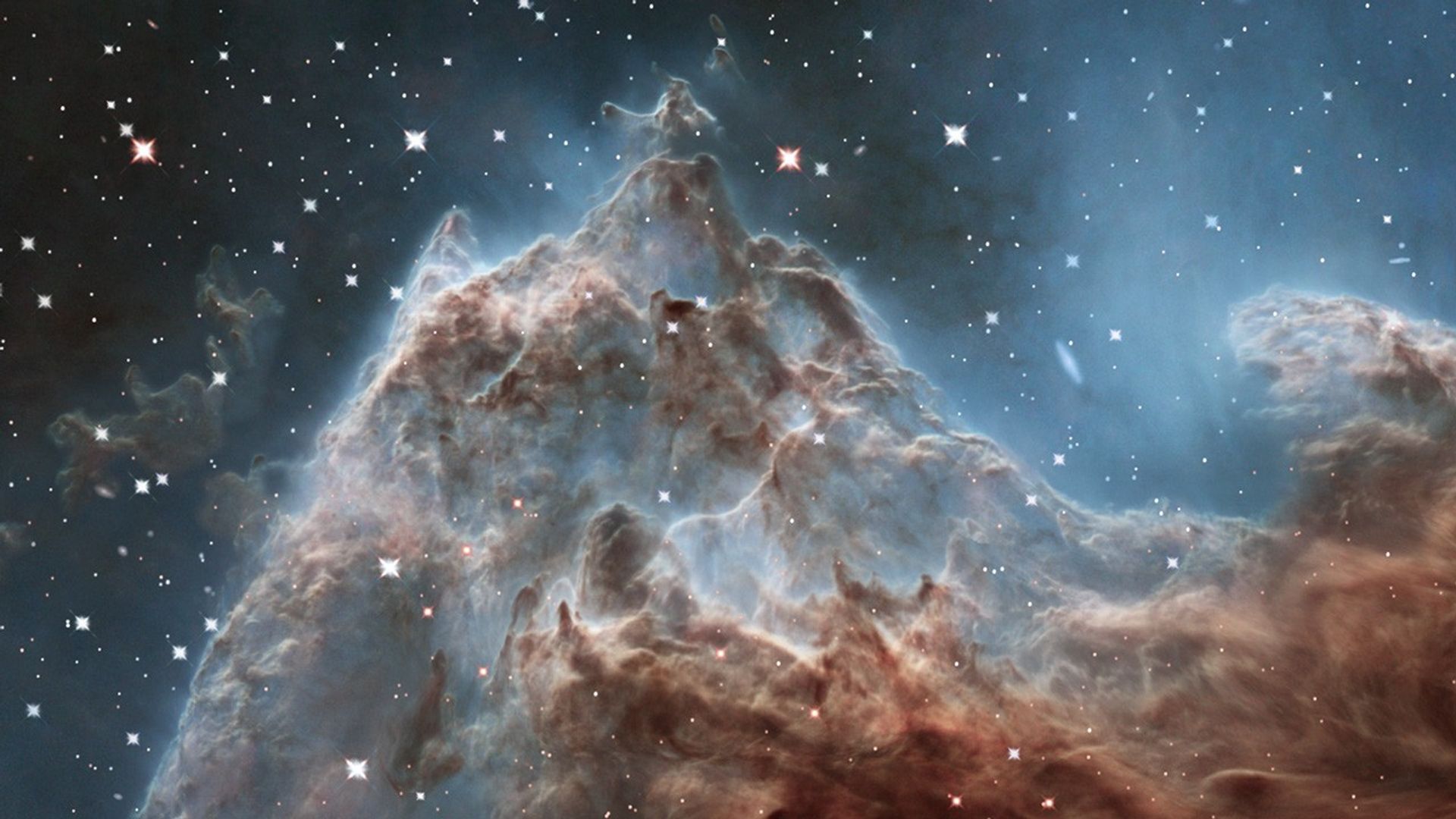
Location of the Hubble IR Detail in NGC 2174
This graphic shows the location of the infrared image from the Hubble Space Telescope in a wider view of the region of NGC 2174. On the left is a ground-based image of the star-forming nebula in visible light by an amateur astrophotographer, with an outline showing the area of...

NGC 2174: Visible 2D Zoom and Infrared 3D Reveal
This video showcases visible and infrared light views of a collection of pillars along the edge of the star-forming region NGC 2174. The sequence begins with a view of the night sky near the constellation of Gemini and Orion. The view zooms through observations from the...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov