1 min read
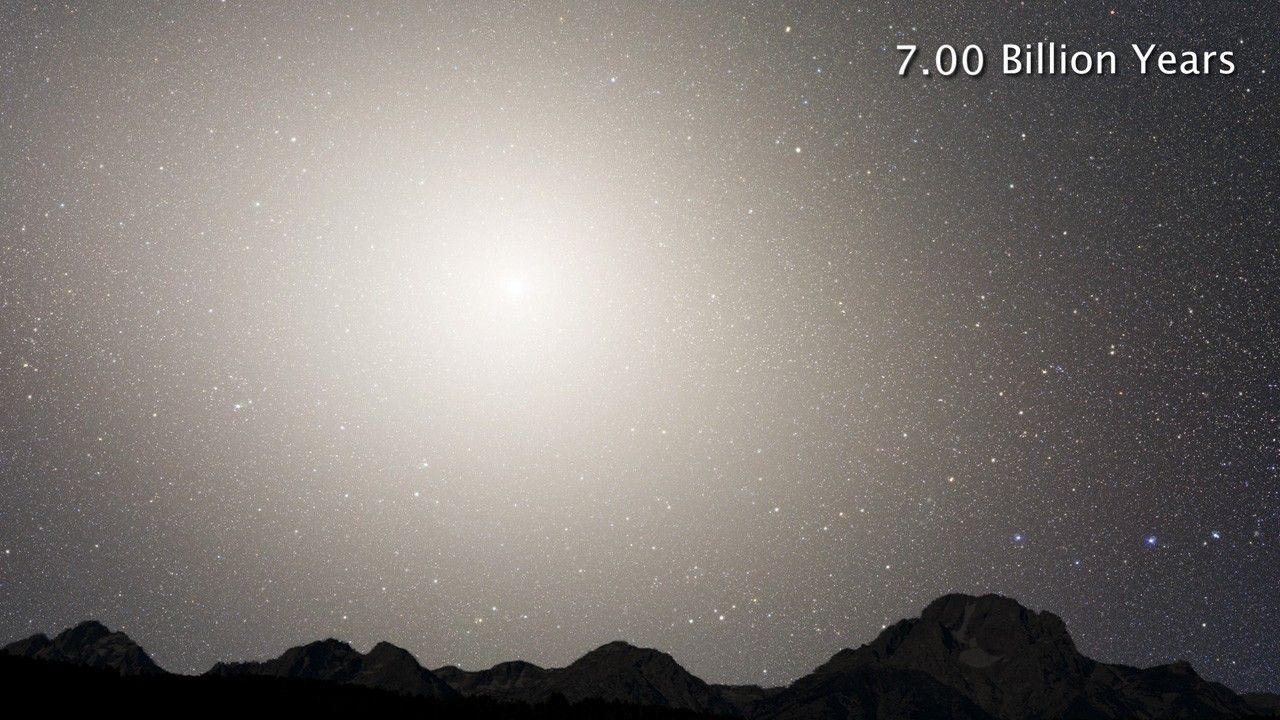
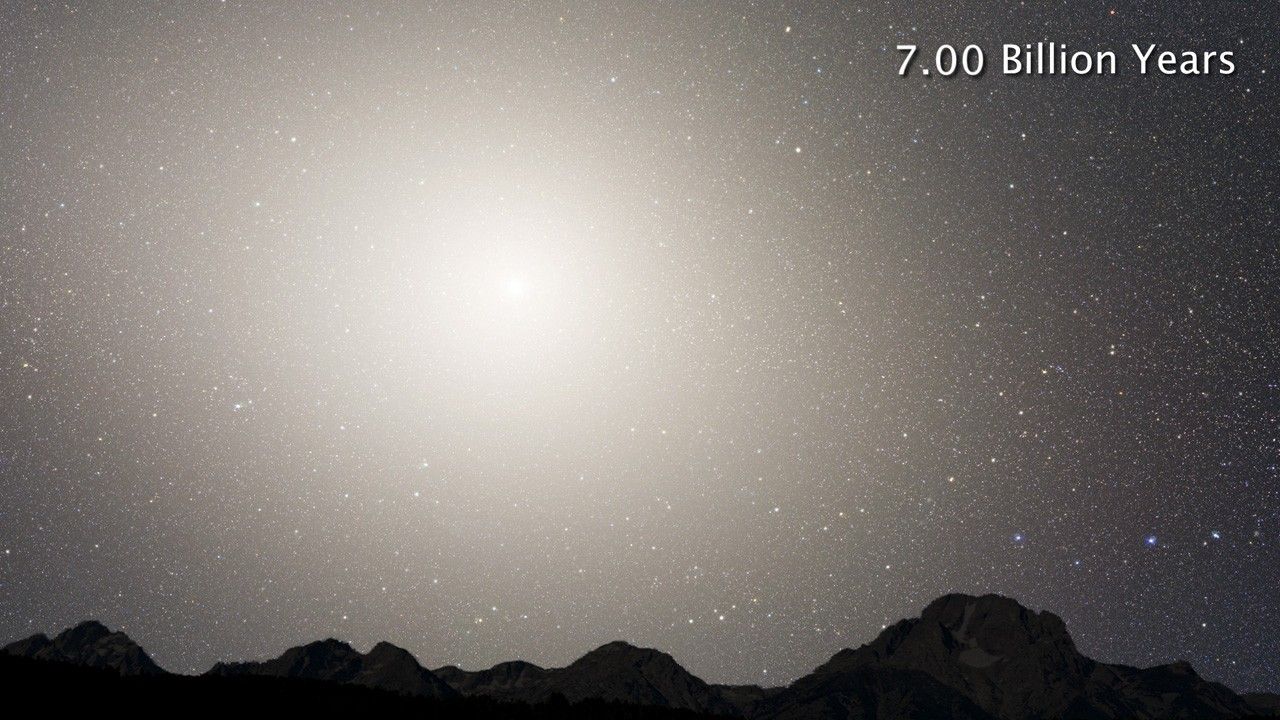
Nighttime Sky View of Future Galaxy Merger: 7 Billion Years

About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.00h 42m 44.0s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.41° 16' 8.99"
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.M31, NGC 224, Andromeda Galaxy
- Release DateMay 31, 2012
- Science ReleaseNASA’s Hubble Shows Milky Way is Destined for Head-on Collision with Andromeda Galaxy
- Credit
Related Images & Videos

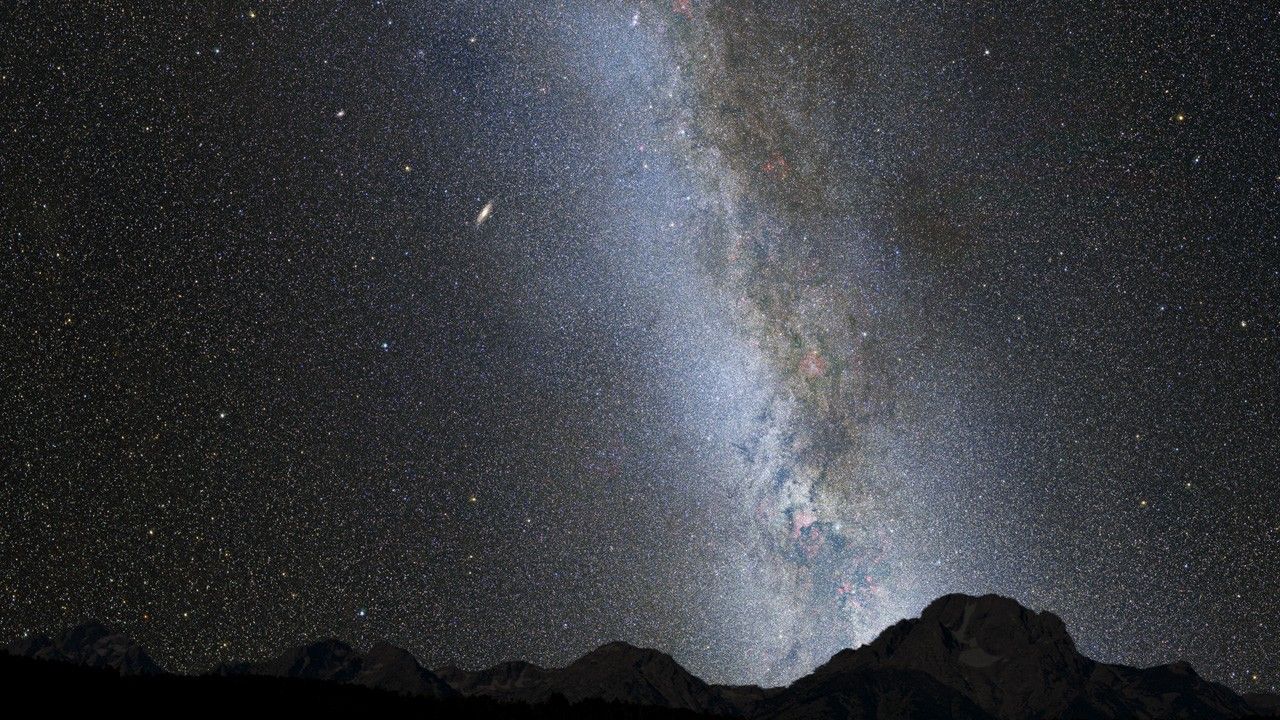
Crash of the Titans: Andromeda Galaxy and the Milky Way Collision
This photo illustration depicts a view of the night sky just before the predicted merger between our Milky Way galaxy and the neighboring Andromeda galaxy. About 3.75 billion years from now, Andromeda's disk fills the field of view and its gravity begins to create tidal...

Nighttime Sky View of Future Galaxy Merger
This series of photo illustrations shows the predicted merger between our Milky Way galaxy and the neighboring Andromeda galaxy, as it will unfold over the next several billion years. The sequence is inspired by dynamical computer modeling of the inevitable future collision...

Nighttime Sky View of Future Galaxy Merger: 5.1 Billion Years
During the second close passage, the cores of the Milky Way and Andromeda appear as a pair of bright lobes. Star-forming nebulae are much less prominent because the interstellar gas and dust has been significantly decreased by previous bursts of star formation.

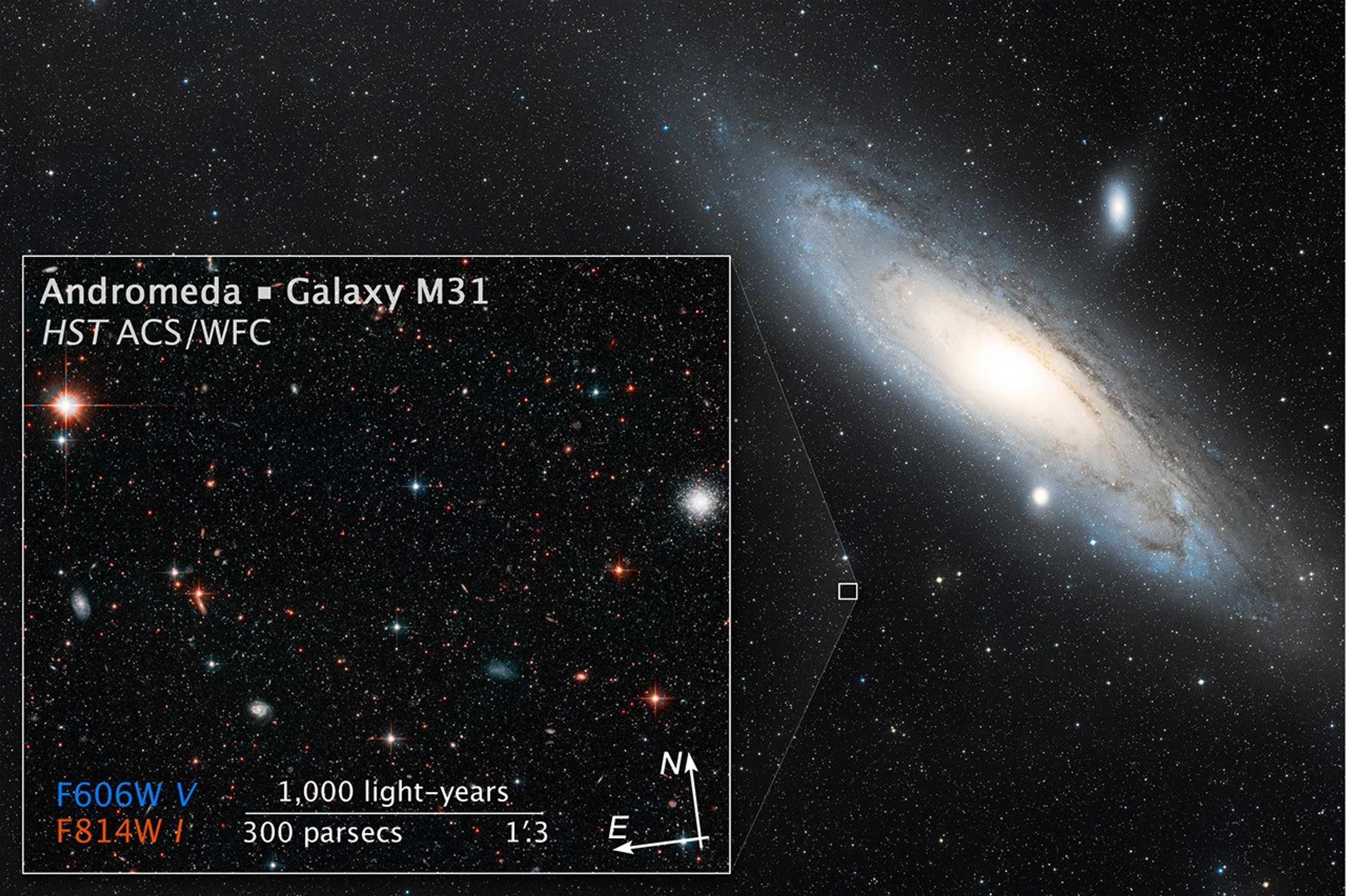
Halo of Andromeda Galaxy Used to Measure Its Drift Across Space
This composite image shows a region in the halo in the neighboring Andromeda galaxy that astronomers used to precisely measure the galaxy's sideways motion on the sky. This has allowed them to predict a direct collision between Andromeda and the Milky Way about 4 billion years...
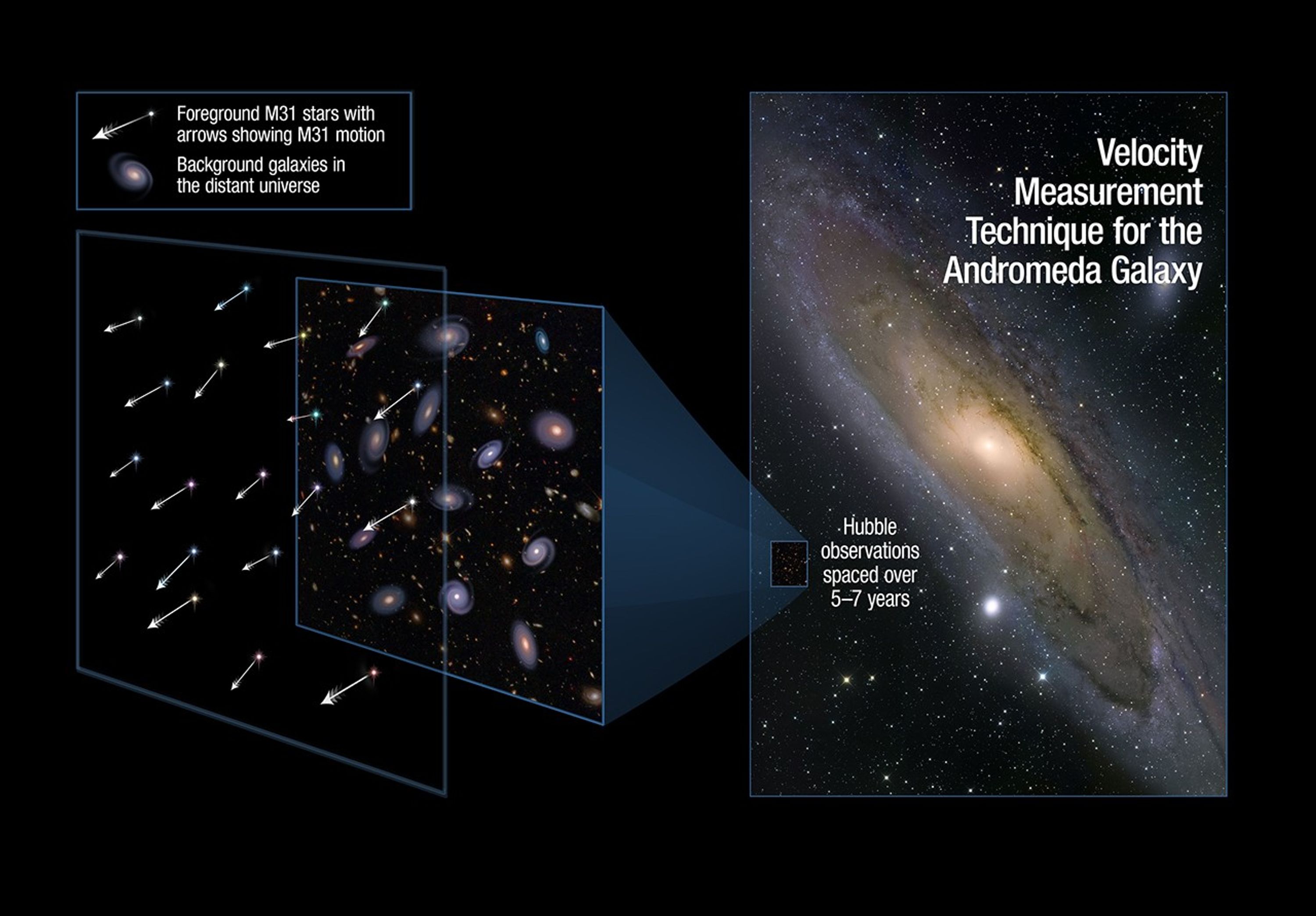
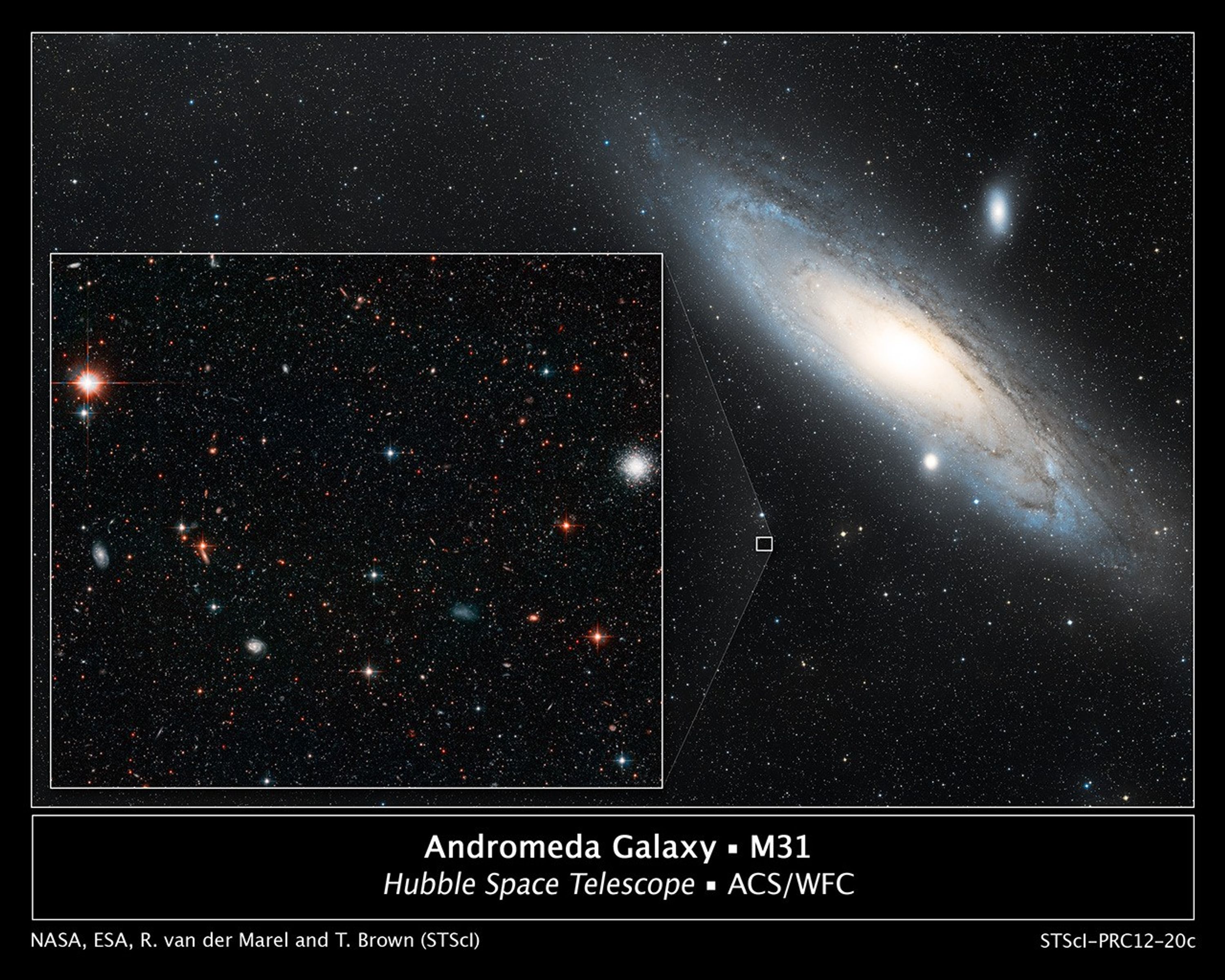
Measuring the Drift of the Andromeda Galaxy
This illustration shows one of the regions in the neighboring Andromeda galaxy where astronomers aimed the Hubble Space Telescope to make precise measurements of the galaxy's lateral motion. As the galaxy drifts through space, the stars will appear to uniformly move against the...
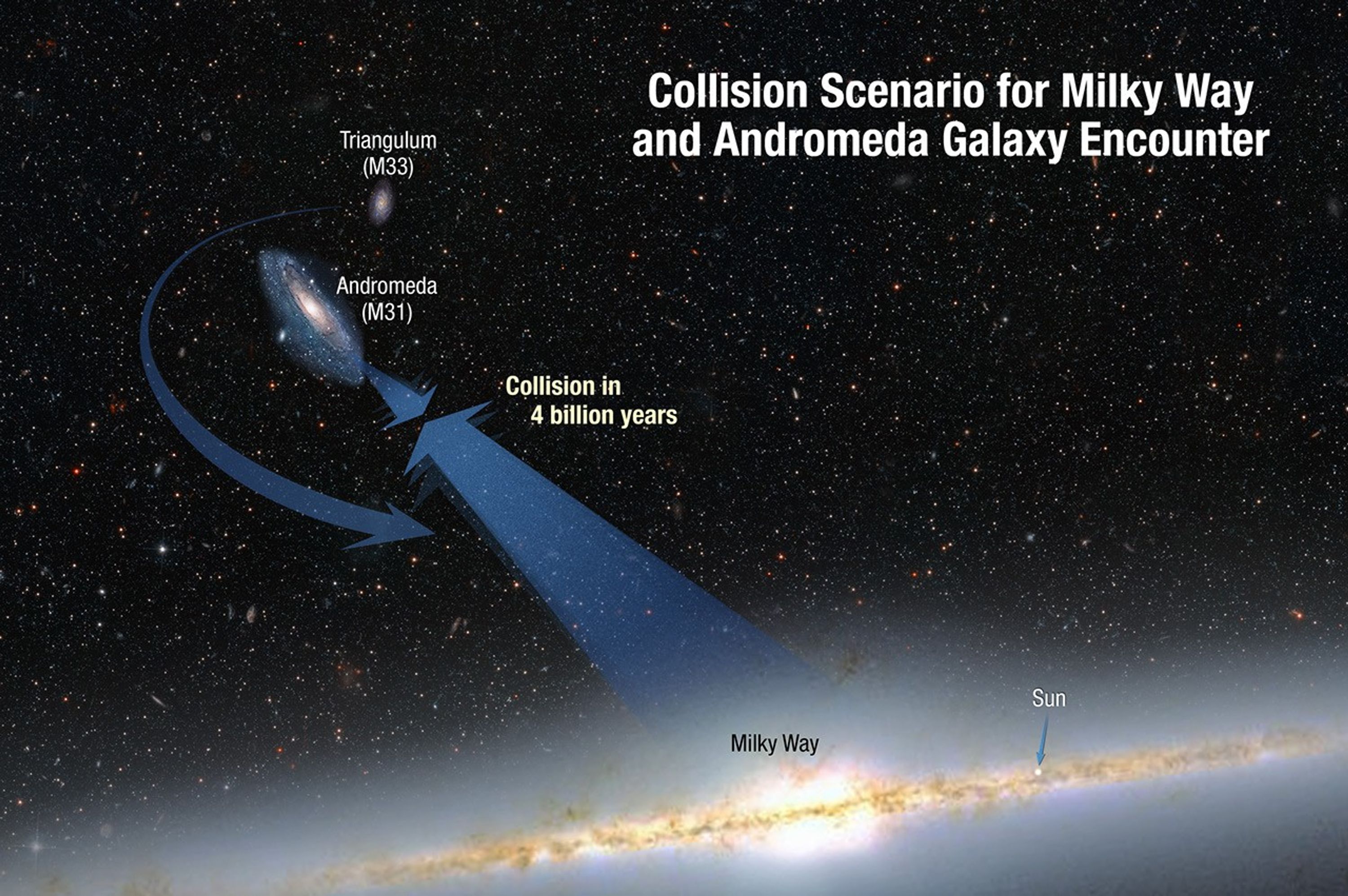
Collision Scenario for Milky Way and Andromeda Galaxy Encounter
This illustration shows the inevitable collision between our Milky Way galaxy and the Andromeda galaxy approximately 4 billion years from now. The galaxies are moving toward each other under the inexorable pull of gravity between them. A smaller galaxy, Triangulum, may be part...
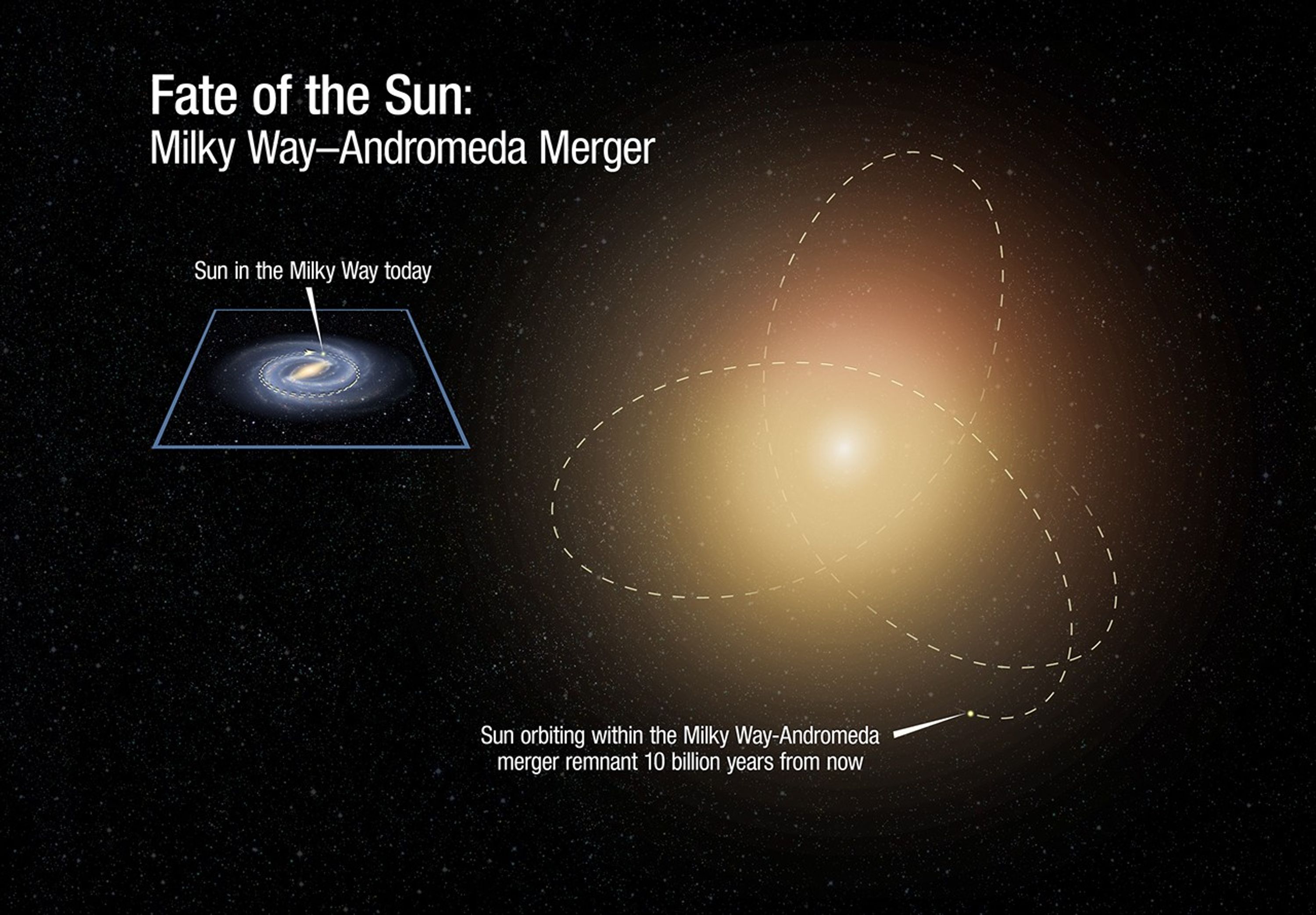
Fate of Sun After Galaxy Collision
This illustration is a before-and-after comparison of the size of our Milky Way galaxy at present, and after it fully completes a merger with the neighboring Andromeda galaxy 10 billion years from now. The merged galaxies will blend together to create an elliptical galaxy of...
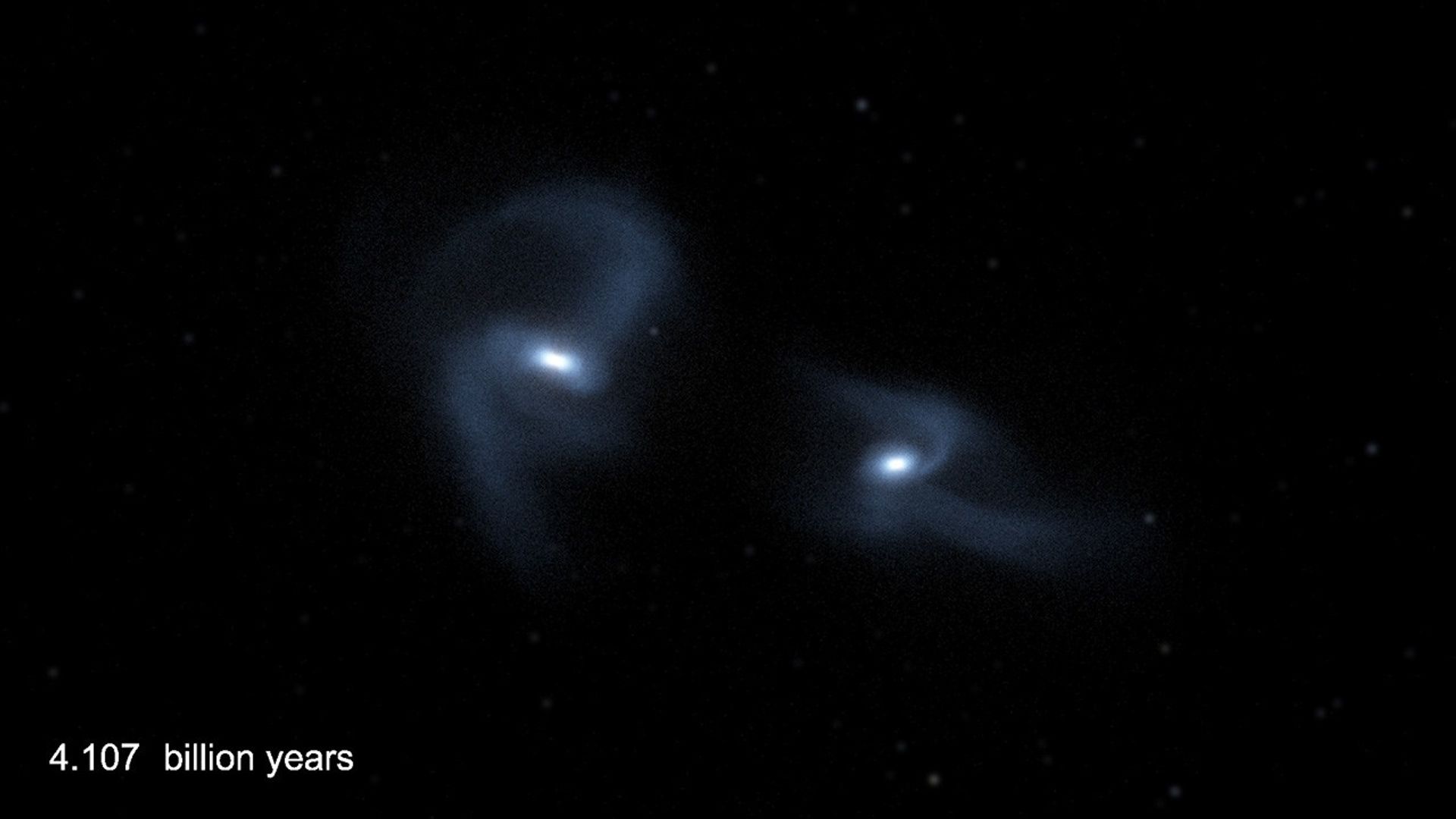

Crash of the Titans Science Visualization (Annotated)
This scientific visualization of a computer simulation depicts the inevitable collision between our Milky Way galaxy and the Andromeda galaxy (also known as Messier 31). NASA Hubble Space Telescope observations indicate that the two galaxies, pulled together by their mutual...
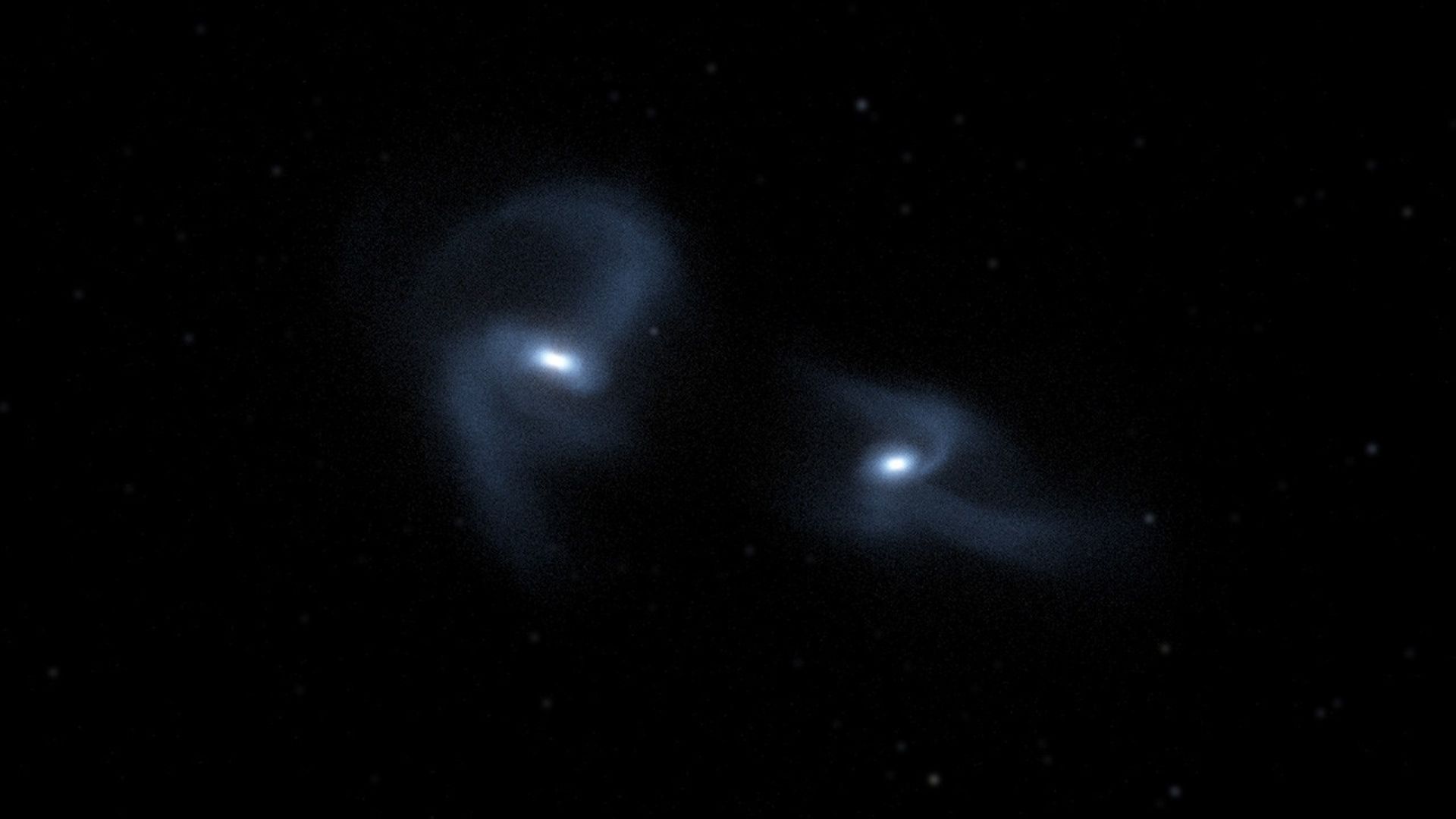

Crash of the Titans Science Visualization
This scientific visualization of a computer simulation depicts the inevitable collision between our Milky Way galaxy and the Andromeda galaxy (also known as Messier 31). NASA Hubble Space Telescope observations indicate that the two galaxies, pulled together by their mutual...

Nighttime Sky View of Future Galaxy Merger (Annotated)
This video series of photo illustrations shows the predicted merger between our Milky Way galaxy and the neighboring Andromeda galaxy, as it will unfold over the next several billion years. The sequence is inspired by dynamical computer modeling of the inevitable future...

Nighttime Sky View of Future Galaxy Merger
This video series of photo illustrations shows the predicted merger between our Milky Way galaxy and the neighboring Andromeda galaxy, as it will unfold over the next several billion years. The sequence is inspired by dynamical computer modeling of the inevitable future...

Nighttime Sky View of Future Galaxy Merger (Annotated, With Holds)
This video series of photo illustrations shows the predicted merger between our Milky Way galaxy and the neighboring Andromeda galaxy, as it will unfold over the next several billion years. The sequence is inspired by dynamical computer modeling of the inevitable future...
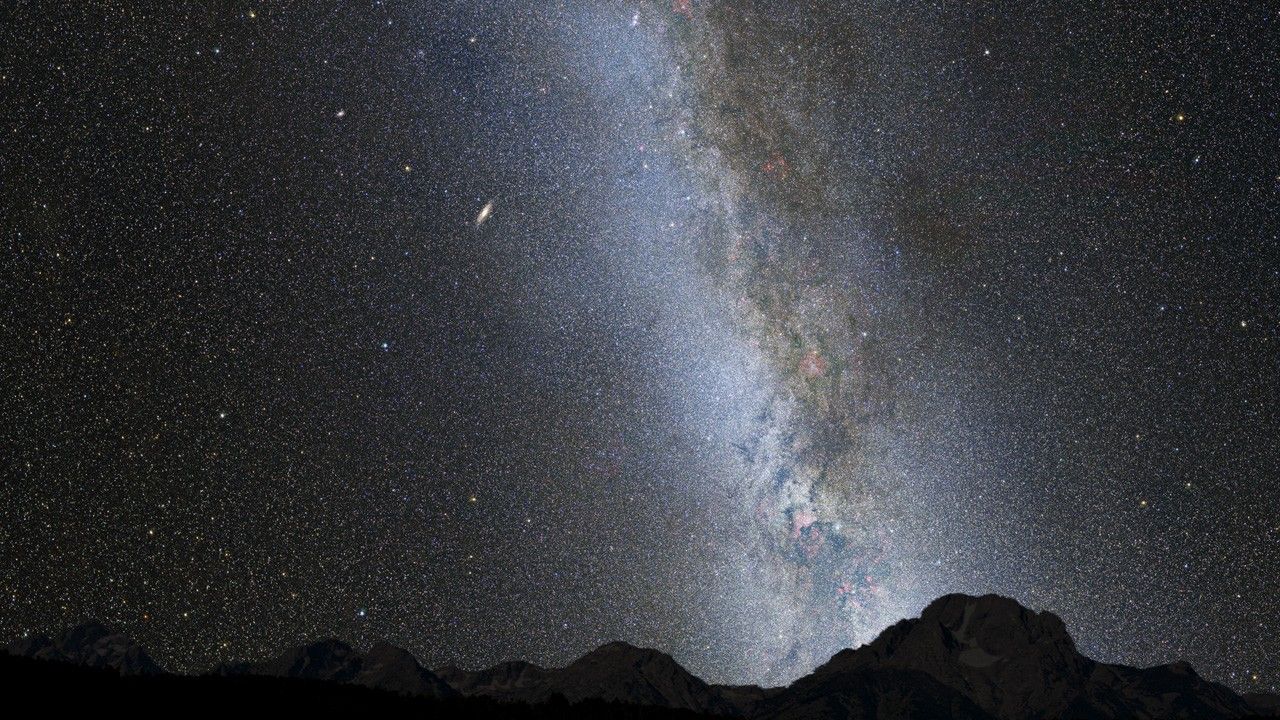

Nighttime Sky View of Future Galaxy Merger (With Holds)
This video series of photo illustrations shows the predicted merger between our Milky Way galaxy and the neighboring Andromeda galaxy, as it will unfold over the next several billion years. The sequence is inspired by dynamical computer modeling of the inevitable future...
Measuring the Drift of the Andromeda Galaxy (Annotated)
This video zooms into a region in the halo of the neighboring Andromeda galaxy that astronomers studied with the Hubble Space Telescope to make precise measurements of the galaxy's motion. Andromeda was previously known to be approaching the Milky Way, but these new measurements...
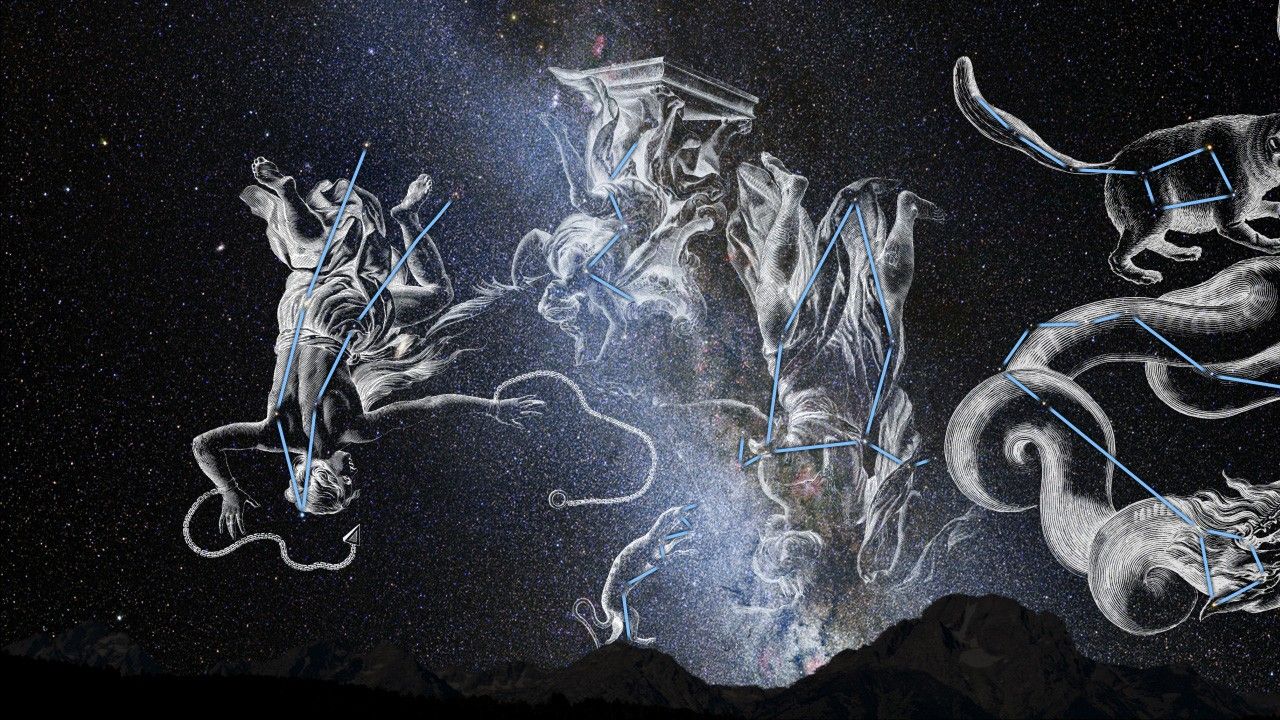

Measuring the Drift of the Andromeda Galaxy
This video zooms into a region in the halo of the neighboring Andromeda galaxy that astronomers studied with the Hubble Space Telescope to make precise measurements of the galaxy's motion. Andromeda was previously known to be approaching the Milky Way, but these new measurements...
Scientists Reflect on Expected Collision Between the Milky Way and the Andromeda Galaxy
This video discusses what the science team's challenges and techniques were in their quest to determine the fate of the Milky Way galaxy. They reflect on the encounter's possible influence on the solar system, and how the Hubble Space Telescope was vital to this research.
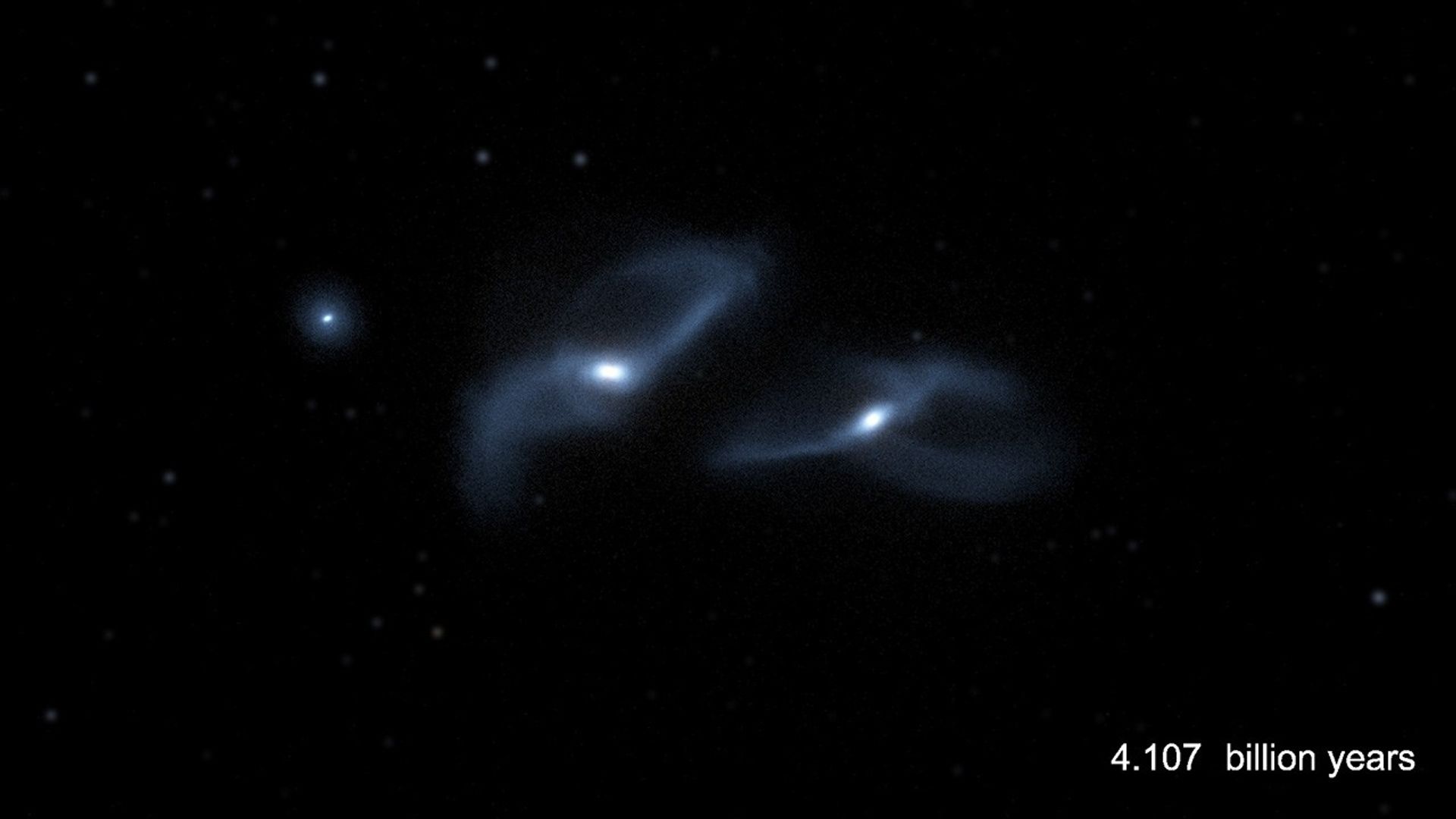

The Fate of the Milky Way, Andromeda, and Triangulum Galaxies (Annotated)
The three largest galaxies in our Local Group of Galaxies are our Milky Way along with the Andromeda (also known as Messier 31) and Triangulum (also known as Messier 33) galaxies. This scientific visualization of a computer simulation depicts their joint evolution over the next...
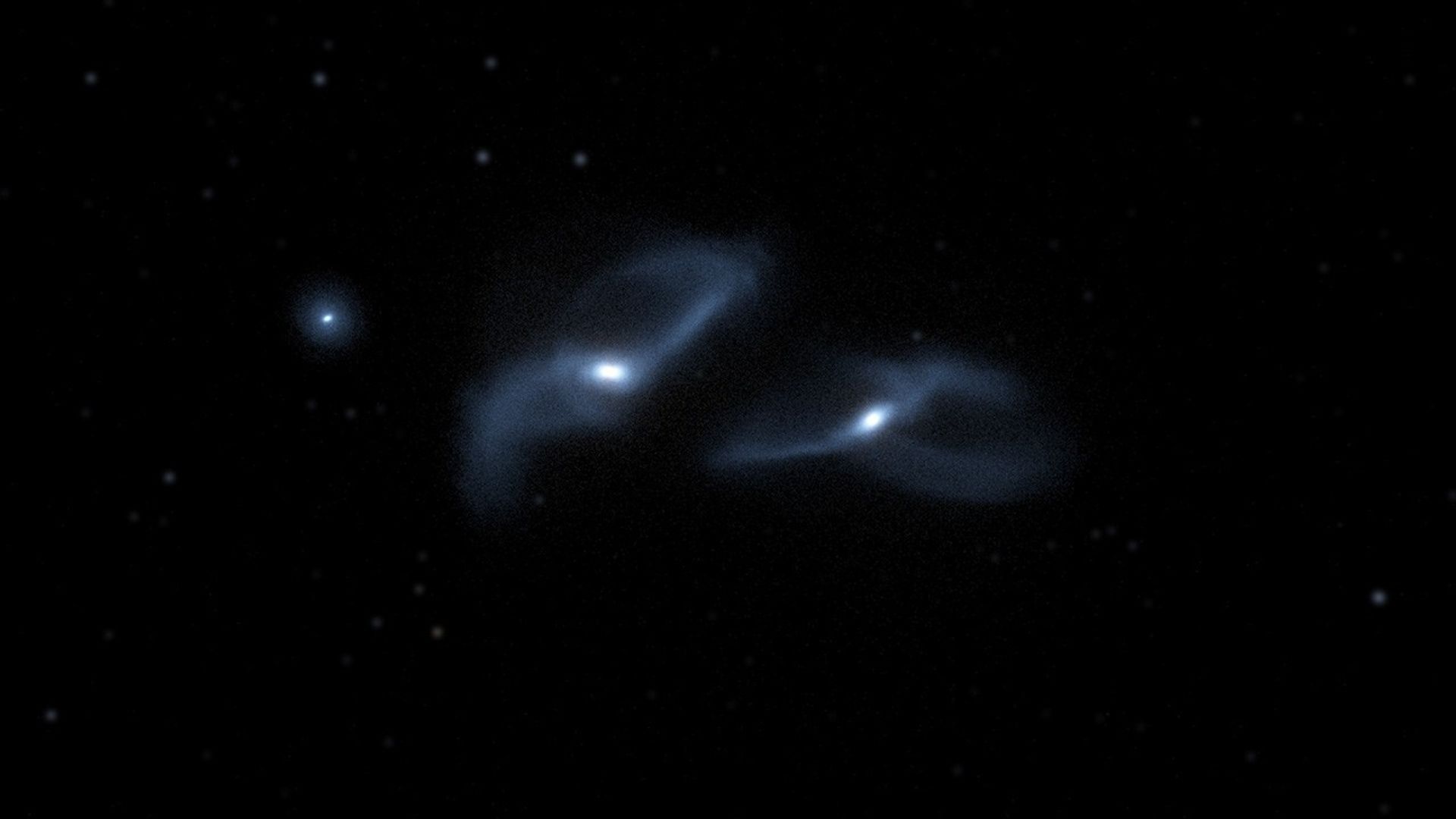

The Fate of the Milky Way, Andromeda, and Triangulum Galaxies
The three largest galaxies in our Local Group of Galaxies are our Milky Way along with the Andromeda (also known as Messier 31) and Triangulum (also known as Messier 33) galaxies. This scientific visualization of a computer simulation depicts their joint evolution over the next...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov



































