1 min read
Saturn ‘s Rings in Visible Light

About the Object
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.The semi-major axis of Saturn's orbit about the sun is 9.5 Astronomical Units (A.U.) or roughly 1.4 billion km.
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.The planet (without rings) has a diameter of roughly 75,000 miles (120,000 km) at the equator.
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created from HST data from proposal 9354: E. Karkoschka and M. Tomasko (University of Arizona) - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>WFPC2
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.March 7, 2003
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.0.59 micrometer
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Saturn
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Planet
- Release DateSeptember 9, 2003
- Science ReleaseThe Slant on Saturn’s Rings
- CreditCredit: NASA and E. Karkoschka (University of Arizona)

Color Info
Color InfoA brief description of the methods used to convert telescope data into the color image being presented.
Visible: 0.47-0.65 micrometers
Related Images & Videos
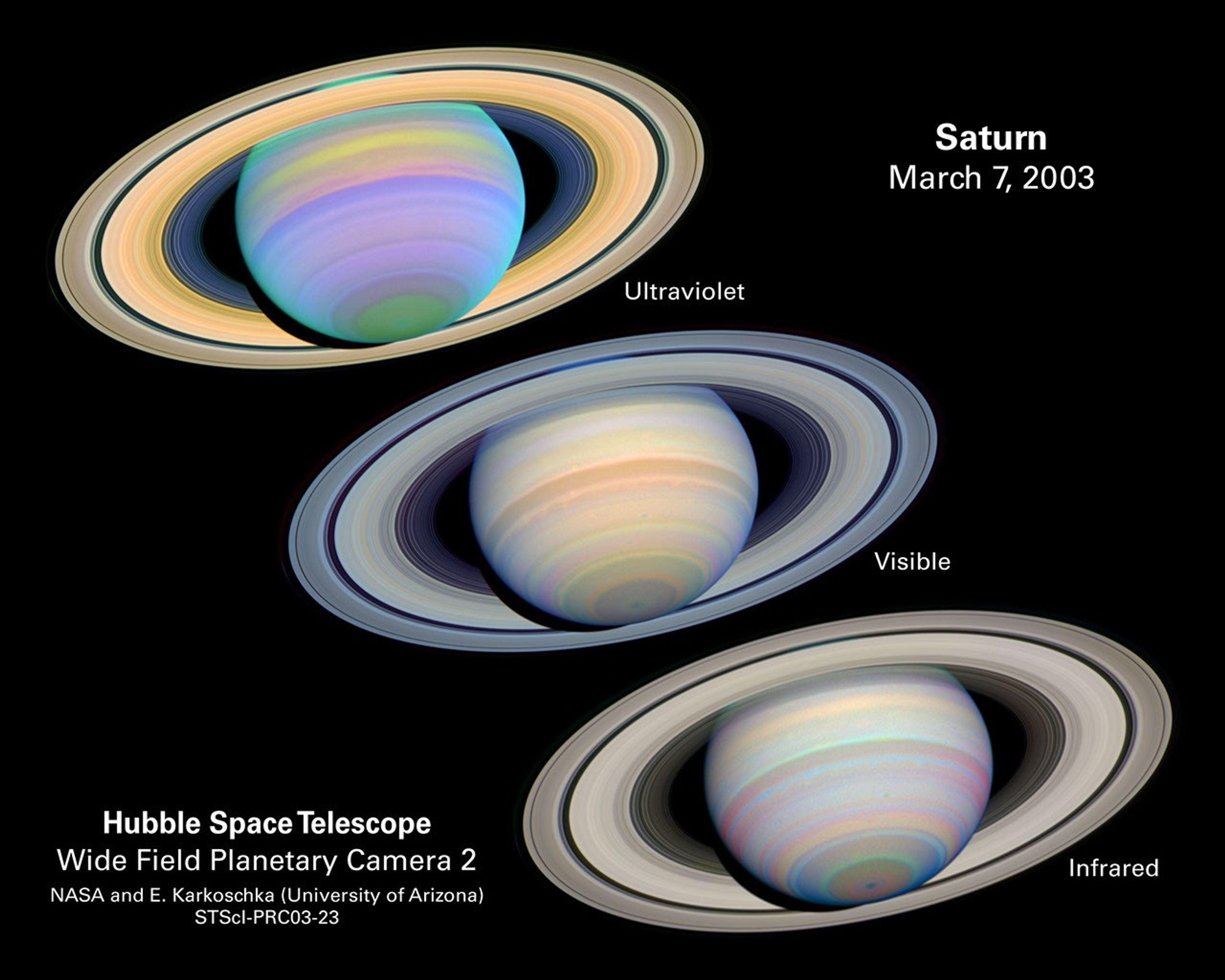
Saturn With Rings Tilted Toward Earth
This is a series of images of Saturn, as seen at many different wavelengths, when the planet's rings were at a maximum tilt of 27 degrees toward Earth. Saturn experiences seasonal tilts away from and toward the Sun, much the same way Earth does. This happens over the course of...
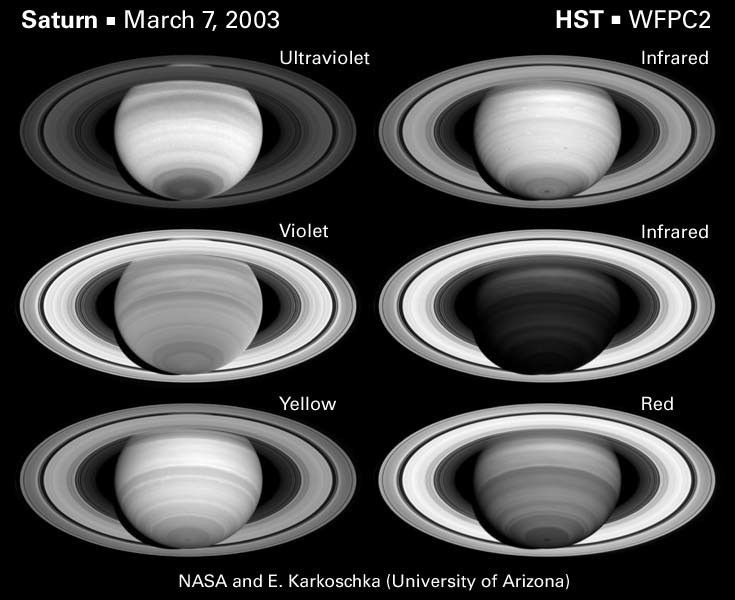
The Spectrally Changing Face of Saturn
This set of images displays Saturn in six different wavelengths. Counterclockwise from top left, the wavelengths are in the ultraviolet, violet, yellow, deep red, and two in the near-infrared. Even a quick look at the set of six images reveals the changing face of Saturn between...
Share
Details
Last Updated
Aug 17, 2025
Contact
Media
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov































