1 min read
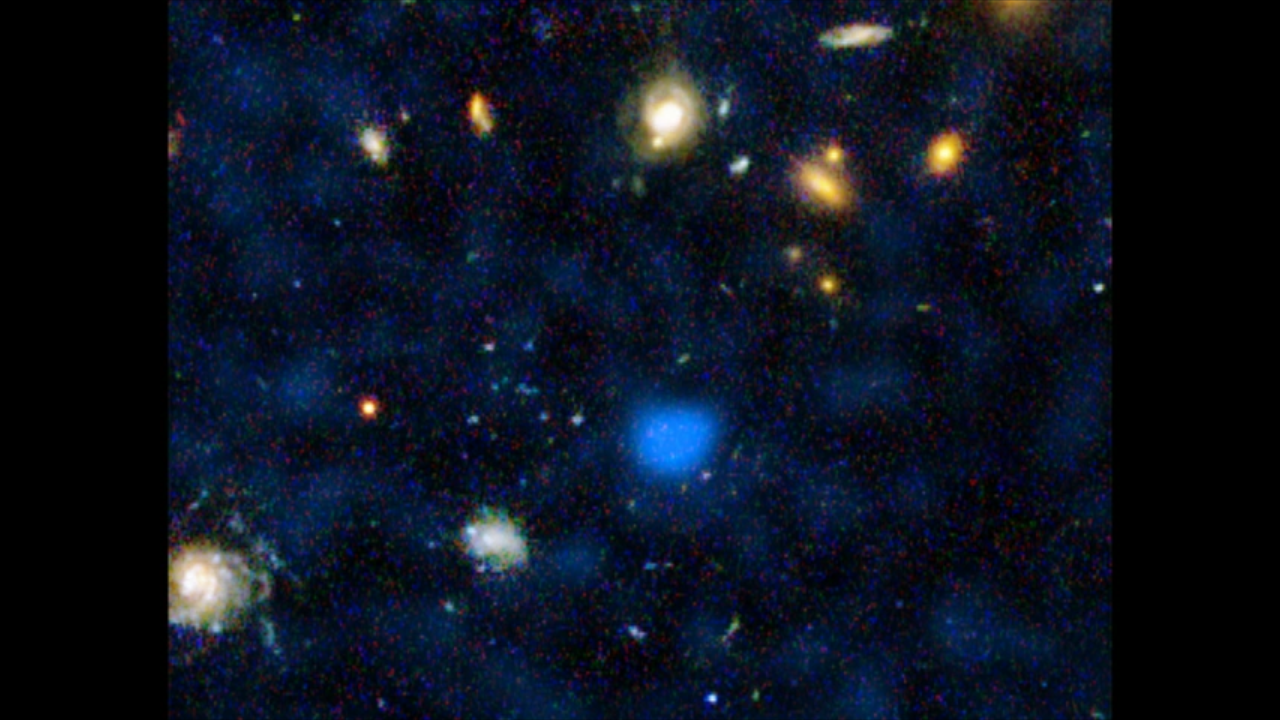
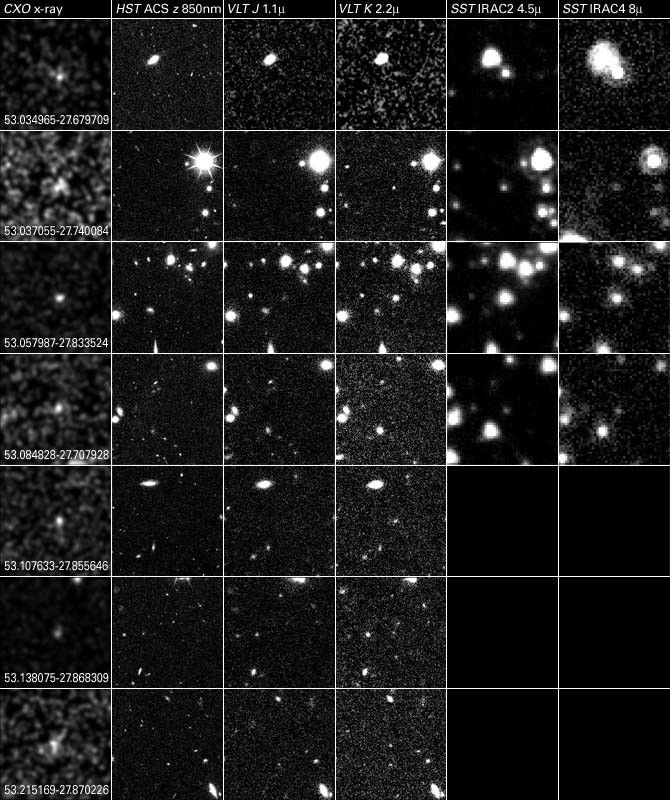
Spitzer+Chandra: Object #7 53.215169-27.870226

About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.03h 32m 30.0s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-27° 48' 20.0"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Fornax
About the Data
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.SST>IRAC
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.February 2004, Exposure Time: 5 days (IRAC)
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.IRAC: 3.6 microns, 4.5microns , 5.8 microns, and 8 microns
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.GOODS (Chandra Deep Field - South)
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Deep Survey field
- Release DateJune 1, 2004
- Science ReleaseSpitzer Leads NASA’s Great Observatories to Uncover Black Holes, Other Hidden Objects in the Distant Universe
- Credit
Related Images & Videos

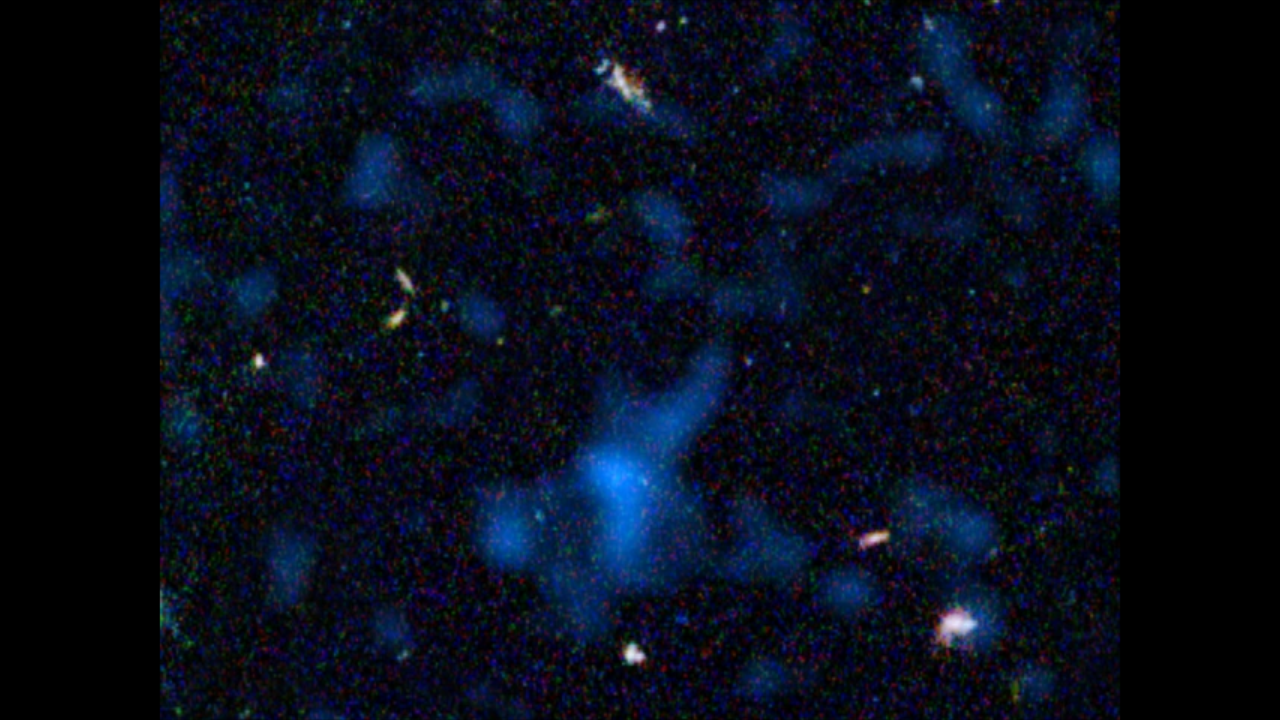
Hidden Black Holes Revealed in GOODS Field
The combined power of NASA's Great Observatories - the Hubble Space Telescope, the Chandra X-ray Observatory, and the Spitzer Space Telescope - have been combined to find a hidden population of supermassive black holes in the universe. It took the penetrating view of Spitzer to...
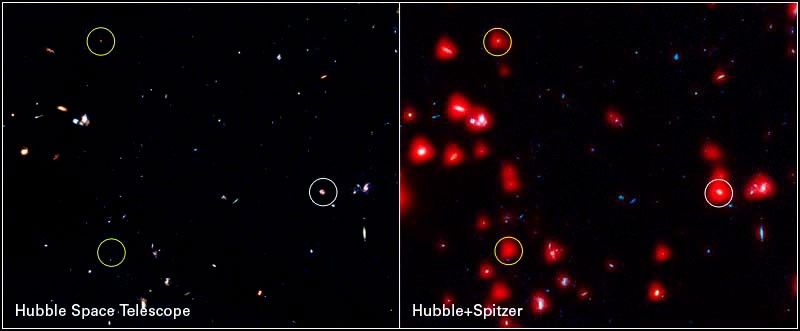
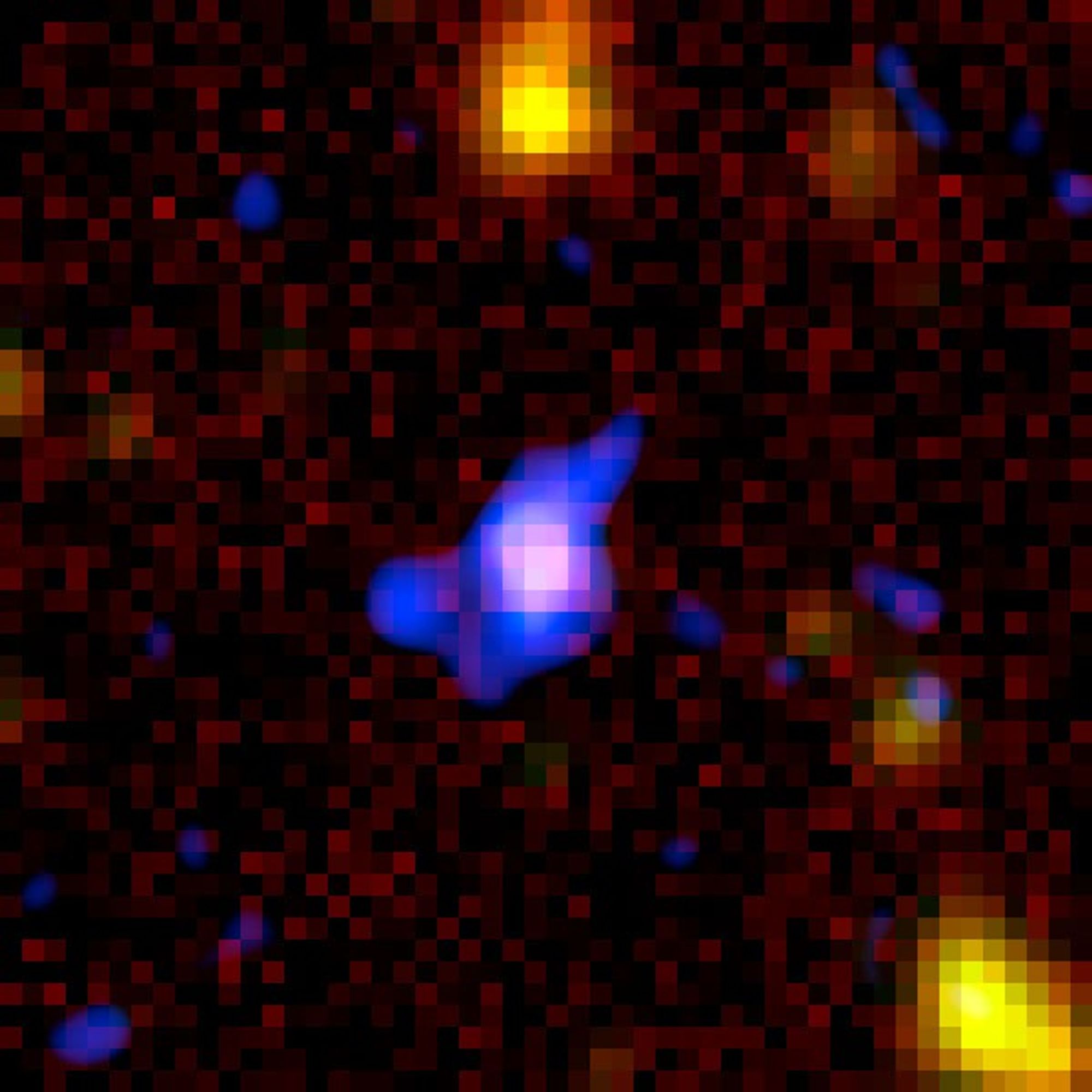
Instrument Comparison of 1/200 of the Full GOODS Fields
(Left) HST ACS image of 1/200 of the full GOODS fields shows three X-ray sources (circled) and many other galaxies. (Right) Combined HST-Spitzer IRAC image of the same region. The two "hard" X-ray sources (yellow circles, indicating sources detected only at the shortest X-ray...

HUDF: If Human Eyes Could See in the Way that Spitzer Can See
The look of the HUDF (outlined area) if human eyes could see in the way that Spitzer can see. The red color of this picture comes from the deepest infrared observations made by the GOODS team using Spitzer. Within the HUDF, which is about 1% the size of the full Moon, the GOODS...
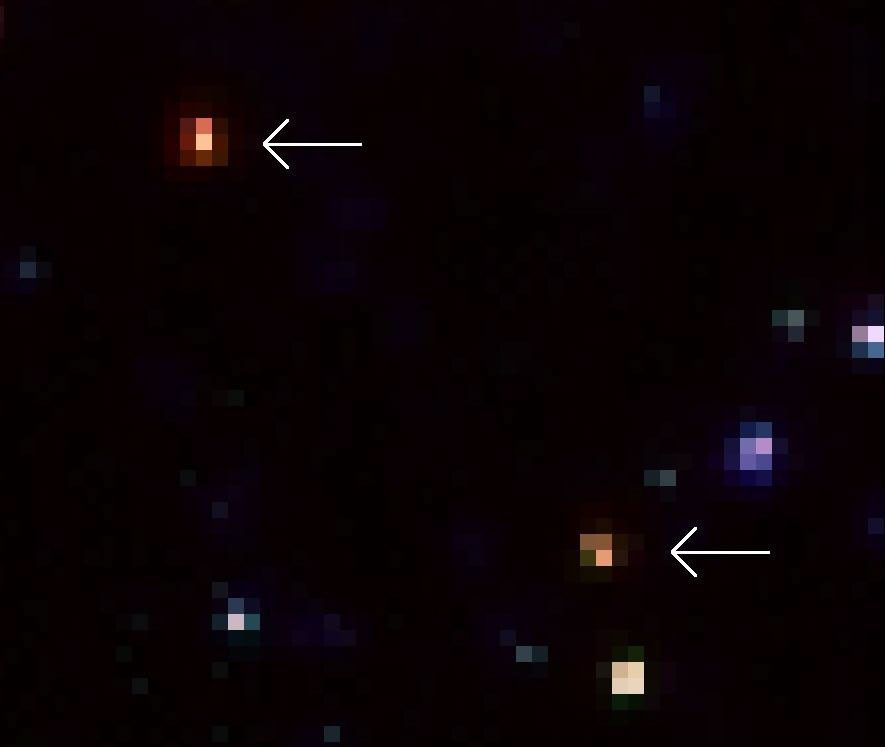

A Close-Up Look of Two of the Extremely Red Galaxies Revealed By Spitzer
A close-up look of two of the extremely red galaxies revealed by Spitzer. While they are very faint (the bottom one) or even completely invisible (the top one) in the deepest-ever optical images obtained by Hubble, Spitzer easily picked them up because of their strong infrared...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov