1 min read
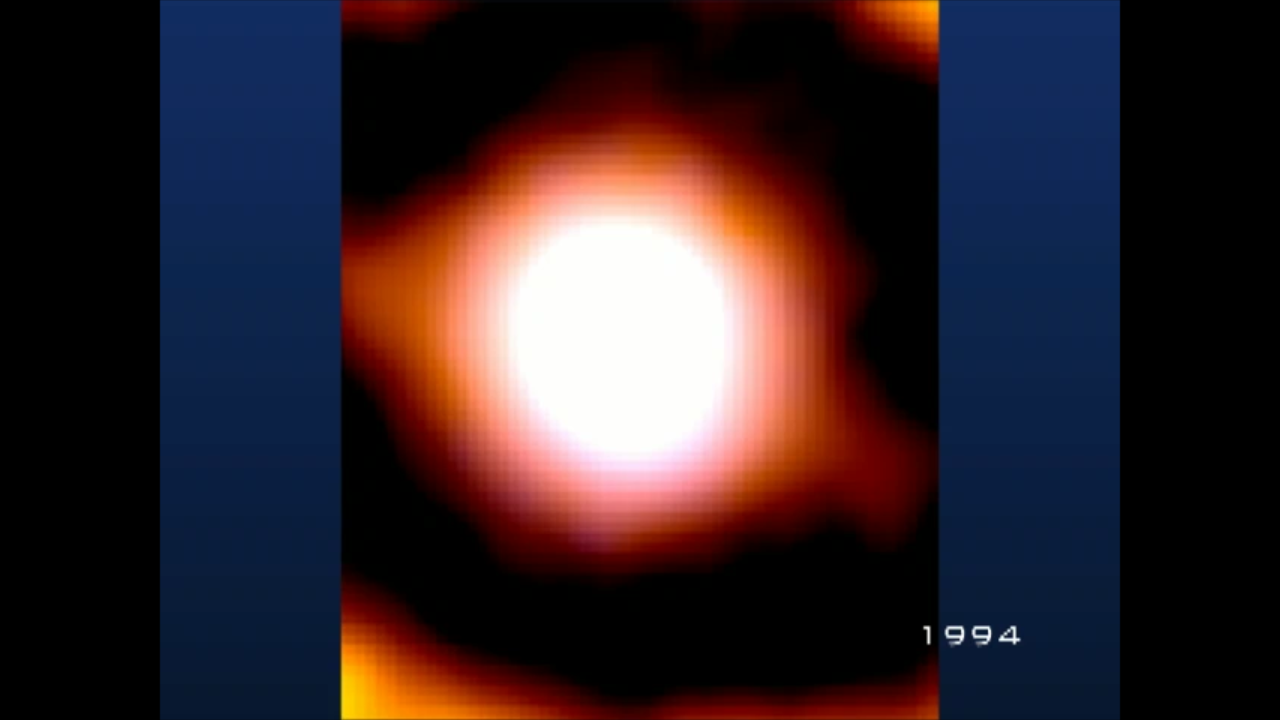
Supernova 1987A: September 24, 1994

About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.05h 35m 28.25s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-69° 16' 13.0"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Dorado
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.Approximately 160,000 light-years (49 kiloparsecs) away
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.Roughly 9 arcseconds wide. At the distance of the LMC, this represents 9.5 light-years (2.9 parsecs).
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The primary image released comes from ACS/HRC data from the HST proposal 10867: R. Kirshner (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>WFPC2
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.September 24, 1994
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.SN 1987A
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Supernova in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC)
- Release DateFebruary 22, 2007
- Science ReleaseNASA’s Hubble Telescope Celebrates SN 1987A’s 20th Anniversary
- Credit
Related Images & Videos

A String of 'Cosmic Pearls' Surrounds an Exploding Star
Two decades ago, astronomers spotted one of the brightest exploding stars in more than 400 years. Since that first sighting, the doomed star, called Supernova 1987A, has continued to fascinate astronomers with its spectacular light show. NASA's Hubble Space Telescope is one of...
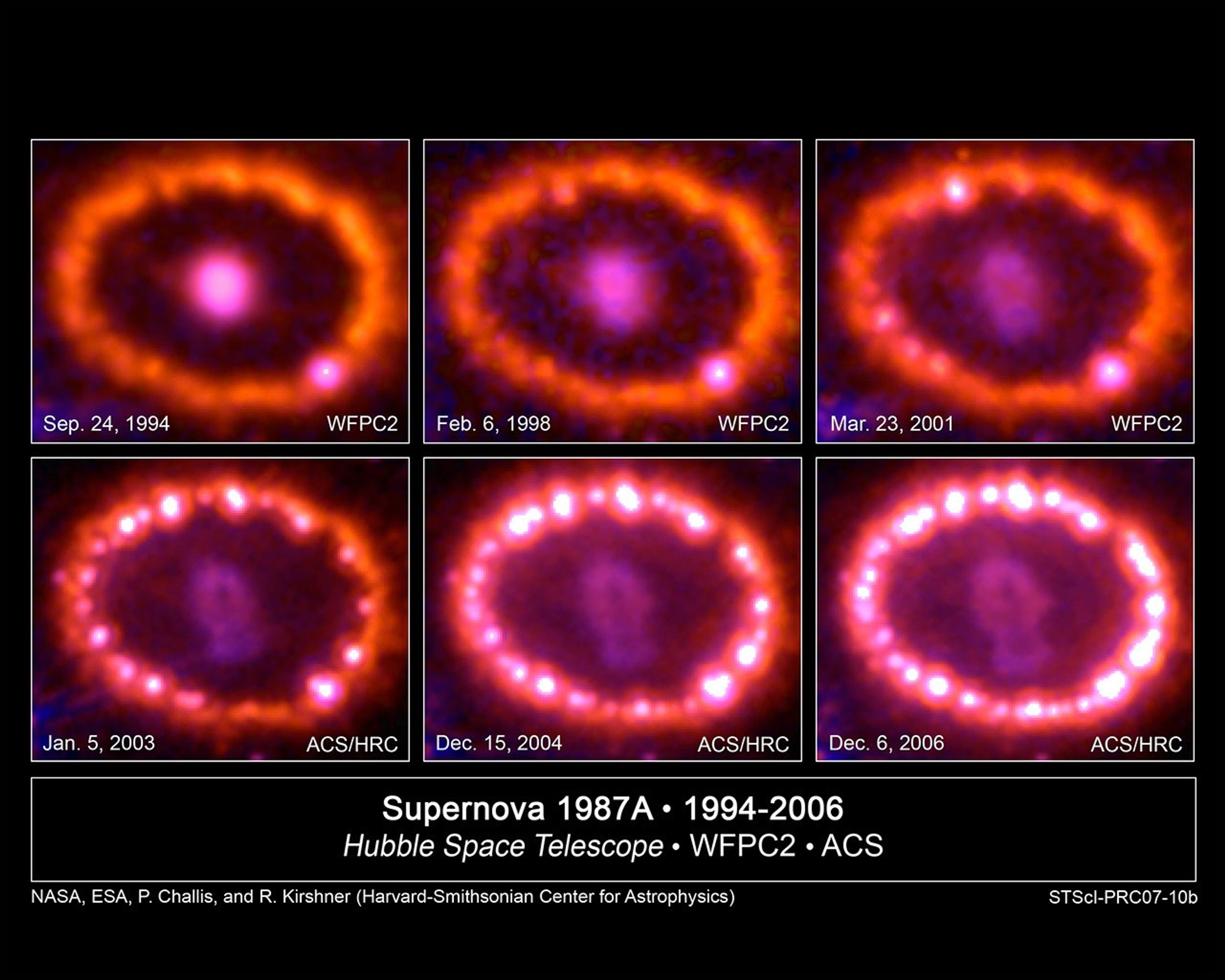
Hubble Images Chronicle the Inner Ring's Light Show
This photo album of images from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope shows a ring of gas beginning to glow around an exploded star. The stellar blast, called Supernova 1987A, was first spotted 20 years ago. The explosion is one of the brightest supernova blasts in more than 400 years....
Share
Details
Last Updated
Aug 17, 2025
Contact
Media
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov









































