1 min read
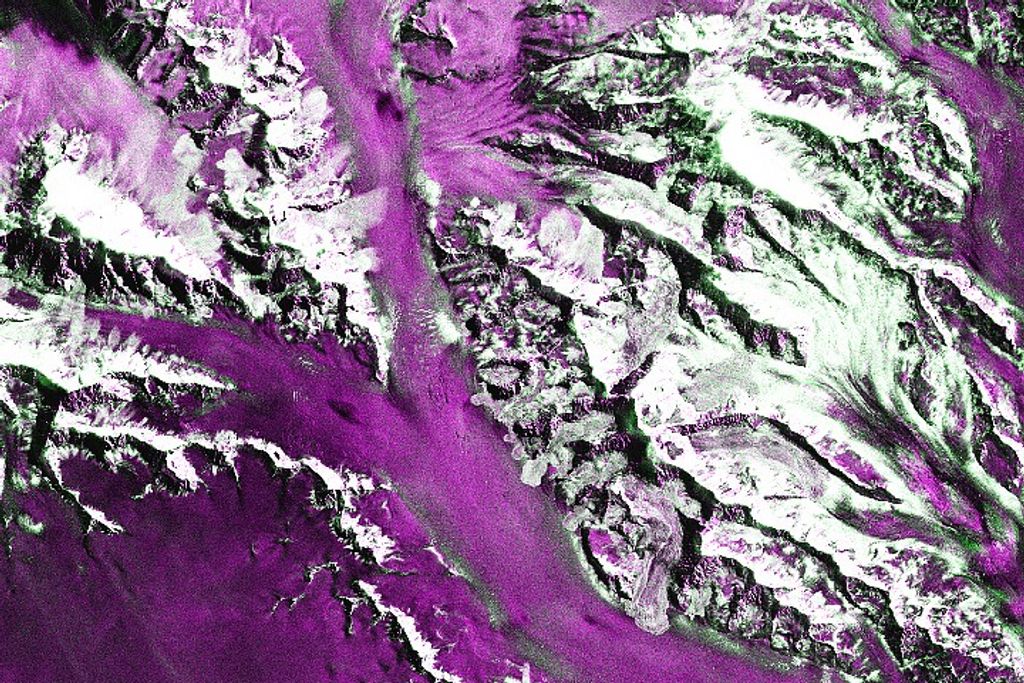
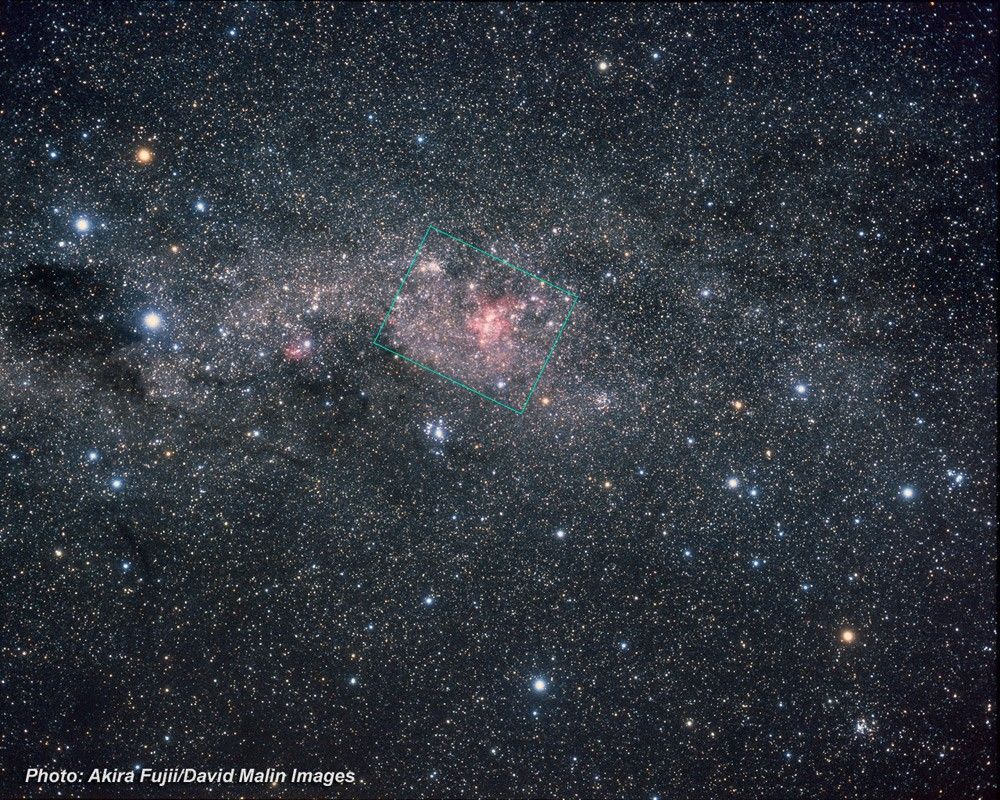
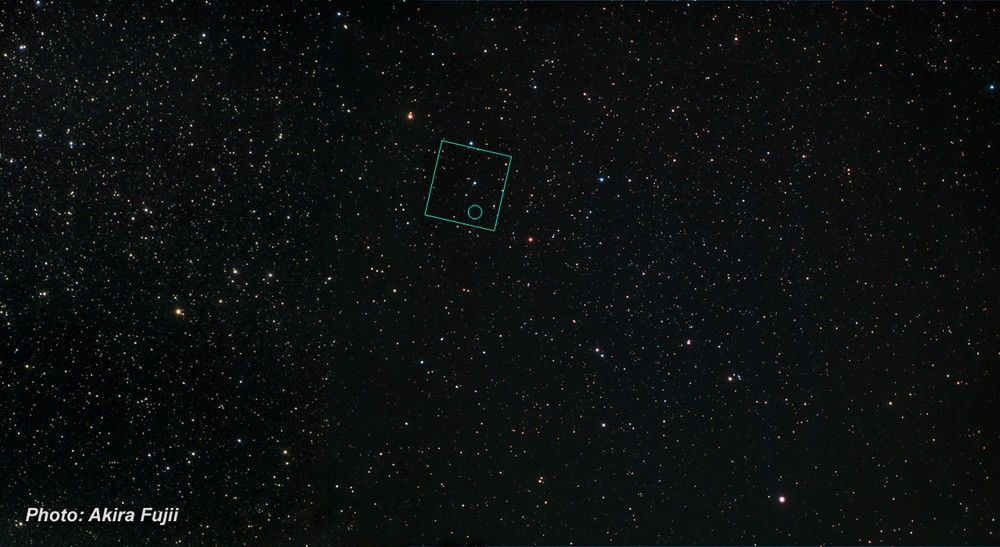
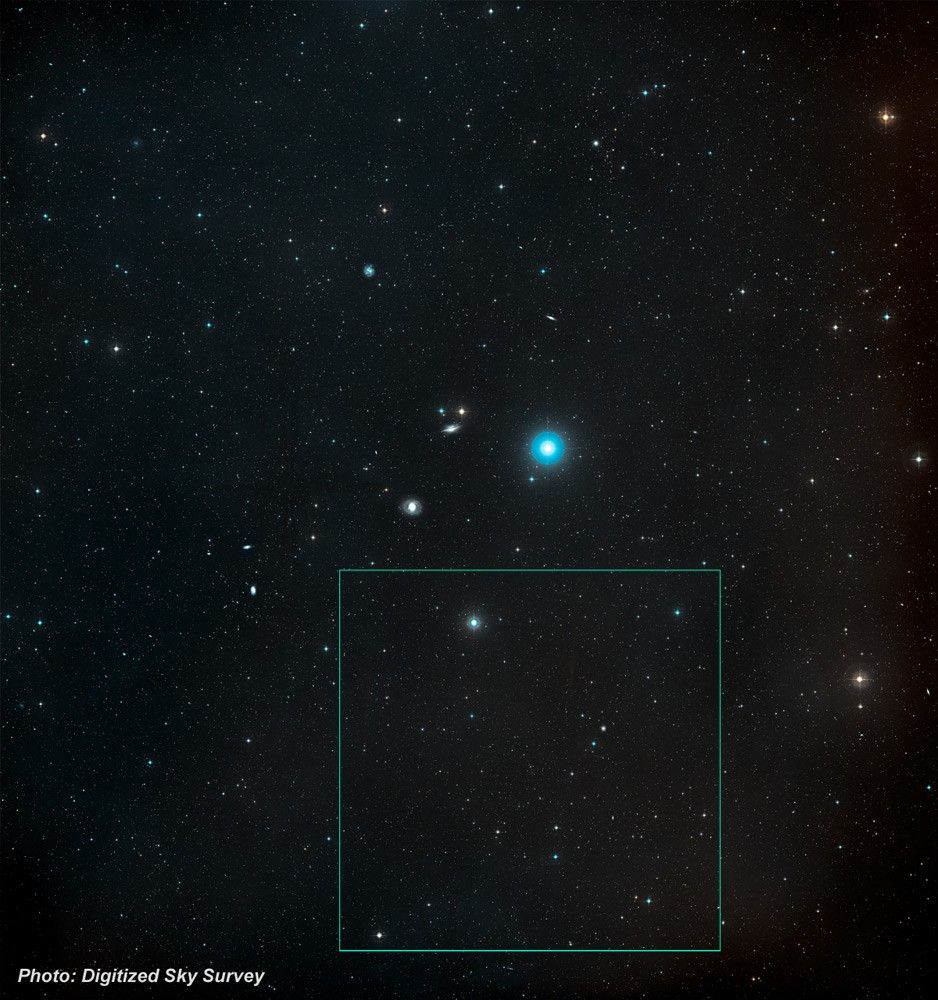
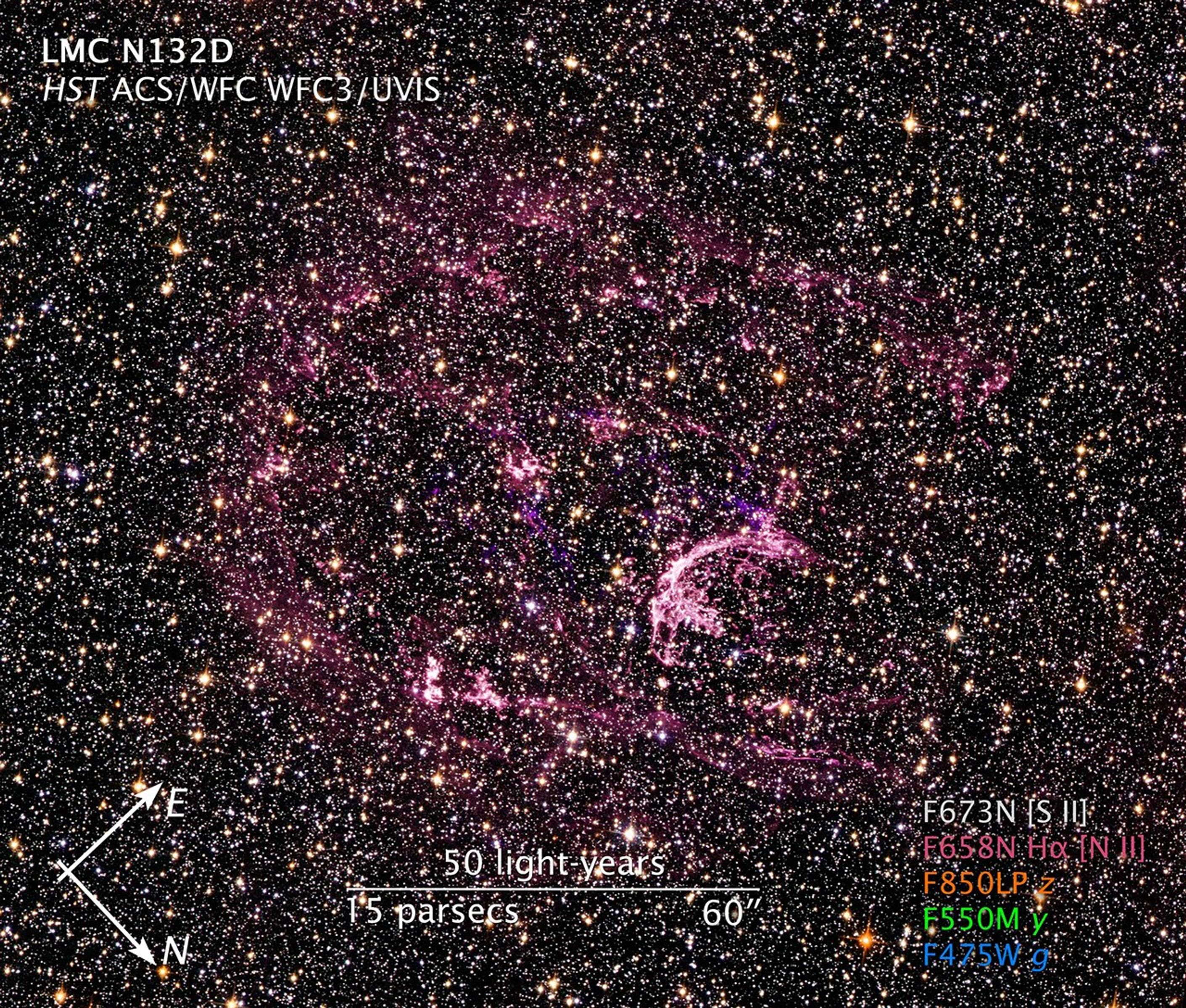
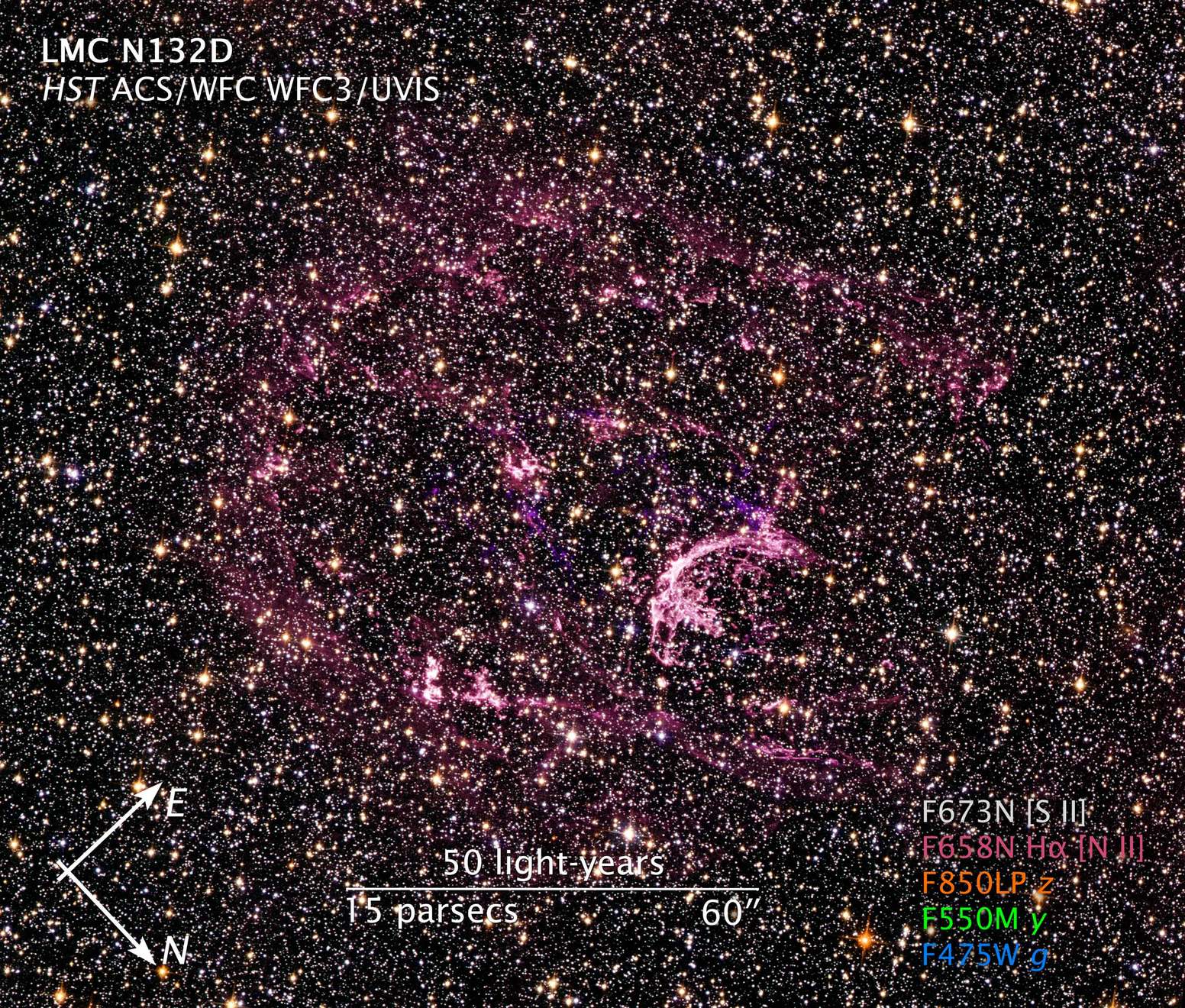
Supernova Remnant LMC N132D

About the Object
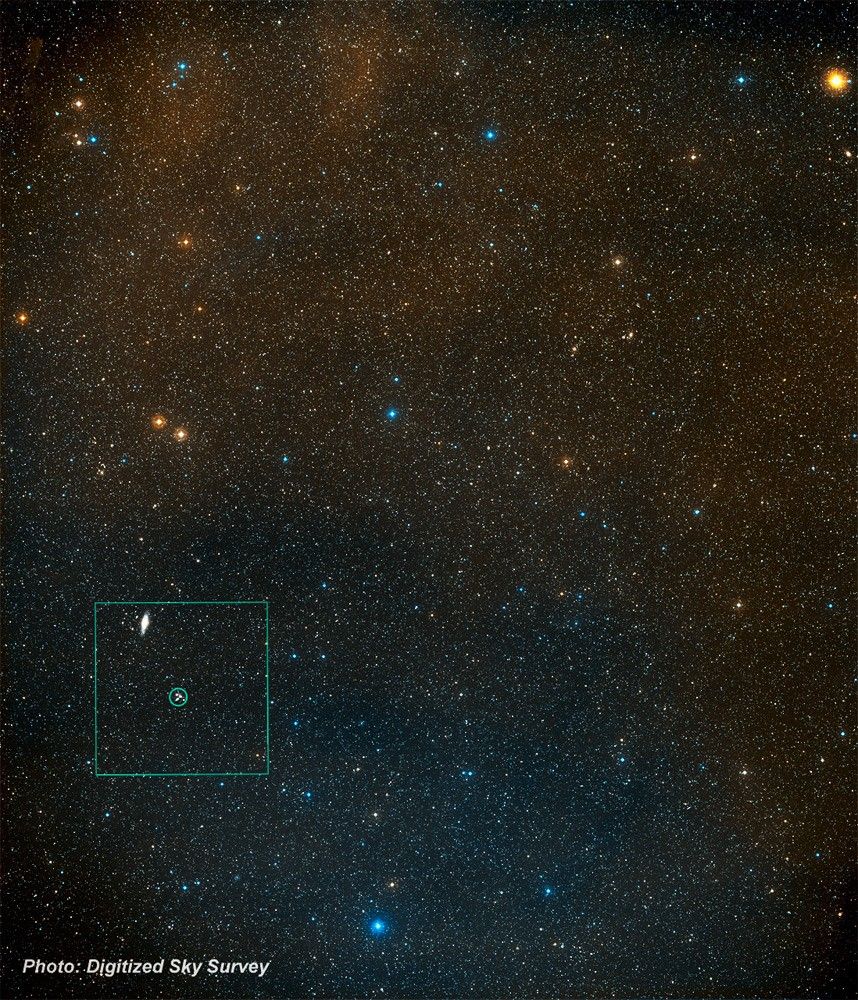
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.05h 25m 1.4s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-69° 38' 31.0"
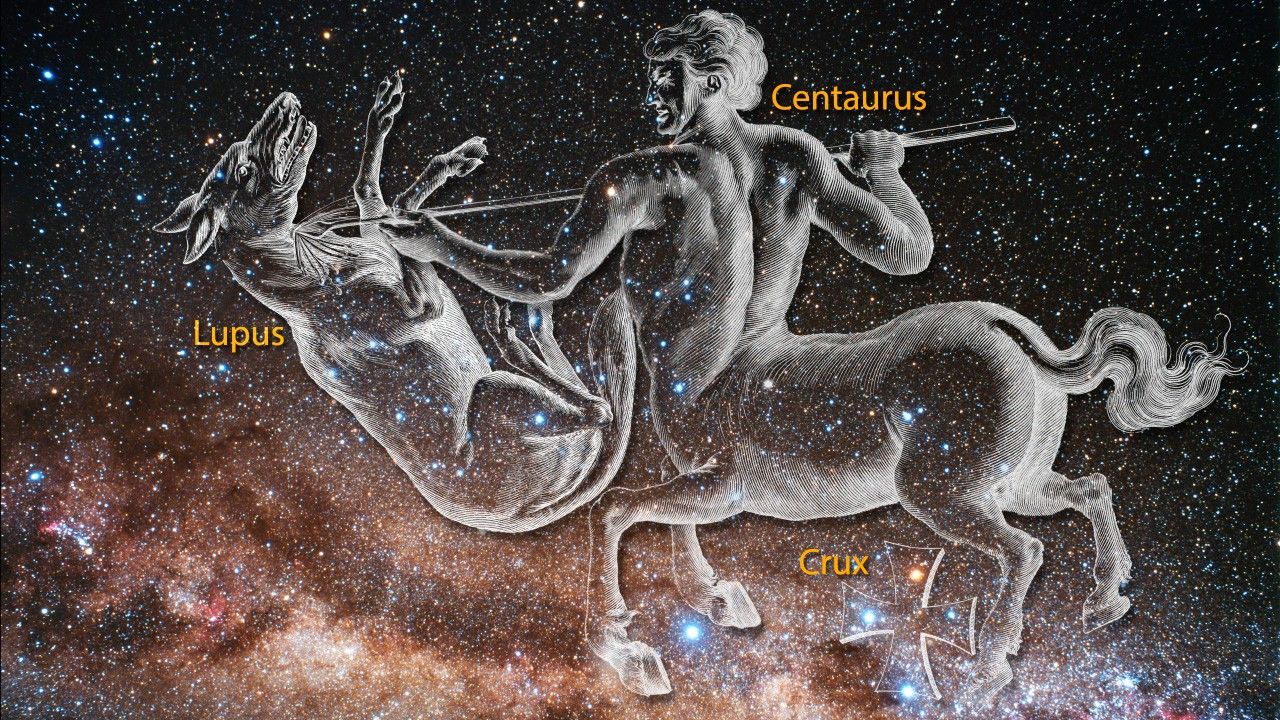
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Dorado
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.170,000 light-years (52,000 parsecs)
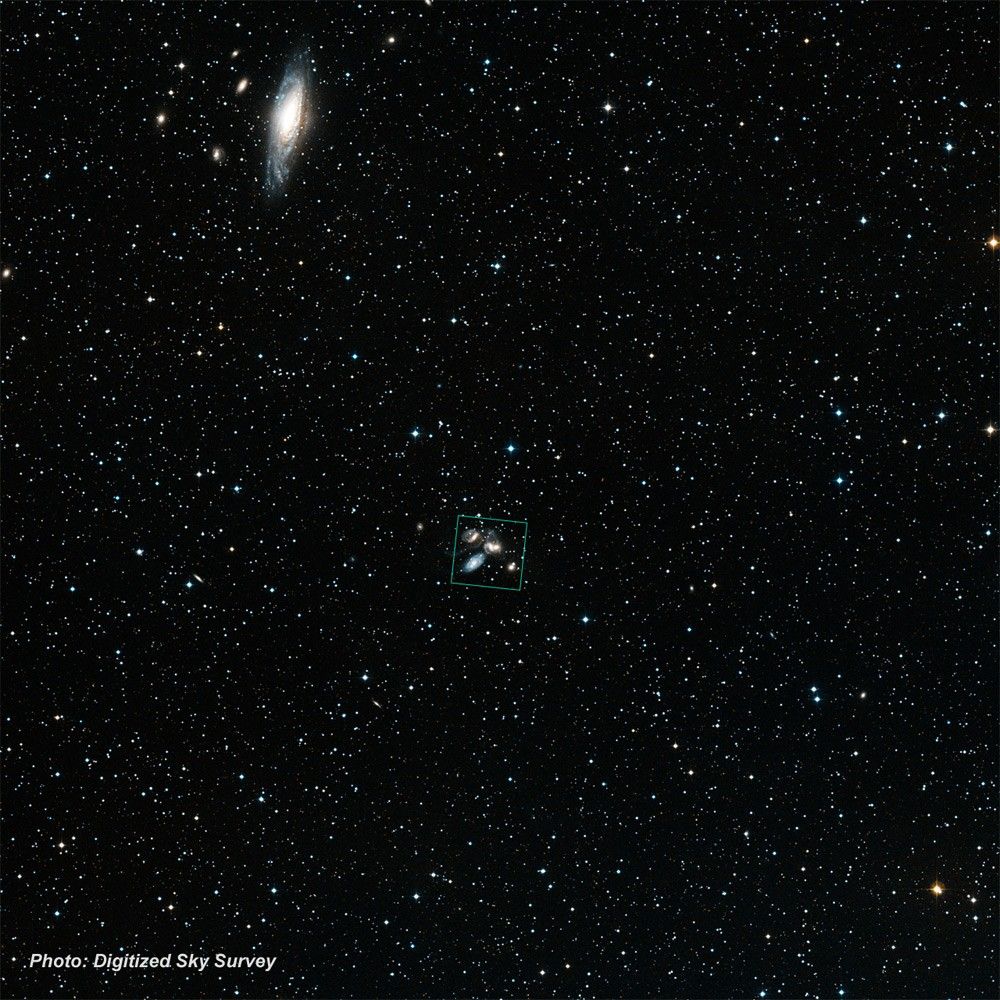
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.This image is 3 arcminutes (150 light-years or 46 parsecs) wide.
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The Hubble images/spectrum were created from data from proposal 11503: K. Noll (STScI) and J. Green, C. Froning, and K. France (University of Colorado, Boulder); and proposal 12001: J. Green (University of Colorado, Boulder). Acknowledgments for N132D Observers: K. Noll (STScI) and J. Green, C. Froning, and K. France (University of Colorado, Boulder) Data Analysis: J. Anderson and M. Mutchler (STScI), and C. Froning and J. Green (University of Colorado, Boulder) Image Composition: Z. Levay and L. Frattare (STScI) Text: L. Frattare, D. Weaver, and R. Villard (STScI) Illustrations: A. Feild and Z. Levay (STScI) Video Animation: G. Bacon (STScI) Science Consultants: M. Livio (STScI) and C. Froning and J. Green (University of Colorado, Boulder) - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS/WFC and HST>WFC3/UVIS
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.January 21-22, 2004 (ACS) and August 2, 2009 (WFC3)
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.ACS: F673N WFC3: F475W (g), F550M (y) F658N (H-alpha + [N II]), and F850LP (z)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.LMC N132D, SNR J052501-693842
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Supernova Remnant
- Release DateSeptember 9, 2009
- Science ReleaseHubble Opens New Eyes on the Universe
- Credit

The image is a composite of separate exposures made by the WFC3 and ACS instruments on the Hubble Space Telescope. Five filters were used to sample broad and narrow wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic image. In this case, the assigned colors are: Pink: F850LP (z) Orange: F658N (H-alpha + [N II]) White: F673N ([S II]) Green: F550M (y) Blue: F475W (g)

Related Images & Videos

Hubble Servicing Mission 4 Early Release Observations
These four images are among the first observations made by the new Wide Field Camera 3 aboard the upgraded NASA Hubble Space Telescope. The image at top left shows NGC 6302, a butterfly-shaped nebula surrounding a dying star. At top right is a picture of a clash among members of...

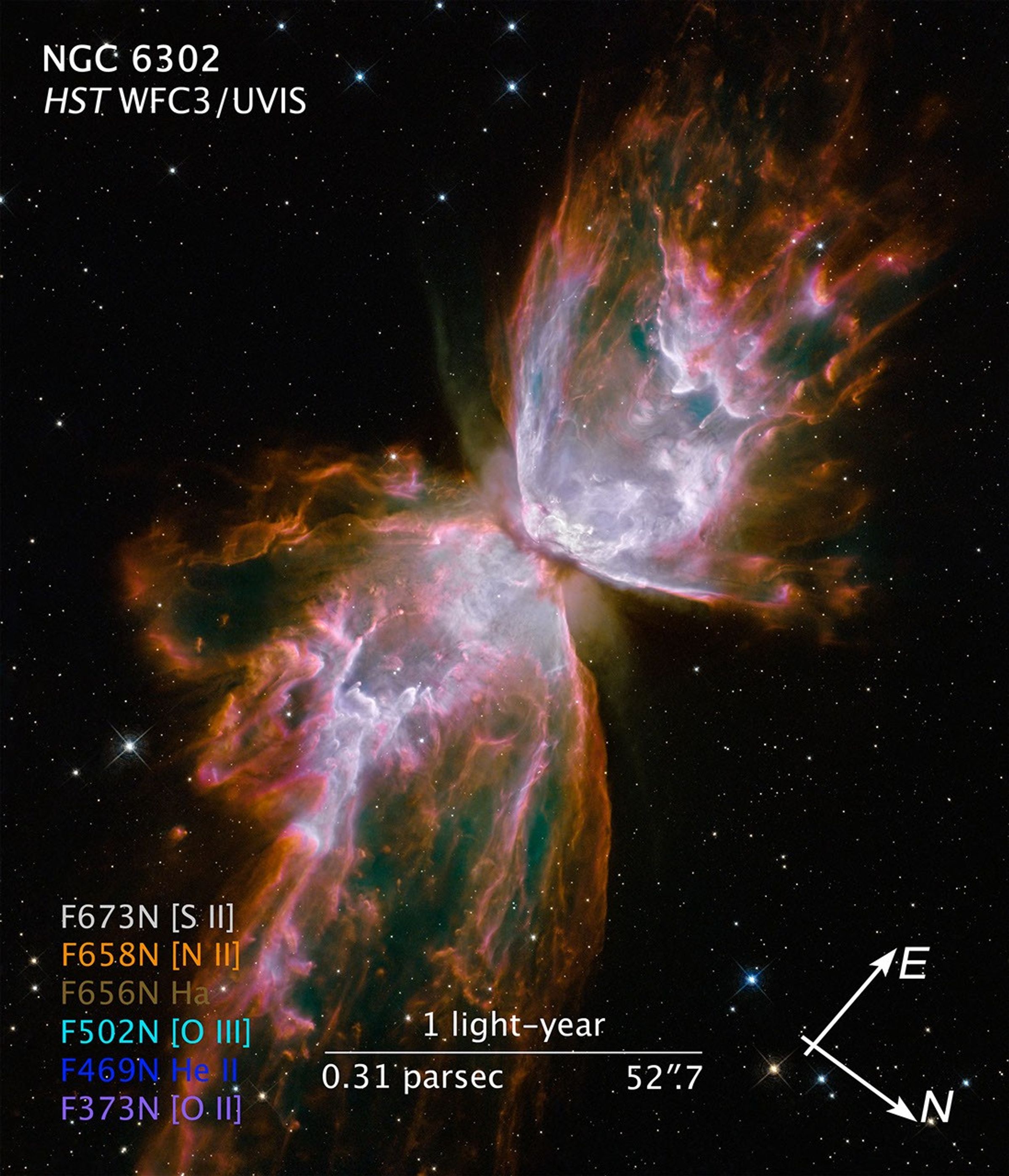
Butterfly Emerges from Stellar Demise in Planetary Nebula NGC 6302
This celestial object looks like a delicate butterfly. But it is far from serene. What resemble dainty butterfly wings are actually roiling cauldrons of gas heated to more than 36,000 degrees Fahrenheit. The gas is tearing across space at more than 600,000 miles an hour – fast...
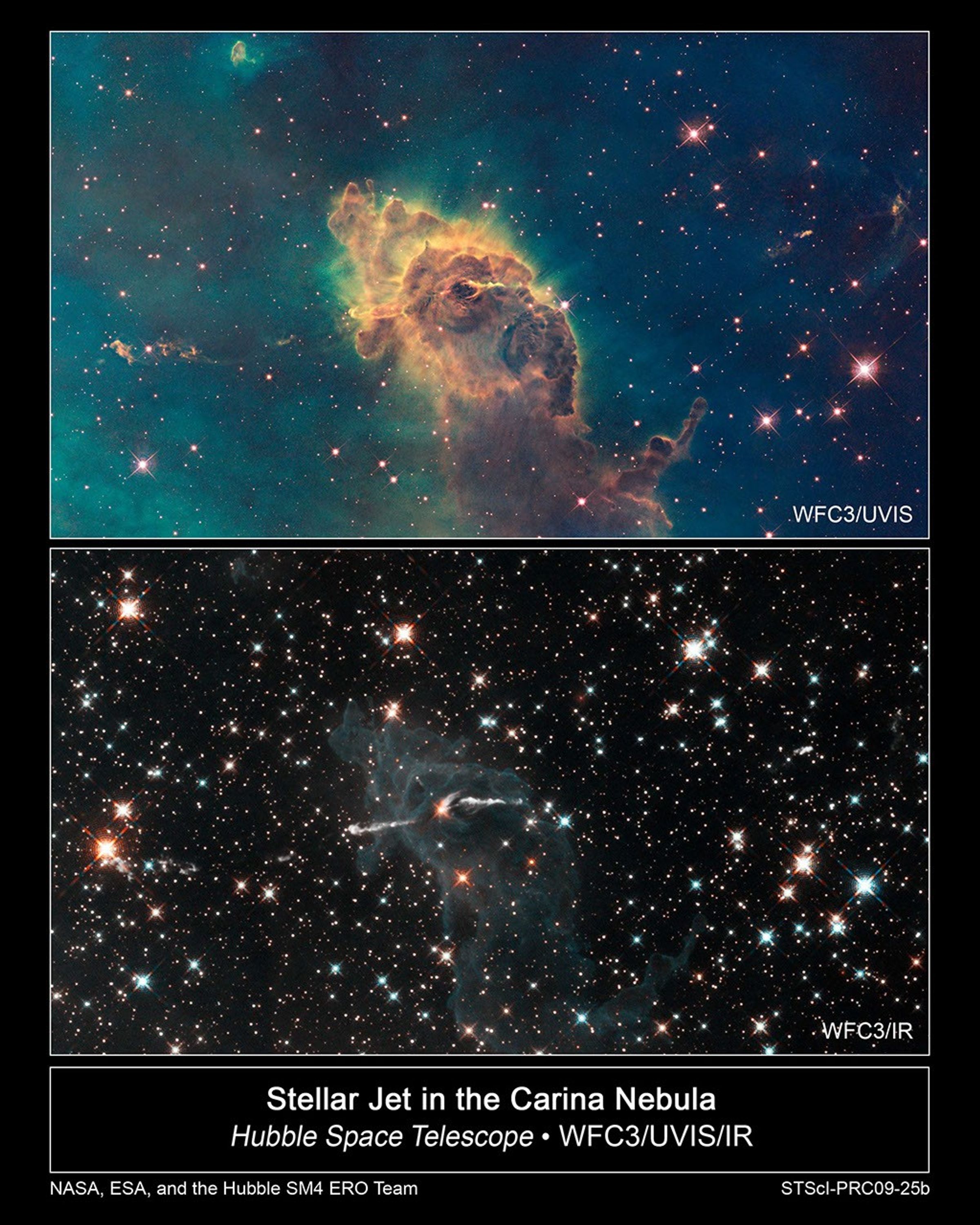

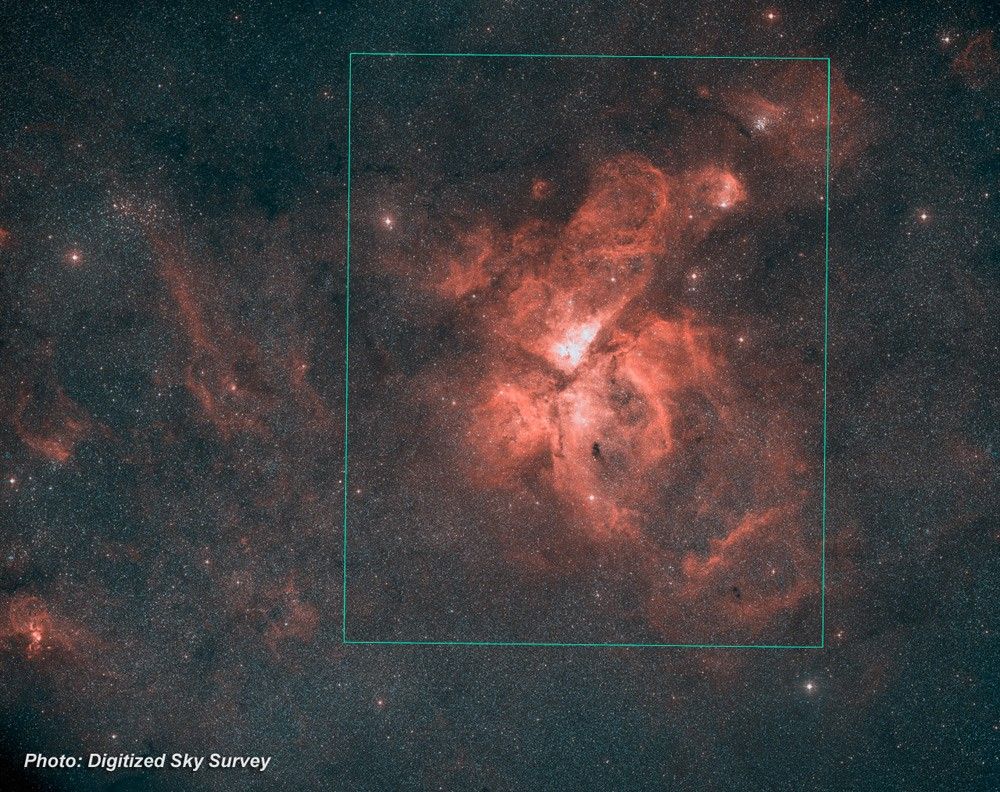
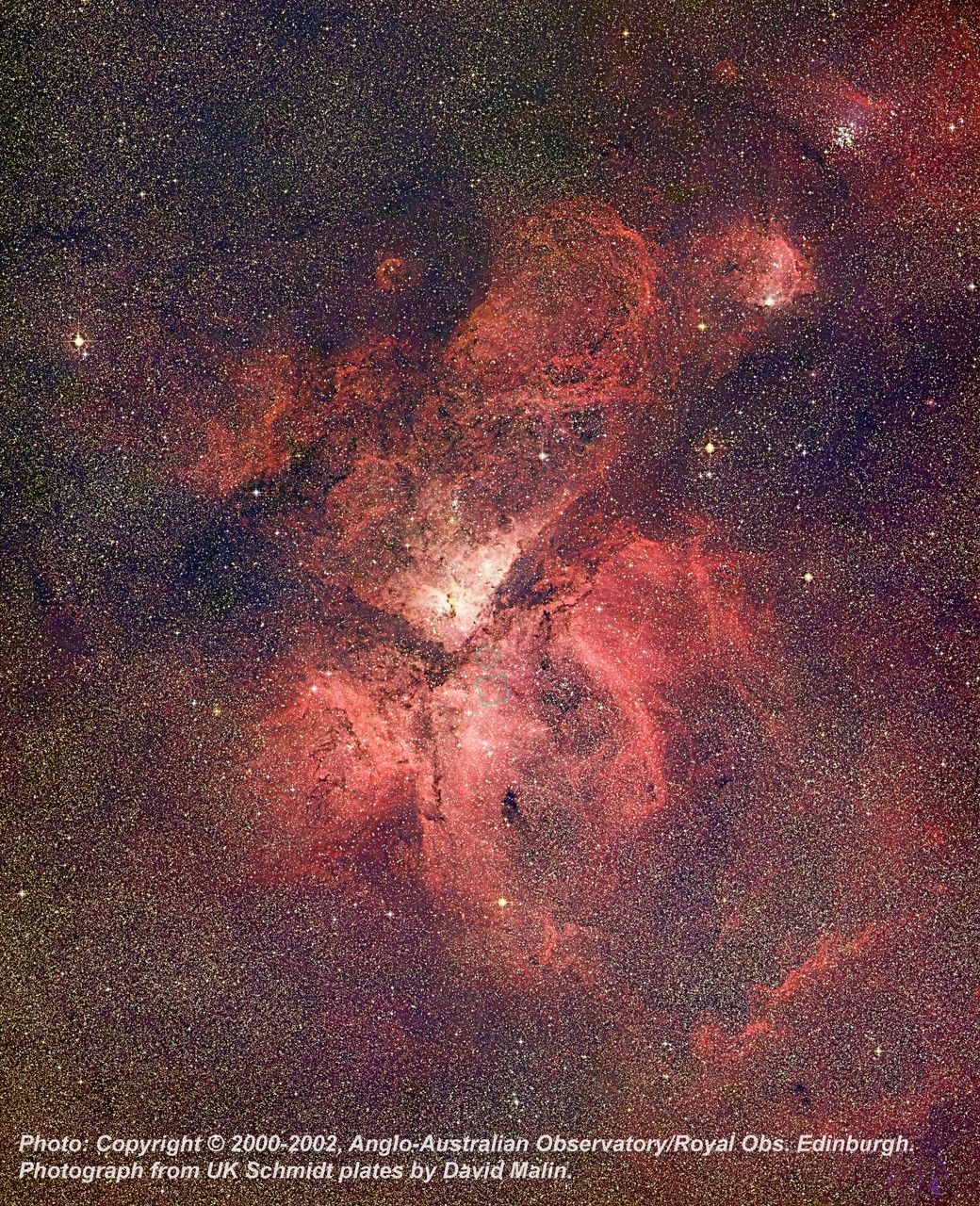
Stars Bursting to Life in the Chaotic Carina Nebula
These two images of a huge pillar of star birth demonstrate how observations taken in visible and in infrared light by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope reveal dramatically different and complementary views of an object. The pictures demonstrate one example of the broad wavelength...

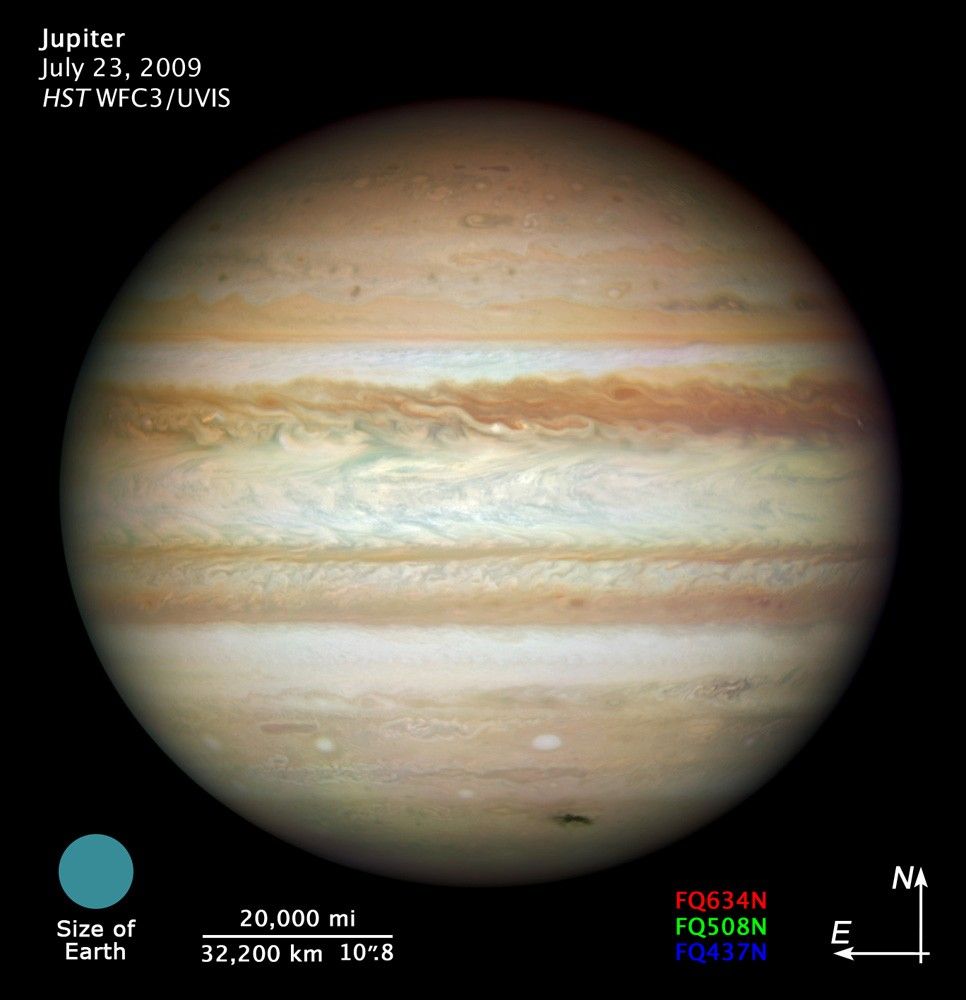
Collision Leaves Giant Jupiter Bruised
This Hubble picture, taken on July 23, is the first full-disk natural-color image of Jupiter made with Hubble's new camera, the Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3). It is the sharpest visible-light picture of Jupiter since the New Horizons spacecraft flew by that planet in 2007. Each...
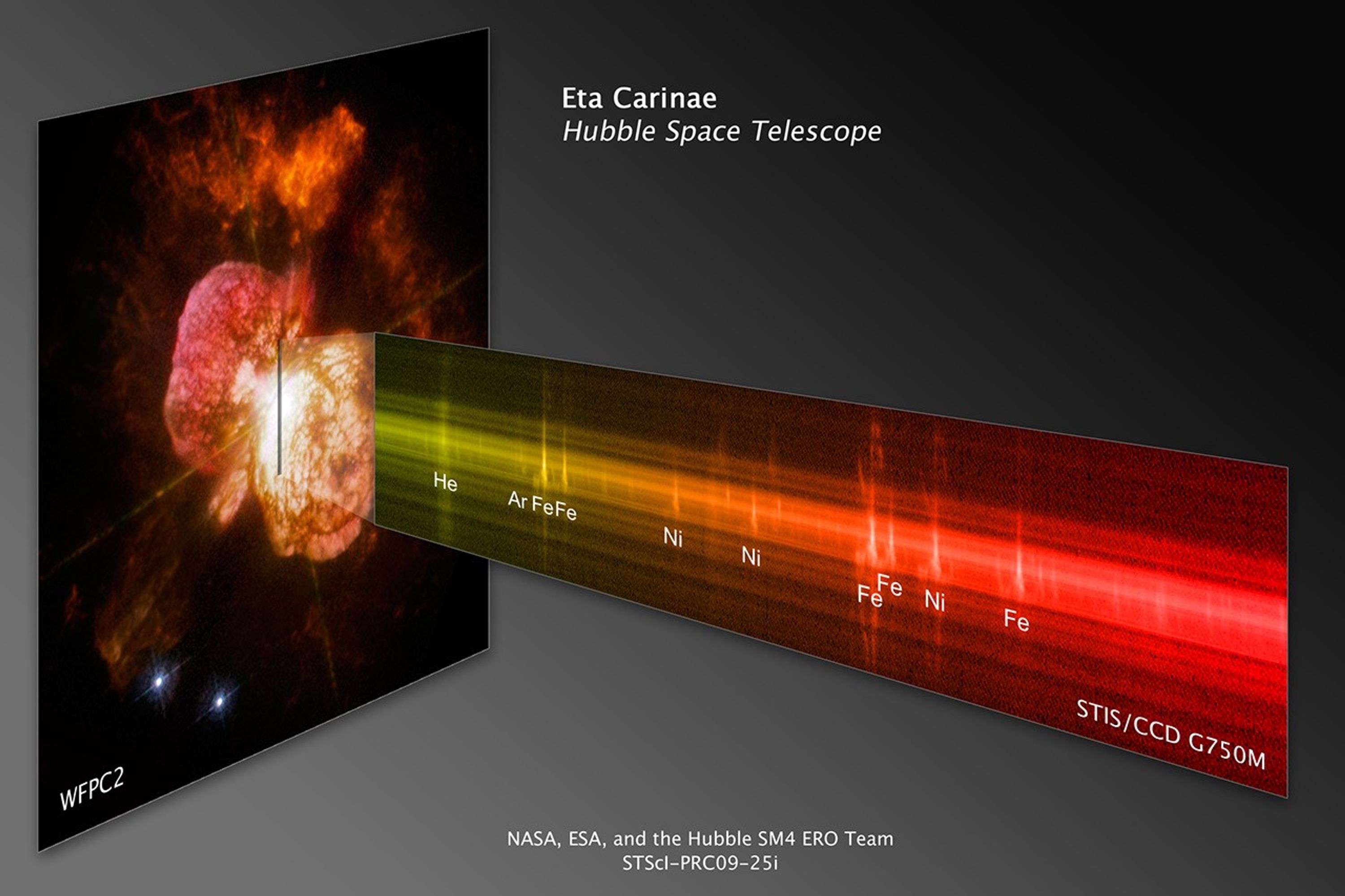
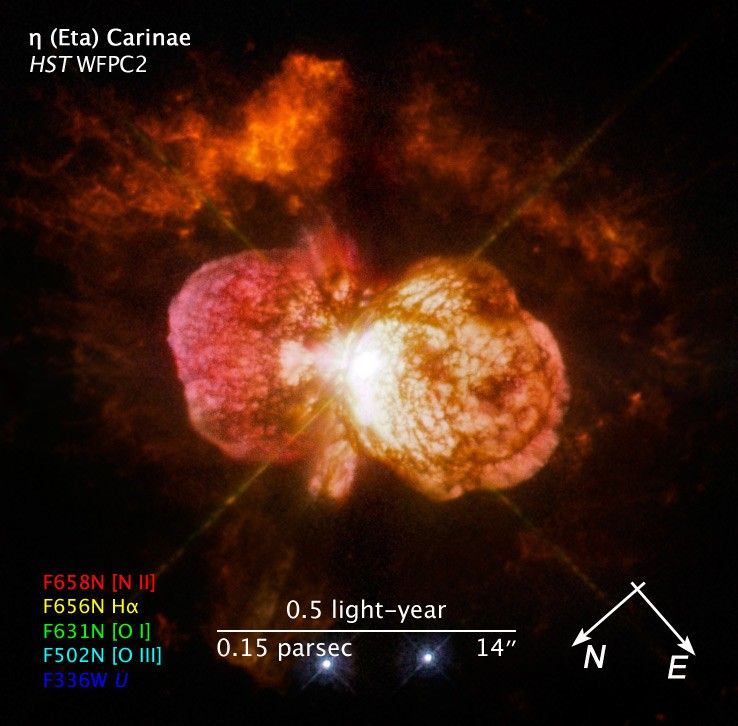
Probing the Last Gasps of the Doomed Star Eta Carinae
The signature balloon-shaped clouds of gas blown from a pair of massive stars called Eta Carinae have tantalized astronomers for decades. Eta Carinae has a volatile temperament, prone to violent outbursts over the past 200 years. Observations by the newly repaired Space...

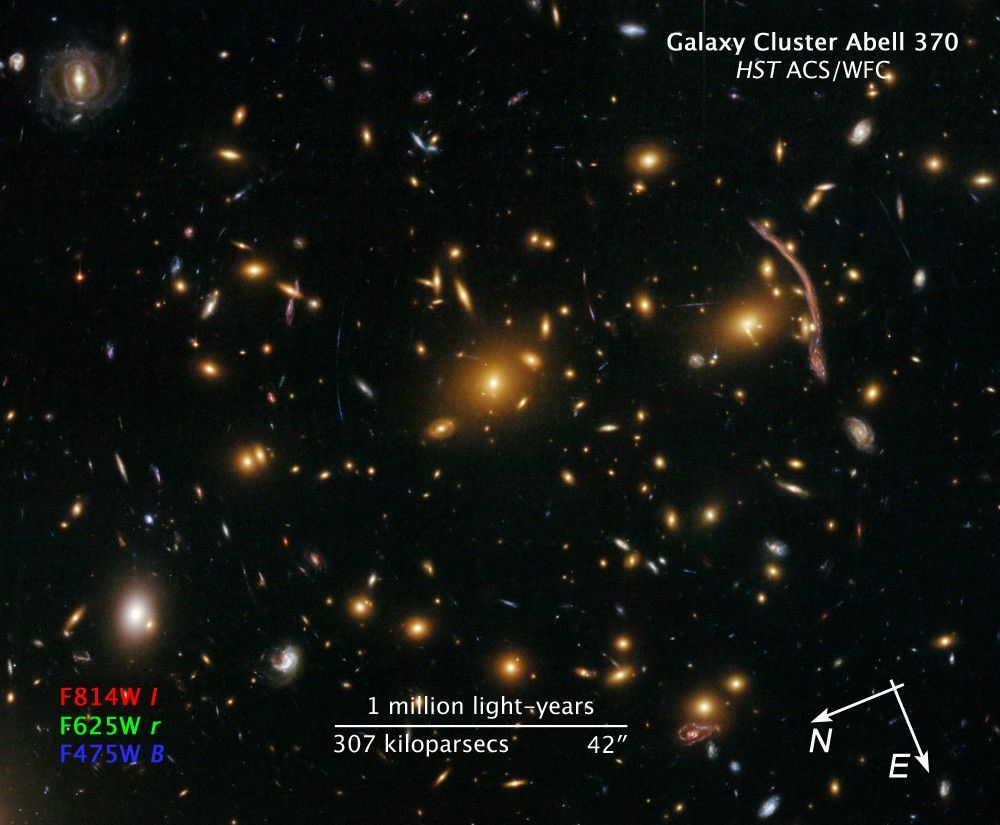
Gravitational Lensing in Galaxy Cluster Abell 370
Hubble Space Telescope's newly repaired Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) has peered nearly 5 billion light-years away to resolve intricate details in the galaxy cluster Abell 370. Abell 370 is one of the very first galaxy clusters where astronomers observed the phenomenon of...
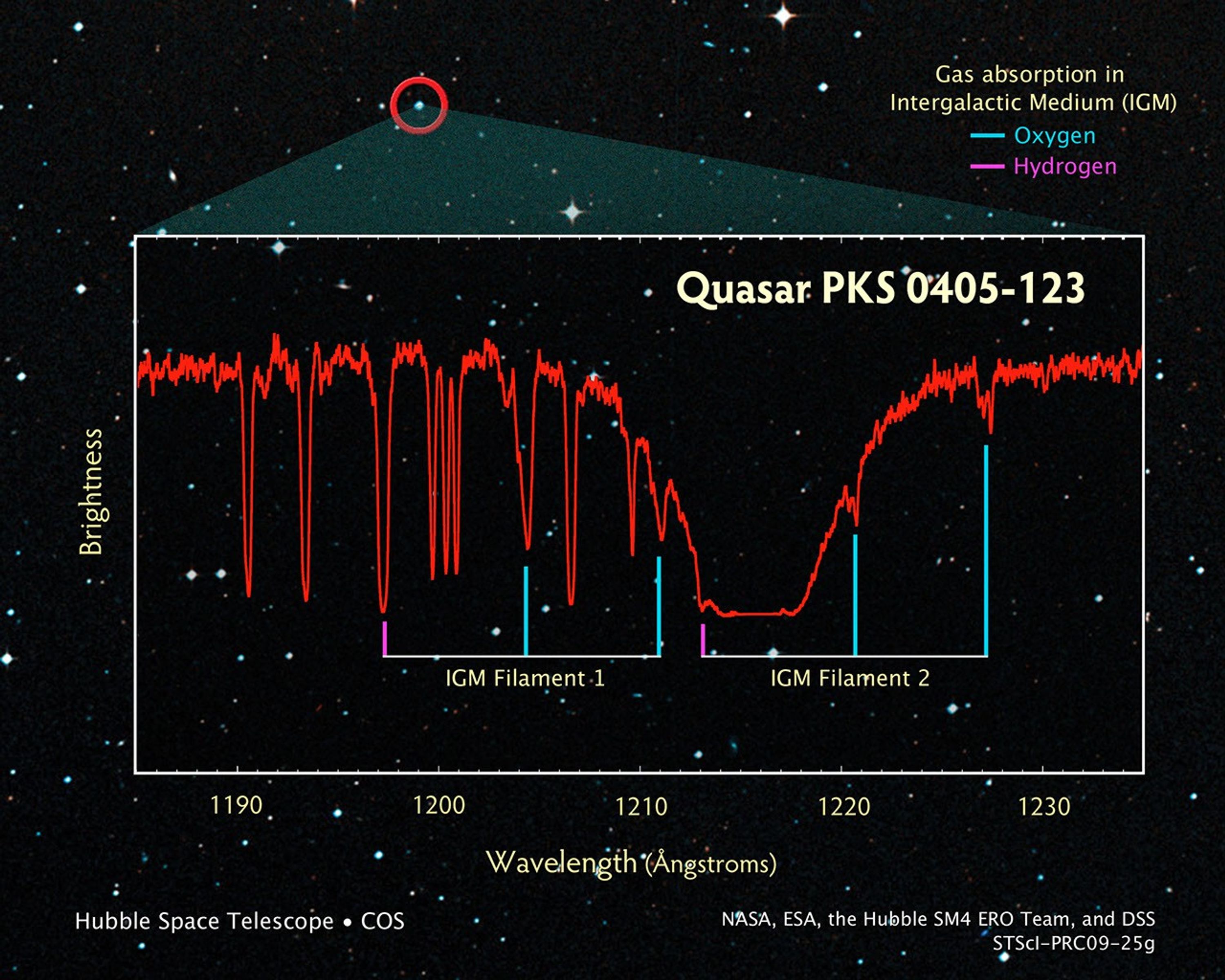
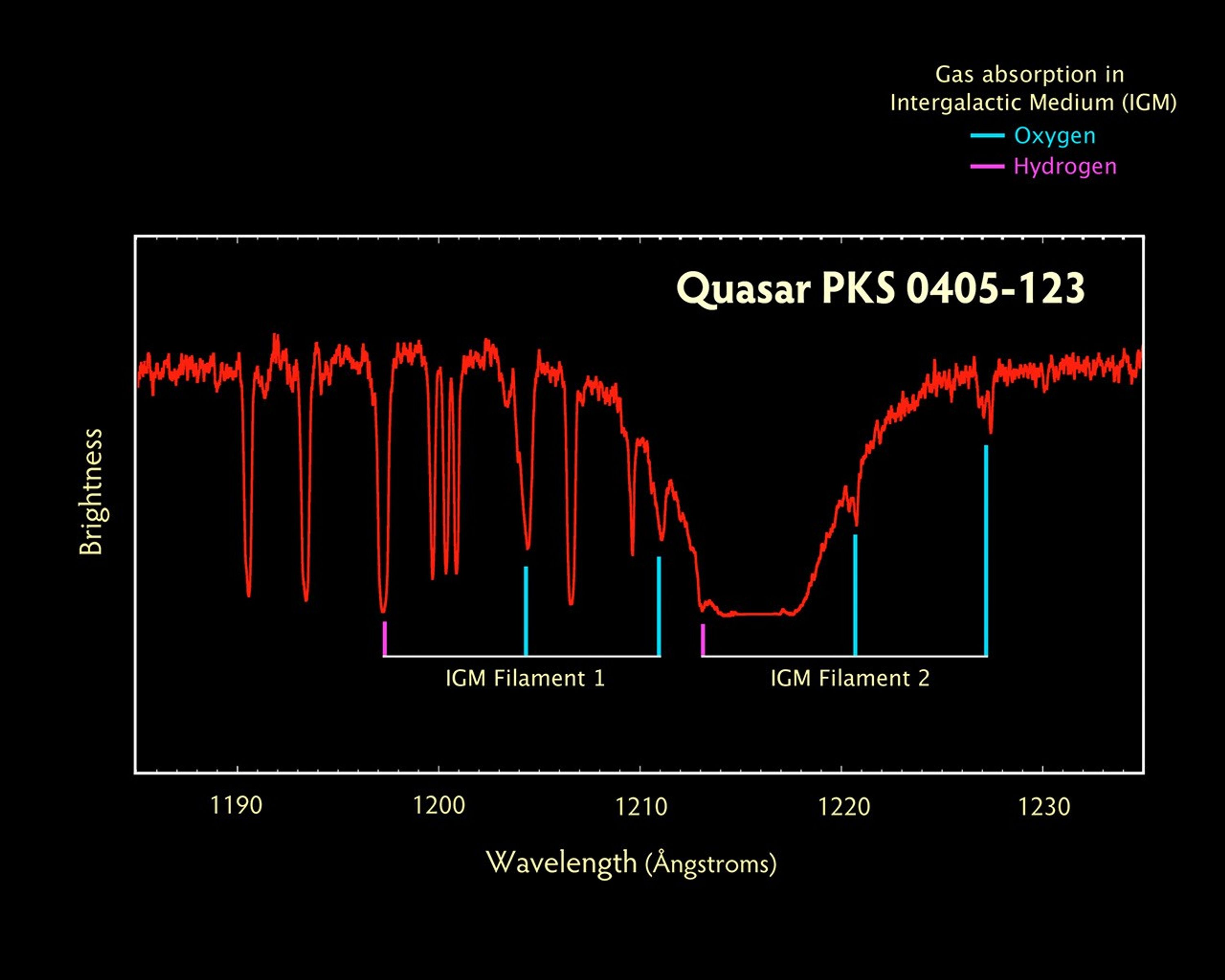
Fingerprinting the Distant Universe Using the Light from Quasar PKS 0405-123
Using a distant quasar as a cosmic flashlight, a new instrument aboard NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has begun probing the invisible, skeletal structure of the universe. Called the cosmic web, it is the diffuse, faint gas located in the space between galaxies. More than half of...

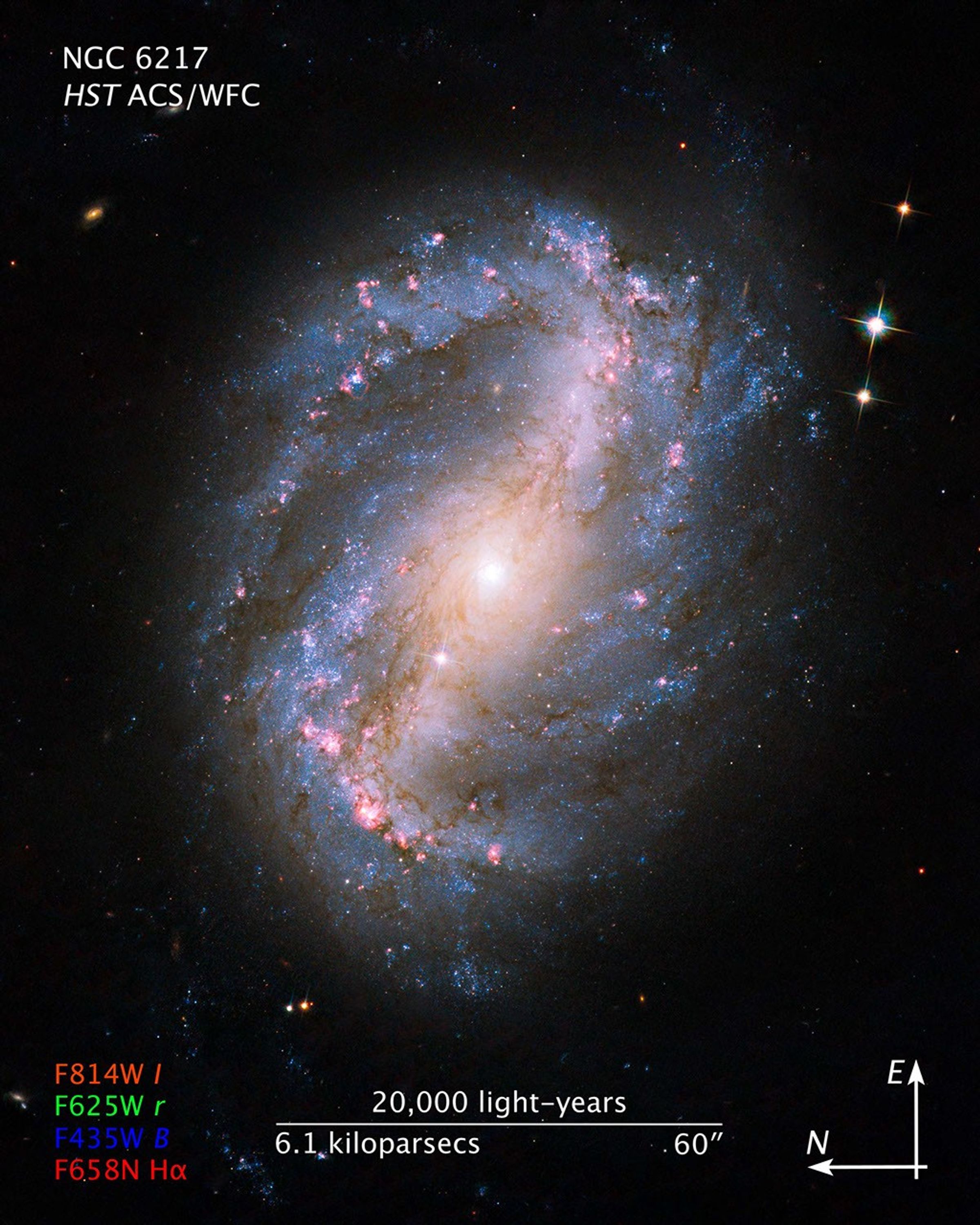
Barred Spiral Galaxy NGC 6217
This is the first image of a celestial object taken with the newly repaired Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS). The camera was restored to operation during the STS-125 servicing mission to upgrade the Hubble Space Telescope. The barred spiral galaxy NGC 6217 was photographed on...
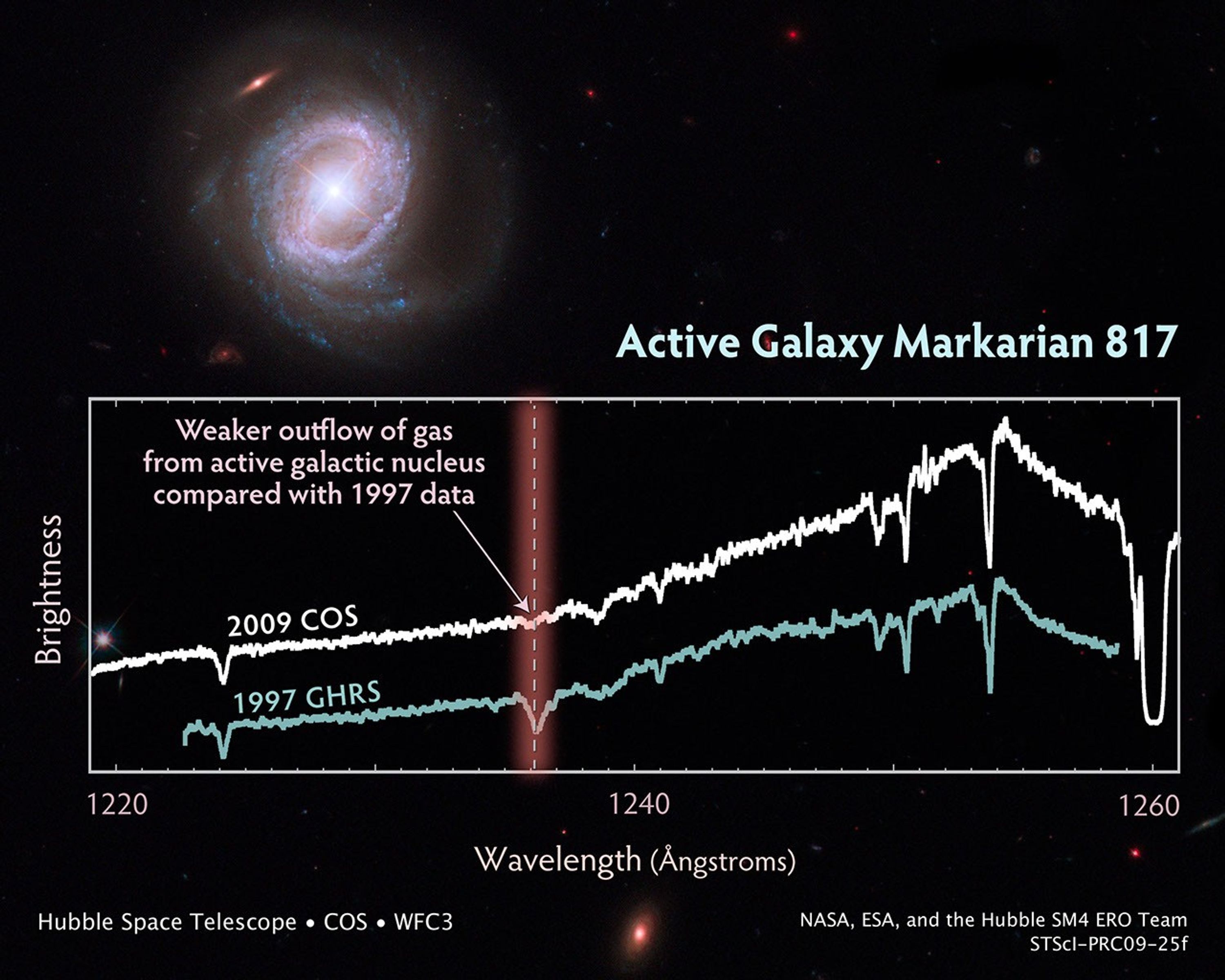
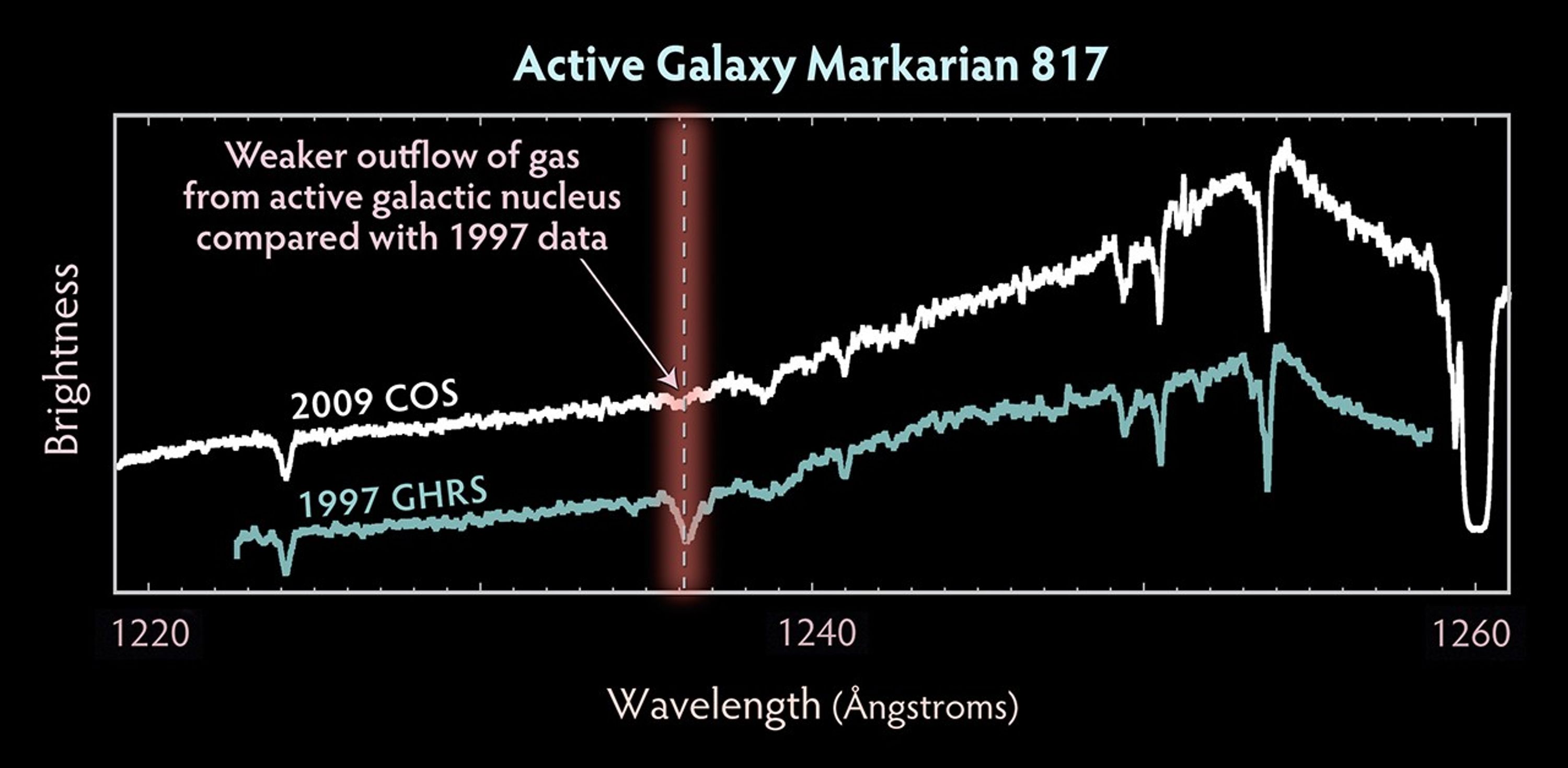
Capturing the Spectacular Outflow from Markarian 817
Rings of brilliant blue stars encircle the bright, active core of this spiral galaxy, whose monster black hole is blasting material into space at 9 million miles an hour. Viewed nearly face-on, the galaxy, called Markarian 817, shows intense star-forming regions and dark bands...
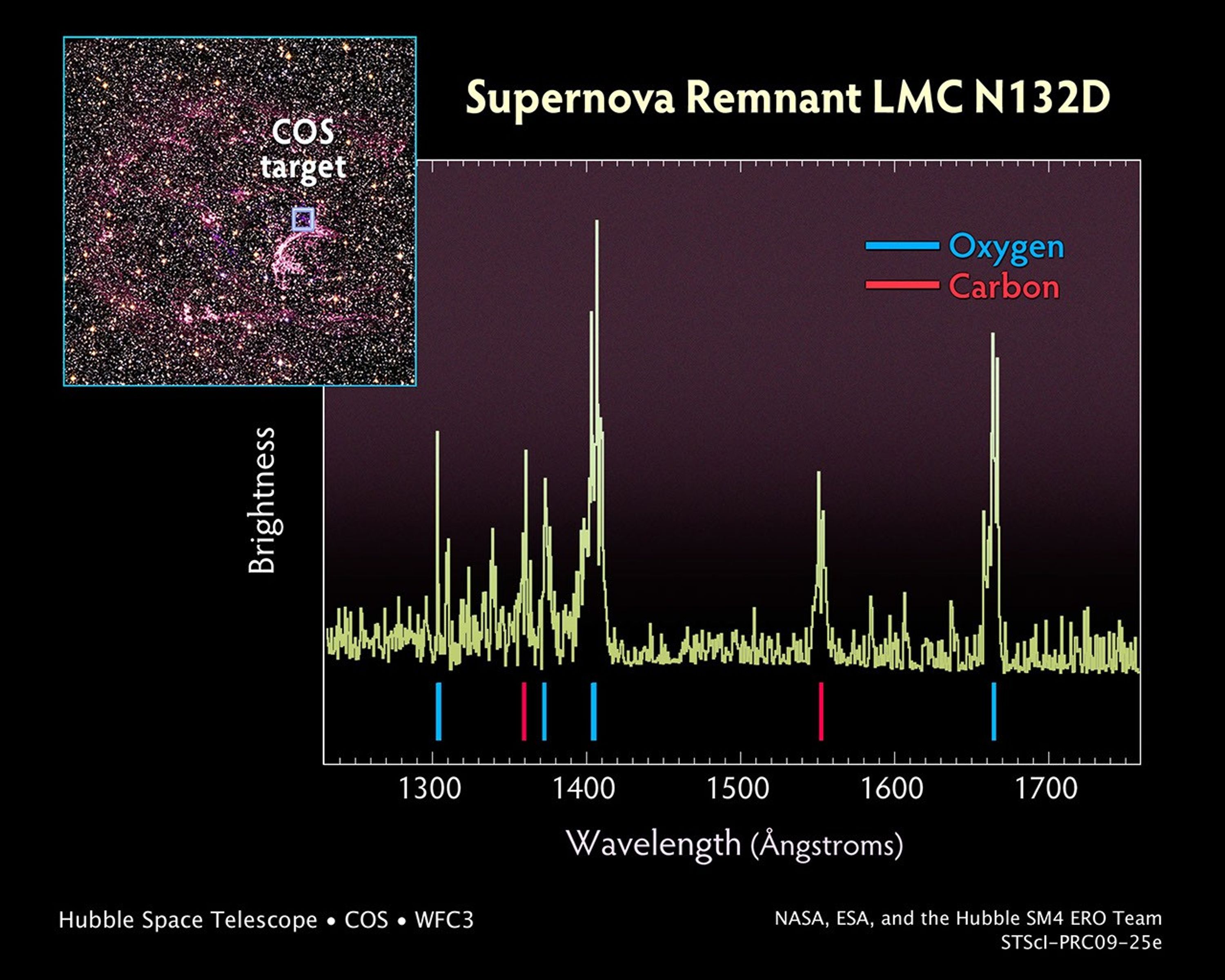
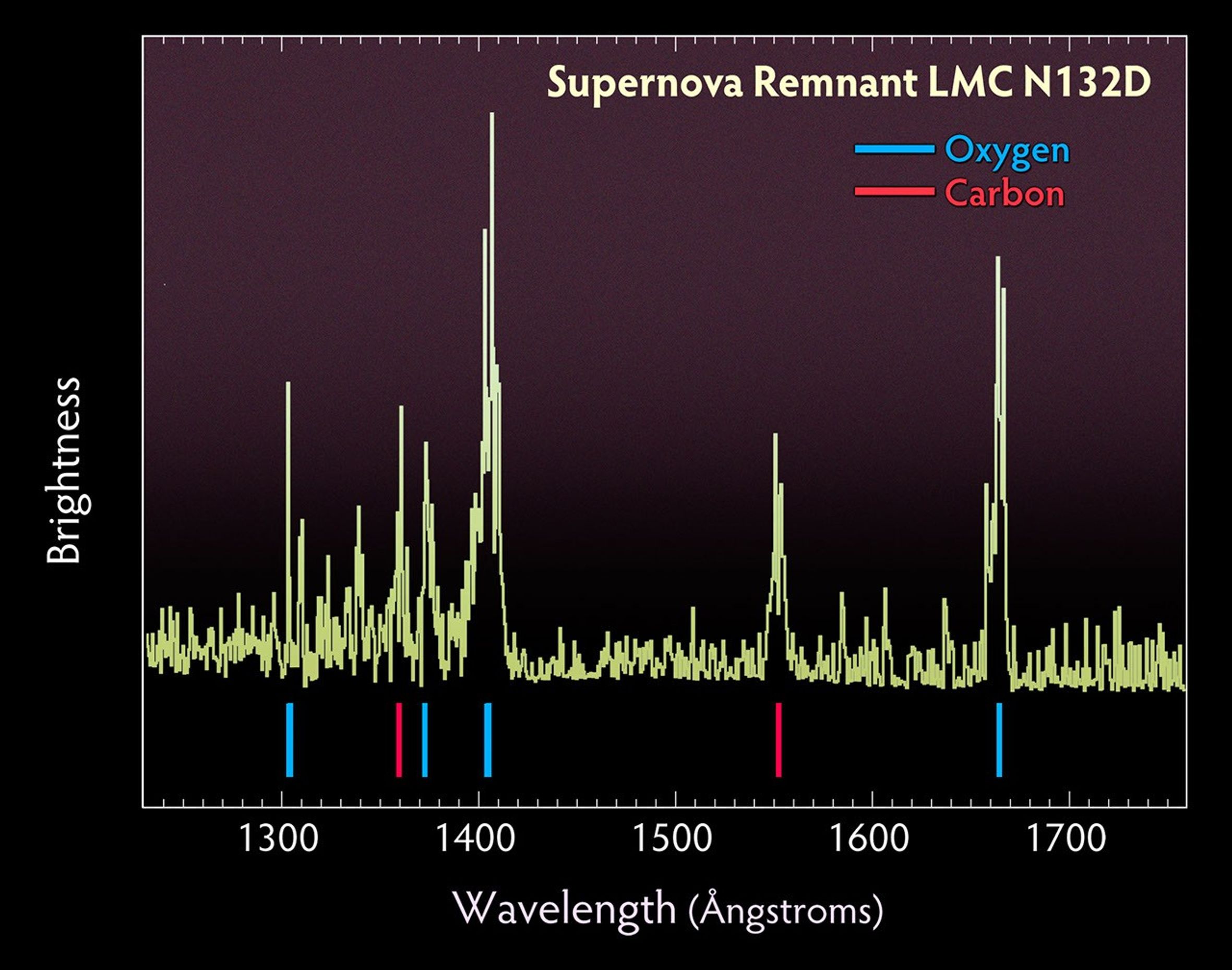
Probing the Tattered Remains of Supernova Remnant N132D
The wispy, glowing, magenta structures in this NASA Hubble Space Telescope image are the remains of a star 10 to 15 times the mass of the Sun that we would have seen exploding as a supernova 3,000 years ago. The remnant's fast-moving gas is plowing into the surrounding gas of...

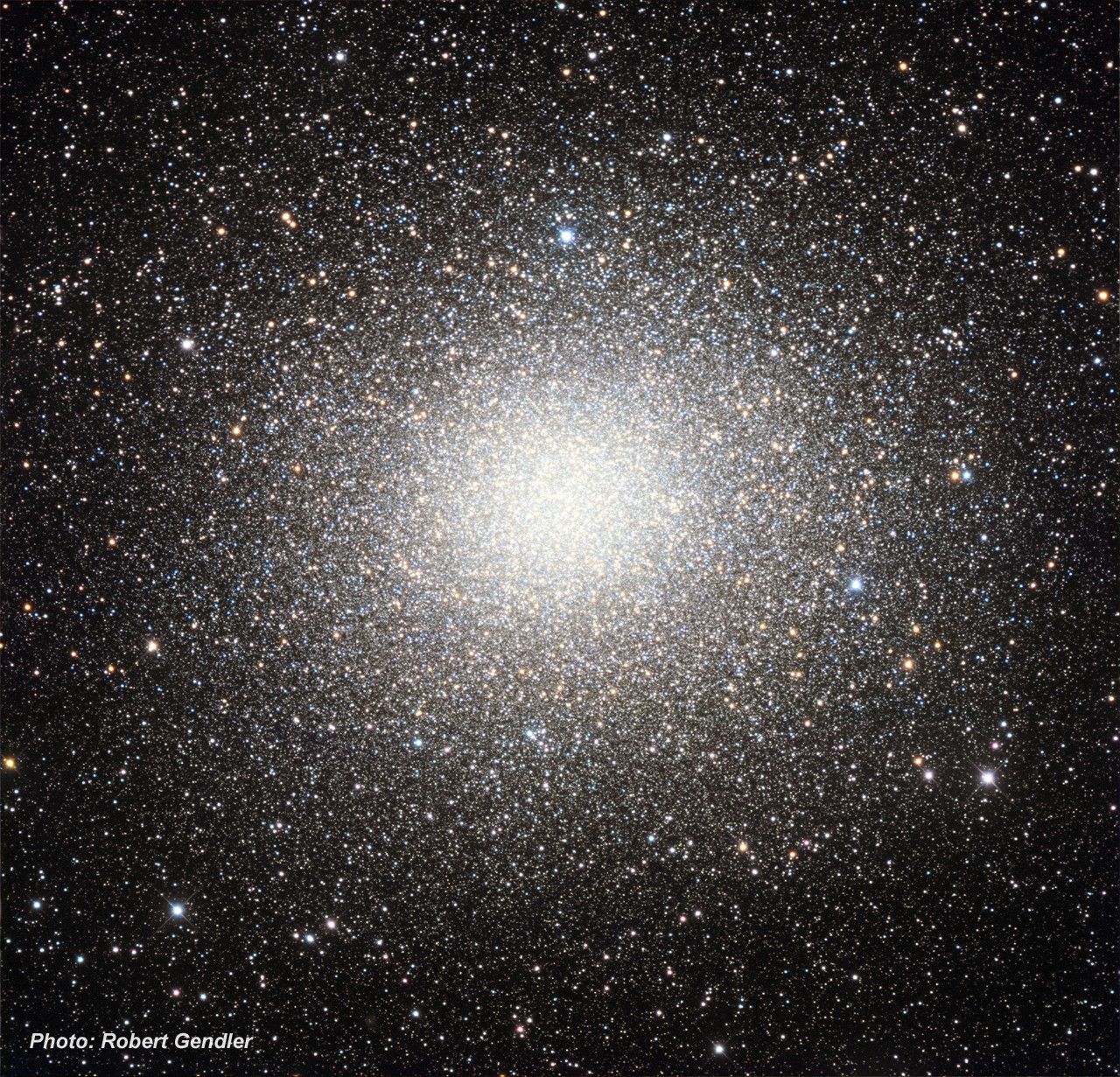
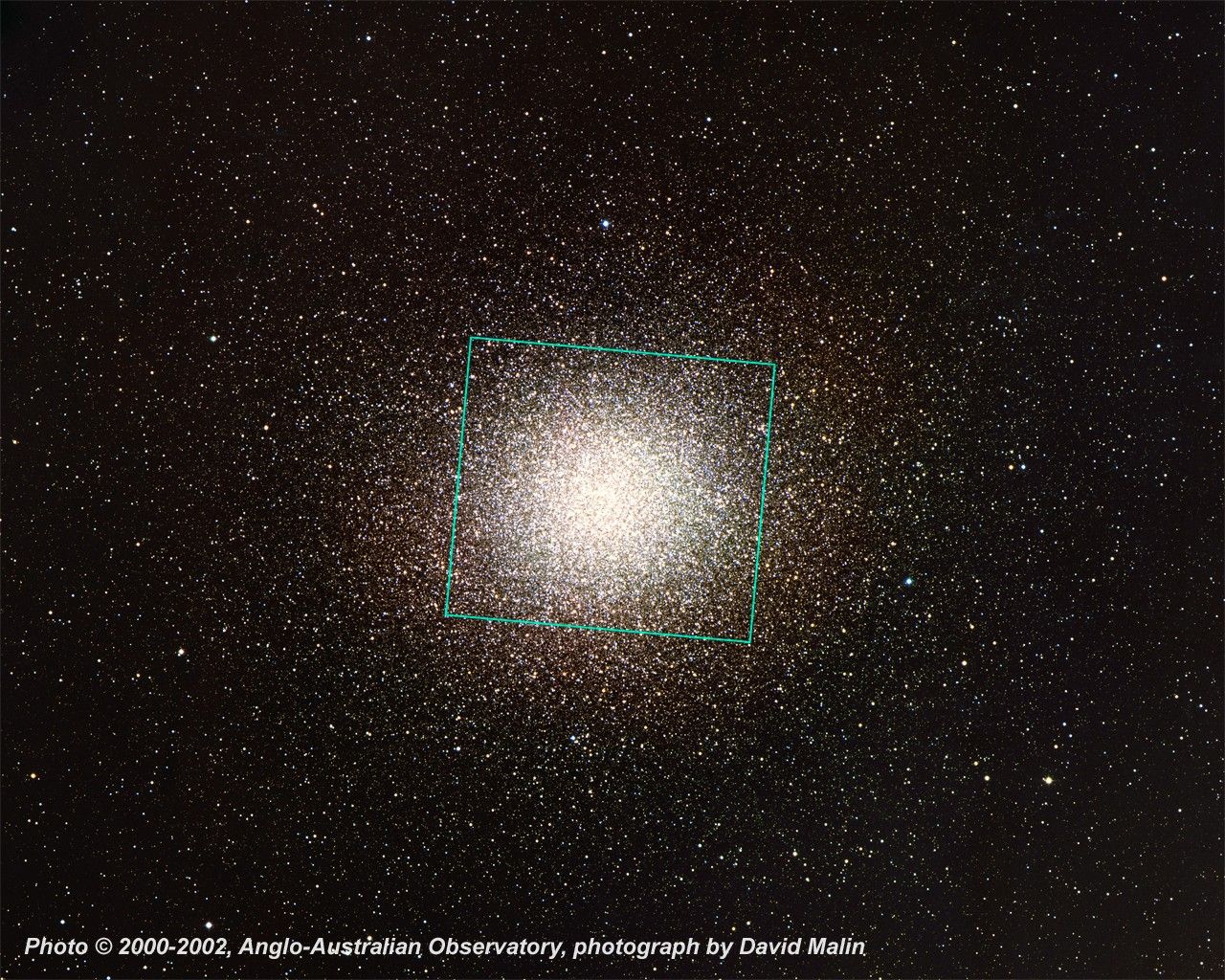
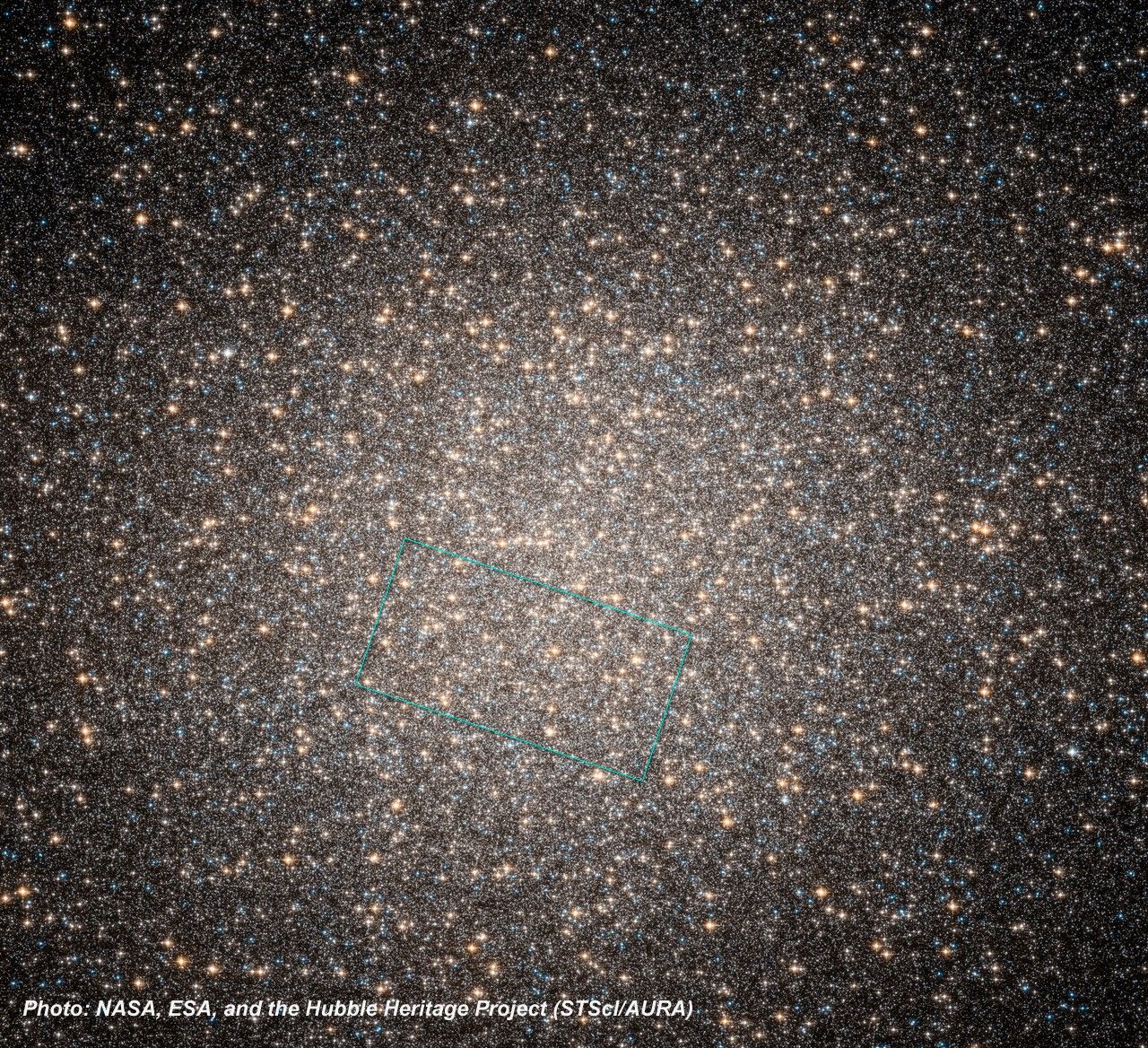
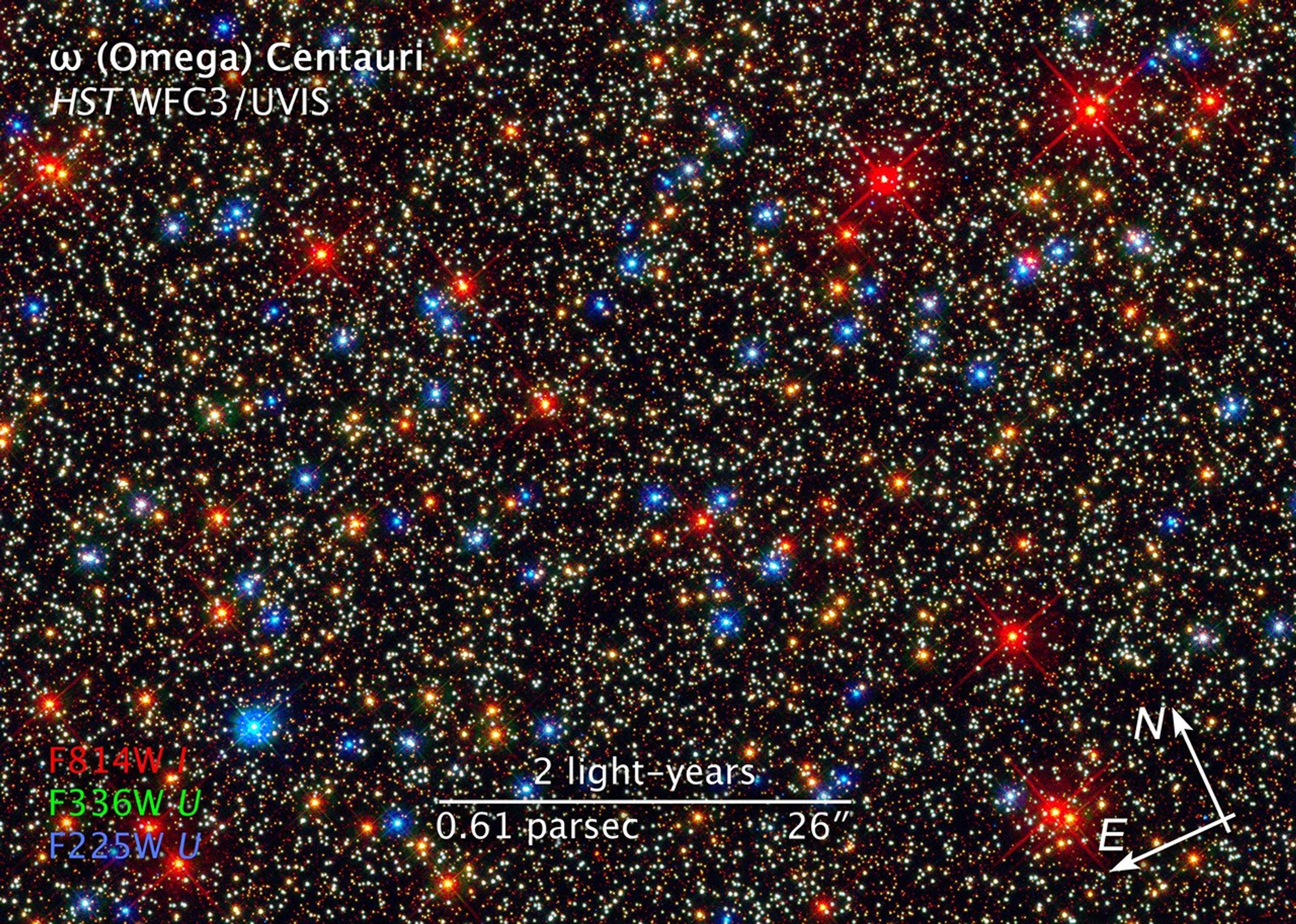
Colorful Stars Galore Inside Globular Star Cluster Omega Centauri
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope snapped this panoramic view of a colorful assortment of 100,000 stars residing in the crowded core of a giant star cluster. The image reveals a small region inside the massive globular cluster Omega Centauri, which boasts nearly 10 million stars....

Galactic Wreckage in Stephan's Quintet
A clash among members of a famous galaxy quintet reveals an assortment of stars across a wide color range, from young, blue stars to aging, red stars. This portrait of Stephan's Quintet, also known as Hickson Compact Group 92, was taken by the new Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3)...

Hubble's Recommissioning Process
Scientists have concluded the checkout period for NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and now are revealing images showcasing the power of the much-improved observatory. This video chronicles the checkout period after Hubble's Servicing Mission 4. Also included is the unexpected...
Hubble Captures Star Birth in the Carina Nebula
Scientists have concluded the checkout period for NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and now are revealing images showcasing the power of the much-improved observatory. In this zoom sequence, one of Hubble's new instruments, the Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3), sets its eyes on a stellar...
Hubble Resolves Myriad Stars in Dense Cluster
Scientists have concluded the checkout period for NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and are now revealing images showcasing the power of the much-improved observatory. This zoom into the globular star cluster Omega Centauri converges onto the Hubble Wide Field Camera 3's panoramic...

Hubble Records Clash of the Titans
Scientists have concluded the checkout period for NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and are now revealing images showcasing the power of the much-improved observatory. In this zoom sequence, Hubble's new Wide Field Camera 3 focuses its attention on a group of five galaxies known as...

Faraway Galaxy Cluster Nets Dark Matter Evidence
Scientists have concluded the checkout period for NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and now are revealing images showcasing the power of the much-improved observatory. This zoom into galaxy cluster Abell 370 brings us to a Hubble image that features a prominent arc near the...

Supernova Explosion Animation
This video animation shows the explosion of a supermassive star. Stars greater than eight times the mass of our Sun will self-detonate as supernovae. Supernovae can briefly outshine an entire galaxy, before fading from view over several weeks or months. During this short...
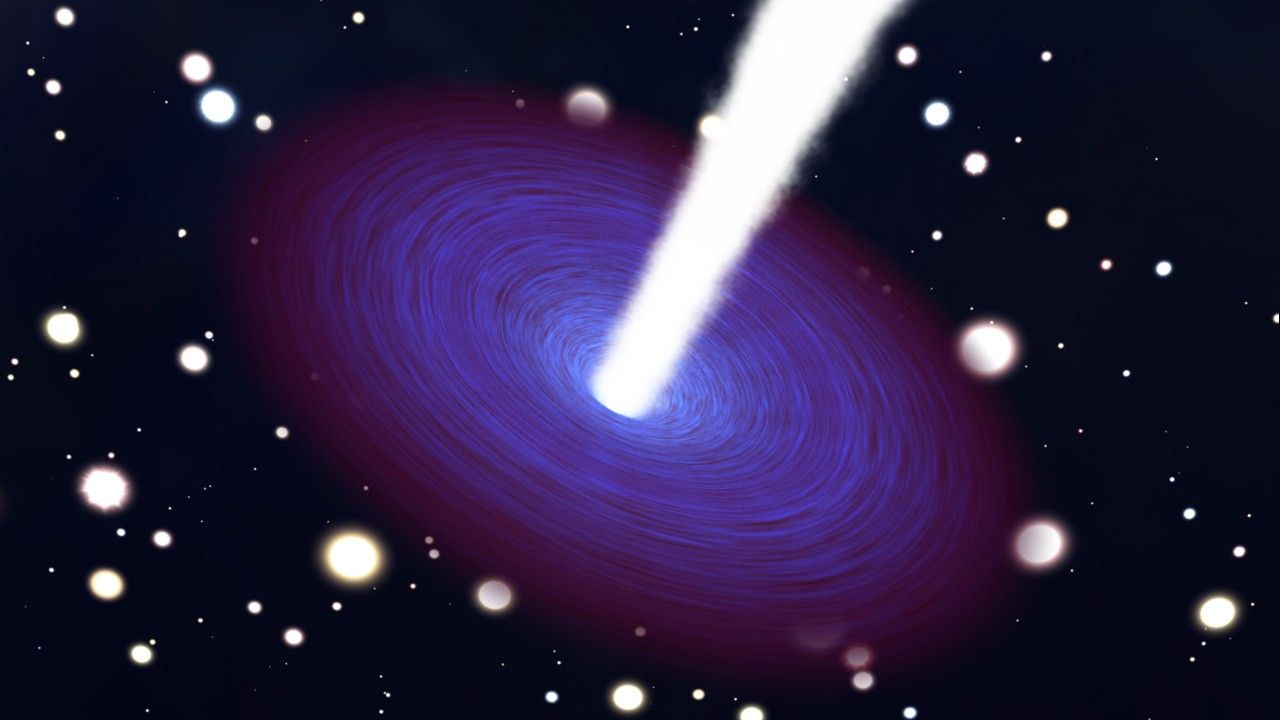

Active Galactic Nucleus Animation
This animation provides a close-up look at the behavior of a central black hole in the nucleus of an active galaxy. An accretion disk of infalling material surrounds a central black hole that may be millions or billions of times the mass of our Sun. Some of the superheated...

Hubble Captures Butterfly Emerging from Stellar Demise in Planetary Nebula NGC 6302
Scientists have concluded the checkout period for NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and are now revealing images showcasing the power of the much-improved observatory. This is a pan sequence of the planetary nebula NGC 6302 (aka the Butterfly Nebula), located 3,800 light-years away,...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov