1 min read
Supernova Remnant N 63A
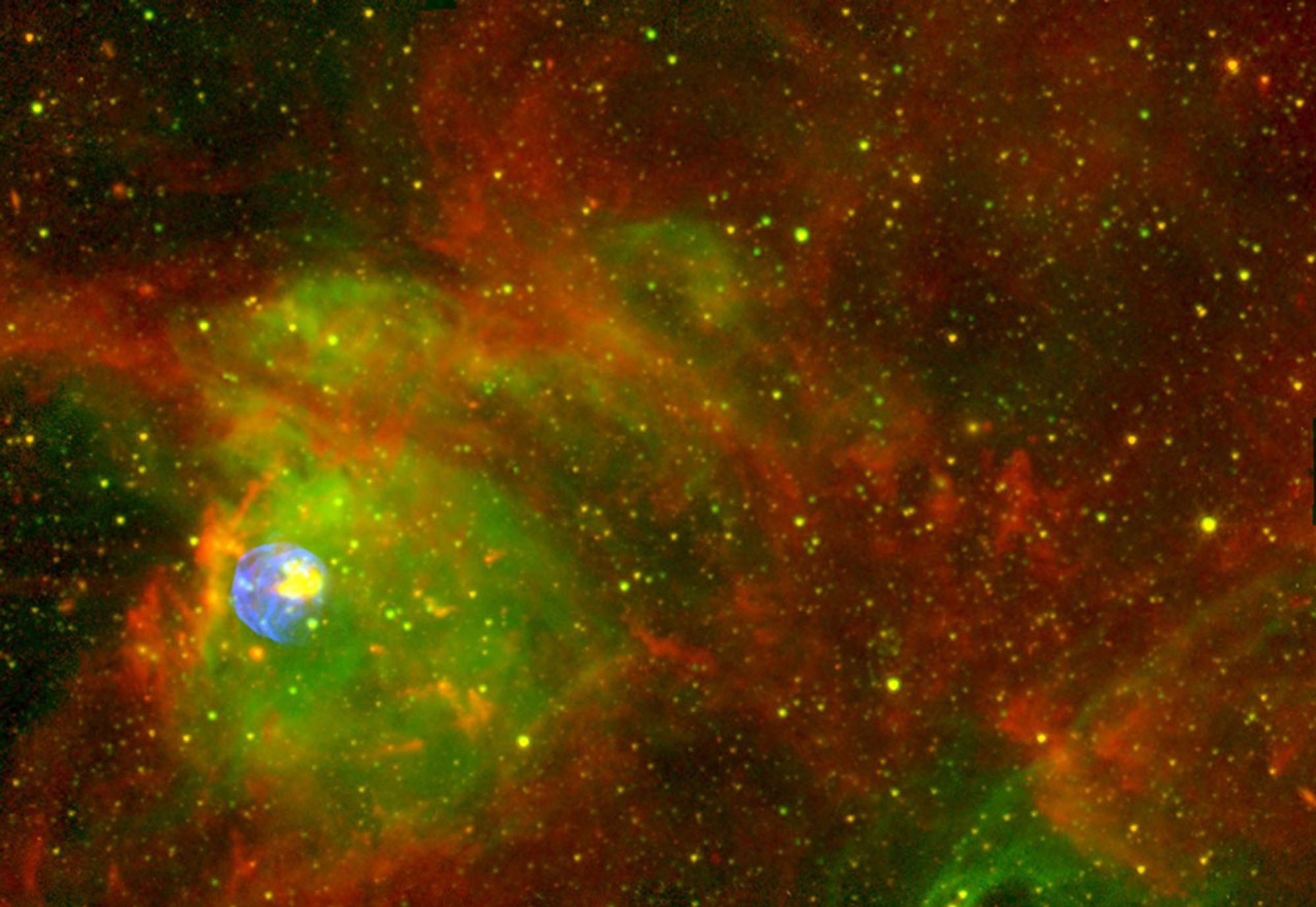

About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.05h 35m 42.99s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-66° 2' 31.99"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Dorado
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.The distance to the LMC is roughly 160,000 light-years (50 kpc).
About the Data
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.SST>IRAC, CXO>X-ray, CTIO>Curtis Schmidt
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.CXO: X-ray CTIO: H-alpha IRAC: 4.5 micro and 8.0 micron
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.LMC N 63A
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Supernova Remnant
- Release DateJune 7, 2005
- Science ReleaseSupernova Remnant Menagerie
- Credit

Blue: X-ray Green: H-alpha Yellow: 4.5 micro Red: 8.0 micron
Related Images & Videos

Supernova Remnant N 63A Menagerie
A violent and chaotic-looking mass of gas and dust is seen in this Hubble Space Telescope image of a nearby supernova remnant. Denoted N 63A, the object is the remains of a massive star that exploded, spewing its gaseous layers out into an already turbulent region. The supernova...

Chandra 3-Color X-ray Image of N 63A
Chandra's image of N63A shows material heated to about ten million degrees Celsius by a shock wave generated by the supernova explosion. The fluffy crescent-shaped X-ray features that appear around the edge of the remnant are thought to be fragments of high-speed matter shot out...

Supernova Remnant LMC N 63A in X-Ray, Optical and Radio Radiation
Chandra has imaged the glowing shell created by the destruction of a massive star. X-rays from Chandra (blue), combined with optical (green) and radio (red) data, reveal new details in the supernova remnant, LMC N 63A. The X-ray glow is from material heated to about ten million...
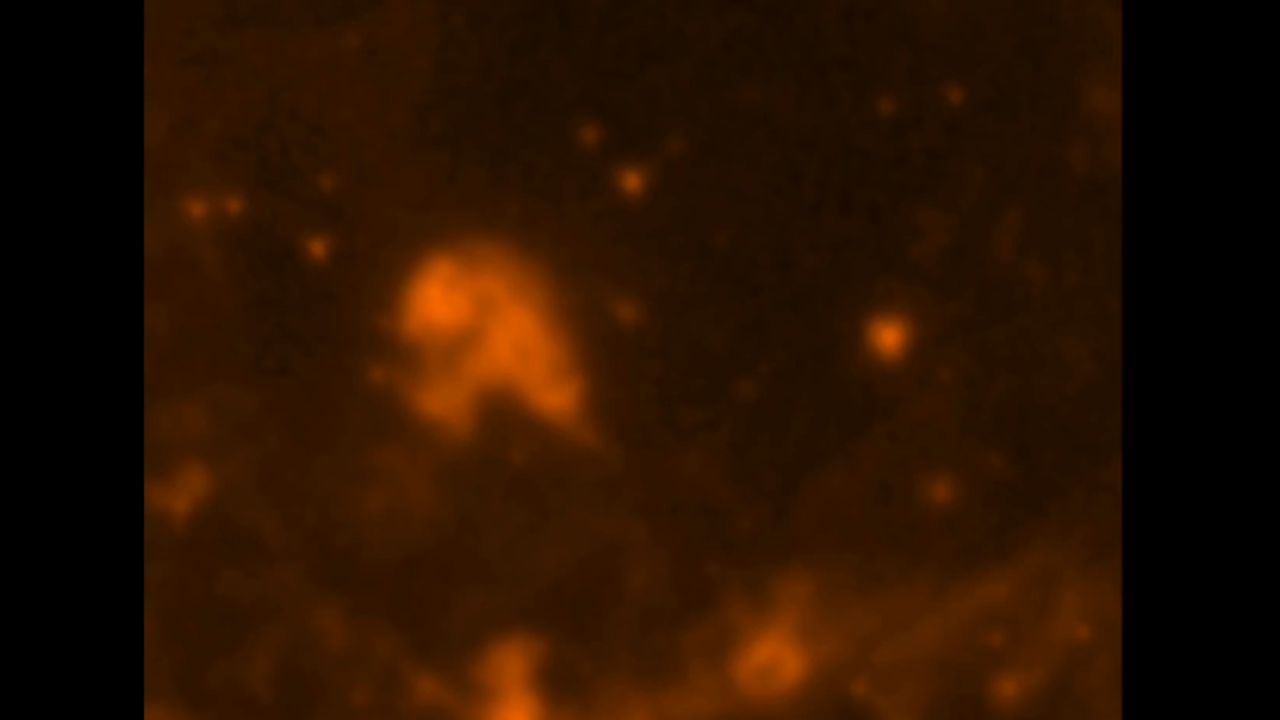
Supernova Remnant Menagerie
The Hubble Space Telescope's Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) was used to obtain images of a violent and chaotic-looking mass of gas and dust known as N 63A. The dissolve sequence builds from a Spitzer telescope infrared image of the area, adding the Chandra X-ray image,...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov






























