1 min read
Tumultuous Collision Between Four Galaxies (IRAS 19297-0406)

Two powerful cameras aboard NASA's Hubble Space Telescope teamed up to capture the final stages in the grand assembly of galaxies.
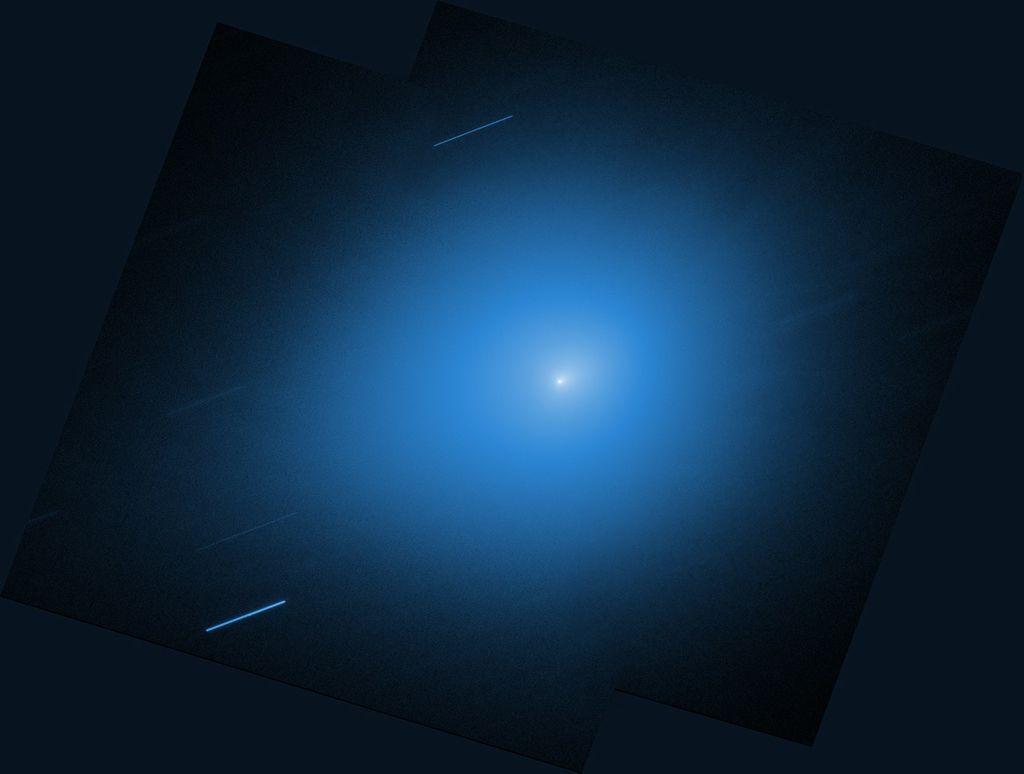
The photograph, taken by the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) and the revived Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS), shows a tumultuous collision between four galaxies located 1 billion light-years from Earth. The galactic car wreck is creating a torrent of new stars.
The tangled up galaxies, called IRAS 19297-0406, are crammed together in the center of the picture. IRAS 19297-0406 is part of a class of galaxies known as ultraluminous infrared galaxies (ULIRGs). ULIRGs are considered the progenitors of massive elliptical galaxies.
ULIRGs glow fiercely in infrared light, appearing 100 times brighter than our Milky Way Galaxy. The large amount of dust in these galaxies produces the brilliant infrared glow. The dust is generated by a firestorm of star birth triggered by the collisions.
IRAS 19297-0406 is producing about 200 new Sun-like stars every year - about 100 times more stars than our Milky Way creates. The hotbed of this star formation is the central region [the yellow objects]. This area is swamped in the dust created by the flurry of star formation.
The bright blue material surrounding the central region corresponds to the ultraviolet glow of new stars. The ultraviolet light is not obscured by dust. Astronomers believe that this area is creating fewer new stars and therefore not as much dust.
The colliding system [yellow and blue regions] has a diameter of about 30,000 light-years, or about half the size of the Milky Way. The tail [faint blue material at left] extends out for another 20,000 light-years.
Astronomers used both cameras to witness the flocks of new stars that are forming from the galactic wreckage. NICMOS penetrated the dusty veil that masks the intense star birth in the central region. ACS captured the visible starlight of the colliding system's blue outer region.
IRAS 19297-0406 may be similar to the so-called Hickson compact groups - clusters of at least four galaxies in a tight configuration that are isolated from other galaxies. The galaxies are so close together that they lose energy from the relentless pull of gravity. Eventually, they fall into each other and form one massive galaxy.
This color-composite image was made by combining photographs taken in near-infrared light with NICMOS and ultraviolet and visible light with ACS. The pictures were taken with these filters: the H-band and J-band on NICMOS; the V-band on the ACS wide-field camera; and the U-band on the ACS high-resolution camera. The images were taken on May 13 and 14.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.19h 32m 22.39s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-4° 0' 2.0"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Aquila
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.About 1 billion light-years (300 Mpc)
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.This image is about 15 arcseconds (22 kiloparsecs or 72,000 light-years) wide.
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.Principal Astronomers: A. Fruchter, B. Mobasher, and A.Schultz (STScI) - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>NICMOS/NIC2
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.May 13-14, 2002, Exposure Time: 4 hours
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.NICMOS/NIC3: F110W (J-band), F160W (H-band) ACS/WFC: F606W (V) ACS/HRD: F330W (U)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.IRAS 19297-0406
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Ultraluminous Infrared Galaxy (ULIRG)
- Release DateJune 5, 2002
- Science ReleaseHubble’s Infrared Camera is Back in Business – New Images Released
- Credit

Related Images & Videos

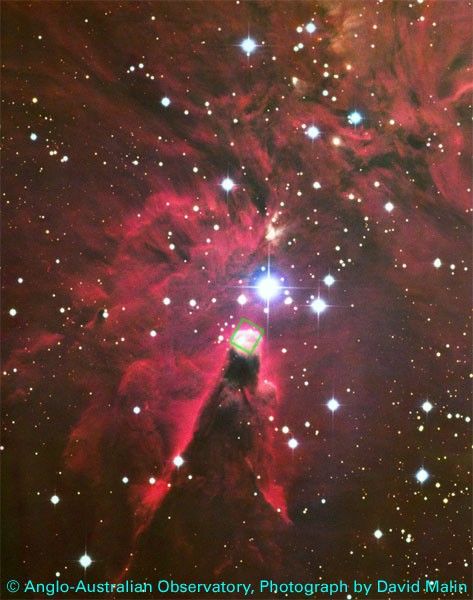
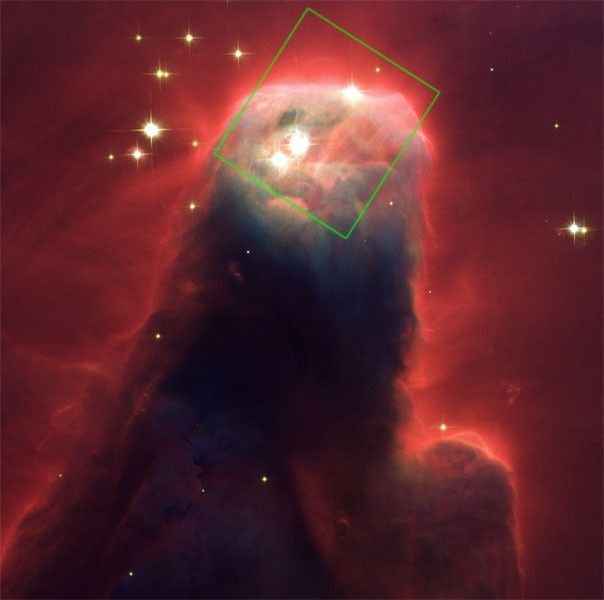
Nicmos Peels Away Layers of Dust to Show Inner Region of Dusty Nebula
The revived Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) aboard NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has penetrated layers of dust in a star-forming cloud to uncover a dense, craggy edifice of dust and gas [image at right]. This region is called the Cone Nebula (NGC...

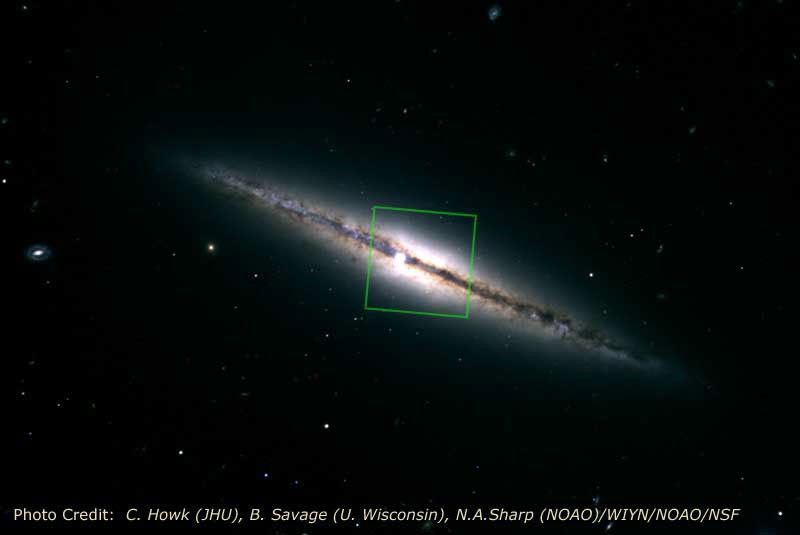
NICMOS Finds a Golden Ring at the Heart of a Galaxy
The revived Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) aboard NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has pierced the dusty disk of the "edge-on" galaxy NGC 4013 and peered all the way to the galactic core. To the surprise of astronomers, NICMOS found a brilliant...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov