1 min read
Exoplanet GJ 486 b (Transmission Spectrum)
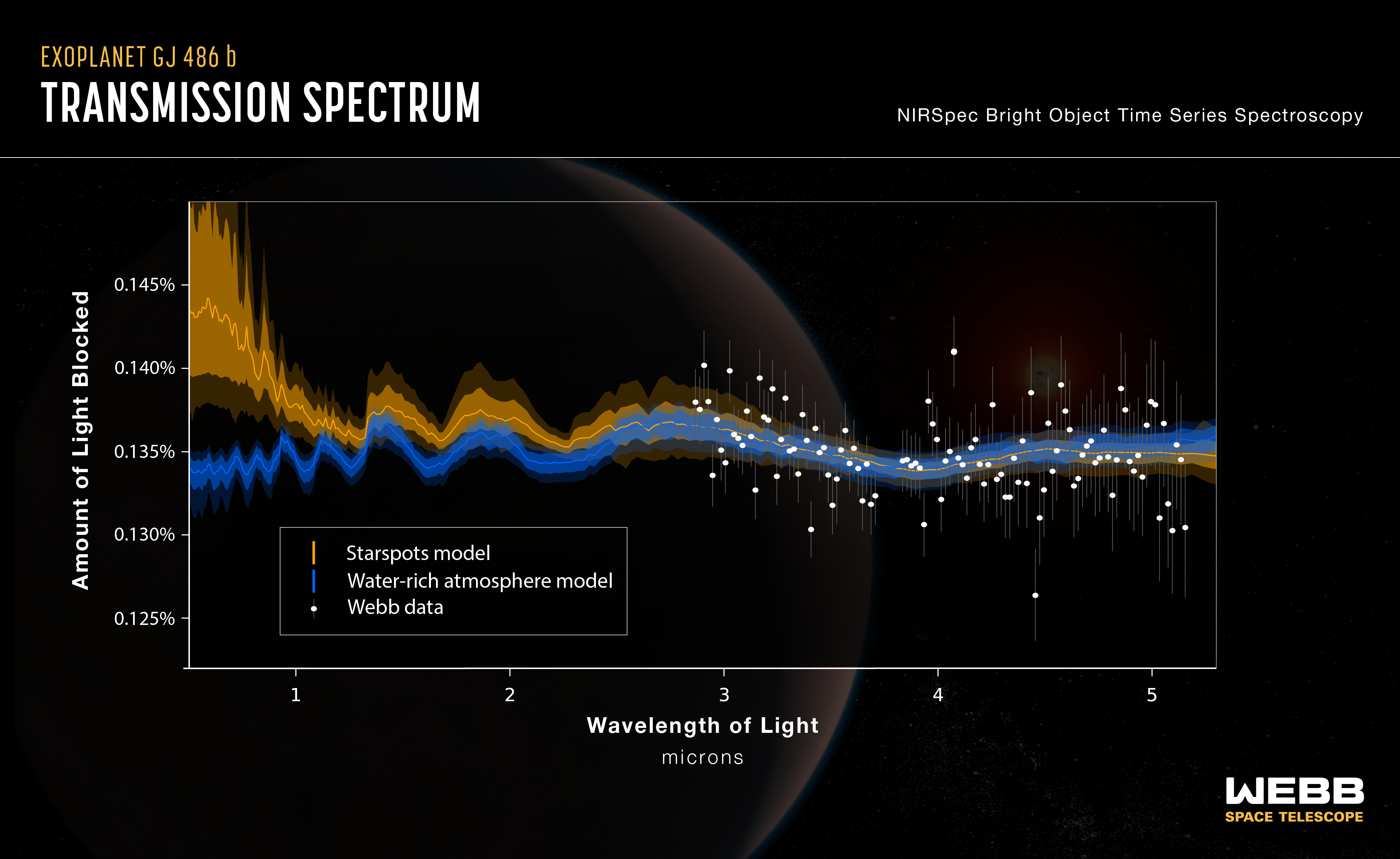
This graphic shows the transmission spectrum obtained by Webb observations of rocky exoplanet GJ 486 b. The science team’s analysis shows hints of water vapor; however, computer models show that the signal could be from a water-rich planetary atmosphere (indicated by the blue line) or from starspots from the red dwarf host star (indicated by the yellow line). The two models diverge noticeably at shorter infrared wavelengths, indicating that additional observations with other Webb instruments will be needed to constrain the source of the water signal.
The background illustration of a planet is an artist concept. Webb has not taken an image of the planet.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.12:47:57.0
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.+09:45:05
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Virgo
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.26 light-years
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.GJ 486 b
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Exoplanet
- Release DateMay 1, 2023
- Science ReleaseWebb Finds Water Vapor, But From a Rocky Planet or Its Star?
- CreditIllustration: NASA, ESA, CSA, Joseph Olmsted (STScI); Science: Sarah Moran (University of Arizona), Kevin Stevenson (APL), Ryan MacDonald (University of Michigan), Jacob Lustig-Yaeger (APL)
Related Images & Videos

Exoplanet GJ 486 b (Artist Concept)
This artist concept represents the rocky exoplanet GJ 486 b, which orbits a red dwarf star that is only 26 light-years away in the constellation Virgo. By observing GJ 486 b transit in front of its star, astronomers sought signs of an atmosphere. They detected hints of water...
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov
NASA, ESA, CSA, Joseph Olmsted (STScI)
Sarah Moran (University of Arizona), Kevin Stevenson (APL), Ryan MacDonald (University of Michigan), Jacob Lustig-Yaeger (APL)




























