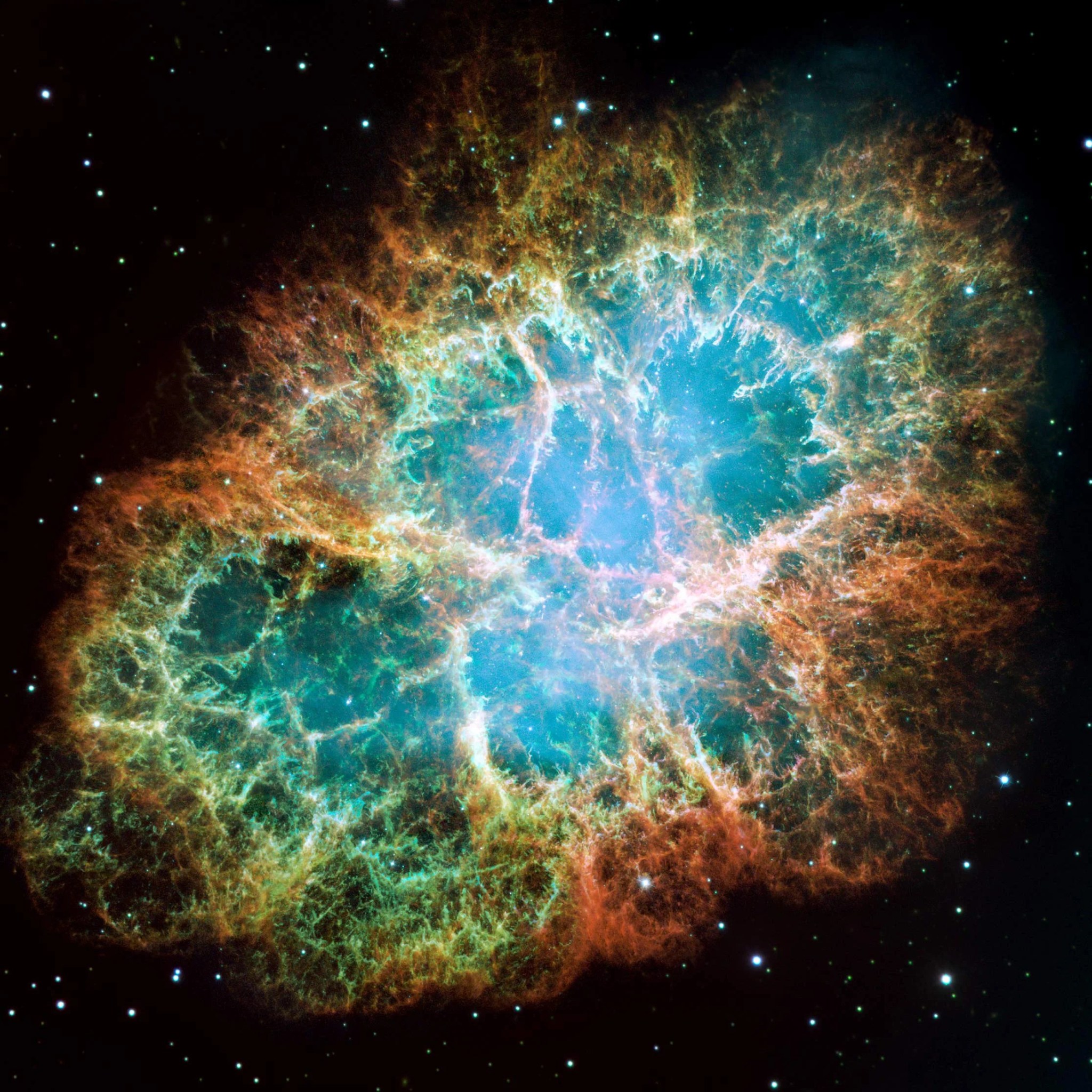
Messier 1
Better known as the Crab Nebula, Charles Messier originally mistook Messier 1 for Halley’s Comet, which inspired him to create his famous catalog of objects.
Distance
6,500 light-years
Apparent Magnitude
8.4
constellation
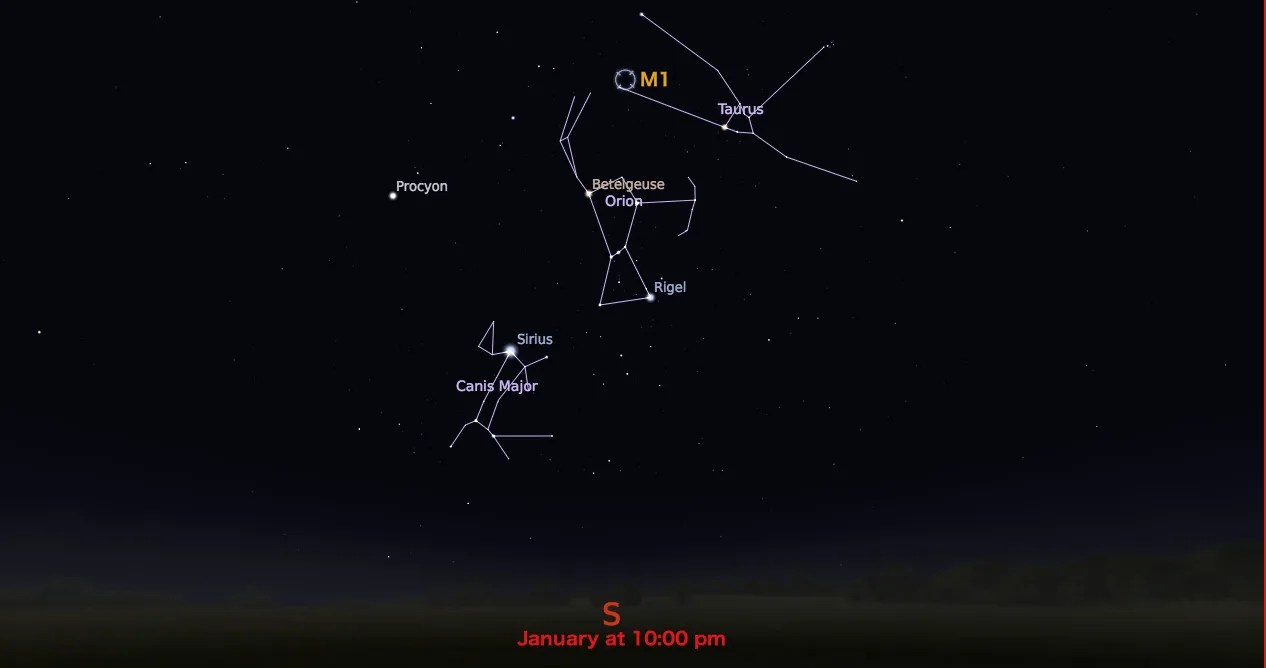
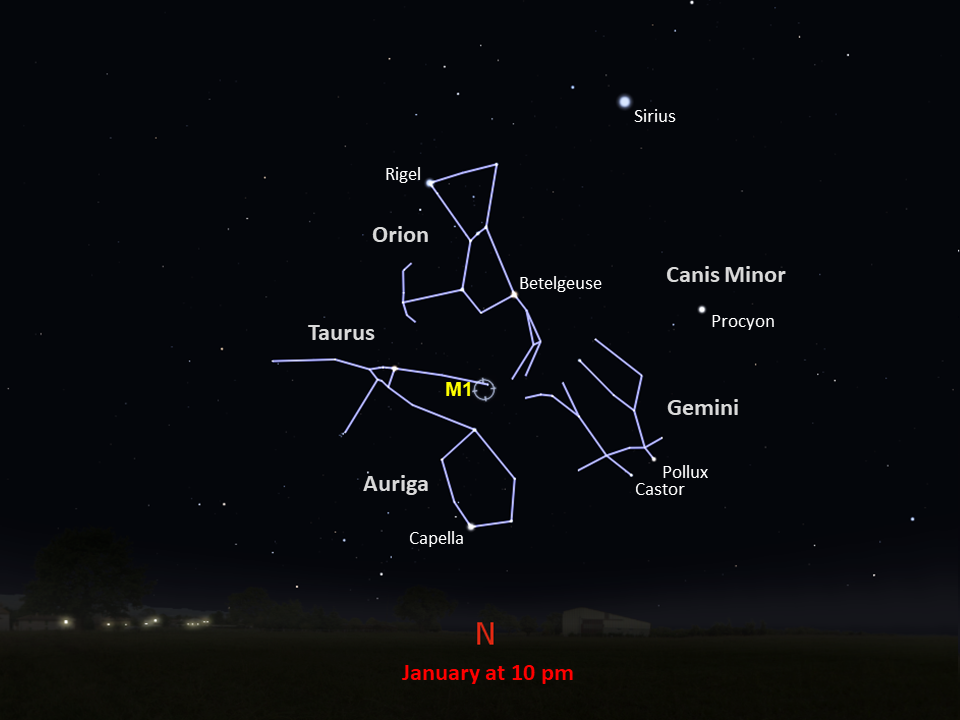
Taurus
object type
Supernova Remnant
In 1054, Chinese astronomers took notice of a “guest star” that was, for nearly a month, visible in the daytime sky. The “guest star” they observed was actually a supernova explosion, which gave rise to the Crab Nebula, a six-light-year-wide remnant of the violent event.

With an apparent magnitude of 8.4 and located 6,500 light-years from Earth in the constellation Taurus, the Crab Nebula can be spotted with a small telescope and is best observed in January. The nebula was discovered by English astronomer John Bevis in 1731, and later observed by Charles Messier who mistook it for Halley’s Comet. Messier’s observation of the nebula inspired him to create a catalog of celestial objects that might be mistaken for comets.
This large mosaic of the Crab Nebula was assembled from 24 individual exposures captured by Hubble over three months. The colors in this image do not match exactly what we would see with our eyes but yield insight into the composition of this spectacular stellar corpse. The orange filaments are the tattered remains of the star and consist mostly of hydrogen. The blue in the filaments in the outer part of the nebula represents neutral oxygen. Green is singly ionized sulfur, and red indicates doubly ionized oxygen. These elements were expelled during the supernova explosion.
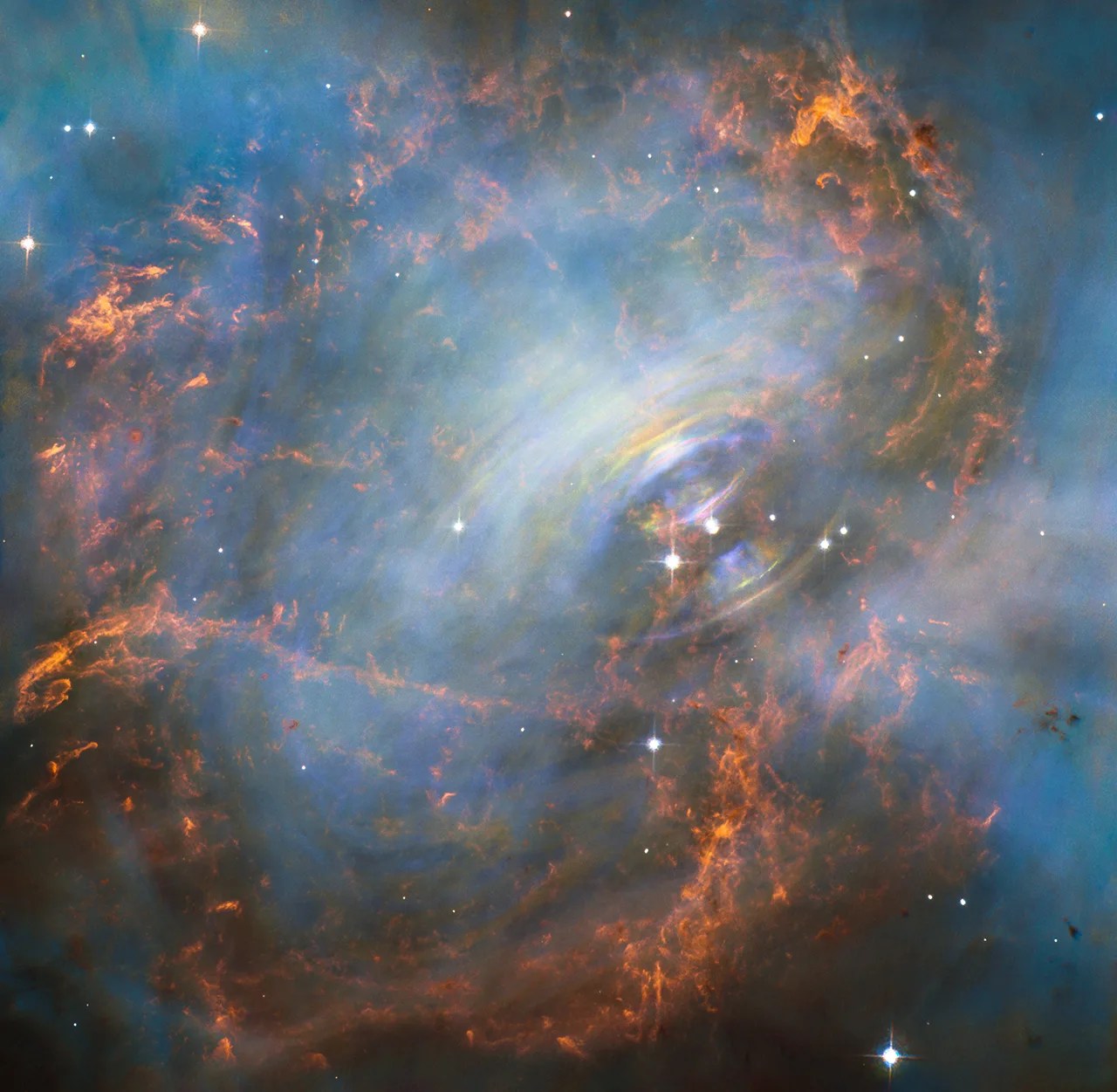
A rapidly spinning neutron star (the ultra-dense core of the exploded star) is embedded in the center of the Crab Nebula. Electrons whirling at nearly the speed of light around the star’s magnetic field lines produce the eerie blue light in the interior of the nebula. The neutron star, like a lighthouse, ejects twin beams of radiation that make it appear to pulse 30 times per second as it rotates.
For more information about Hubble’s observations of M1, see:
- A Giant Hubble Mosaic of the Crab Nebula
- Hubble Captures the Beating Heart of the Crab Nebula
- Space Movie Reveals Shocking Secrets of the Crab Pulsar
- Hubble Astronomers Unveil "Crab Nebula – The Movie"
Explore Hubble's Messier Catalog
The following pages contain some of Hubble’s best images of Messier objects.

Overview The Messier catalog, begun by astronomer Charles Messier in the 18th Century and revised over the years, includes some…
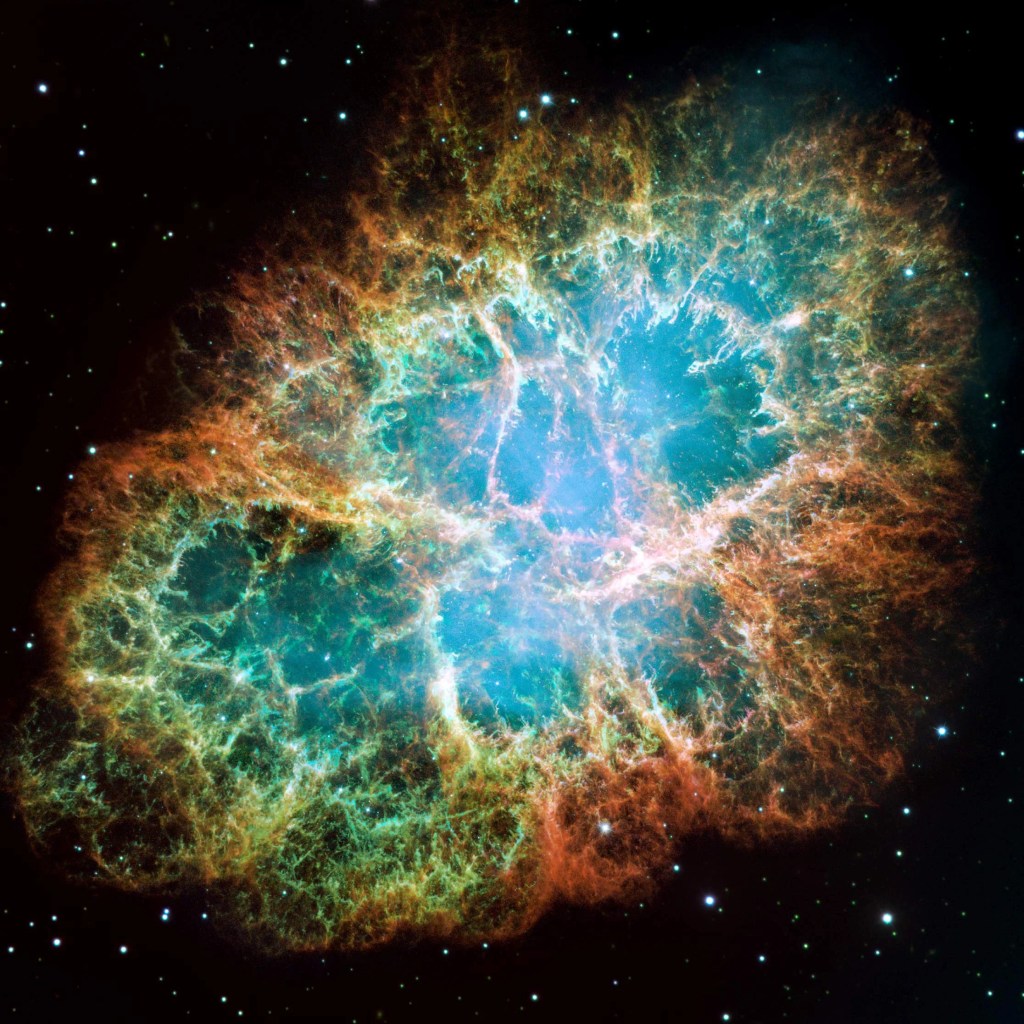

Better known as the Crab Nebula, Charles Messier originally mistook Messier 1 for Halley’s Comet, which inspired him to create…

Hubble's image of Messier 2 is comprised of visible and infrared wavelengths of light.